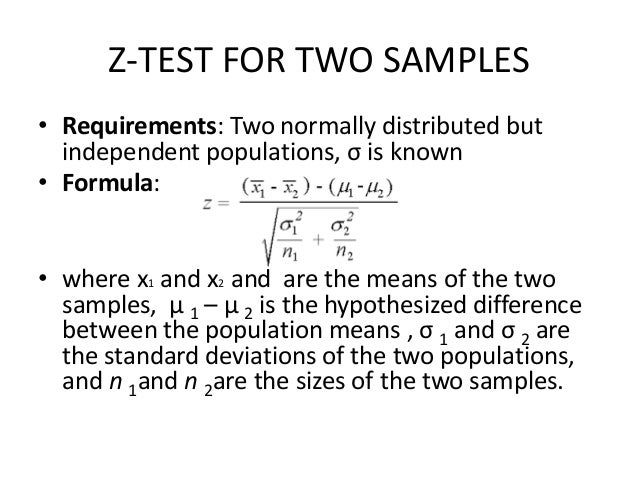
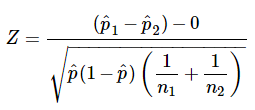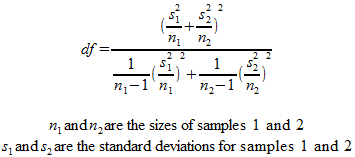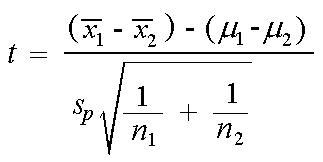Z Formula For Two Samples
More about the z test for two means so you can better use the results delivered by this solver.

Z formula for two samples. The amount of a certain trace element in blood is known to vary with a standard deviation of 141 ppm parts per. More specifically we are interested in assessing whether or not it is reasonable to claim that the two population means the population means. Z test tests the mean of a distribution.
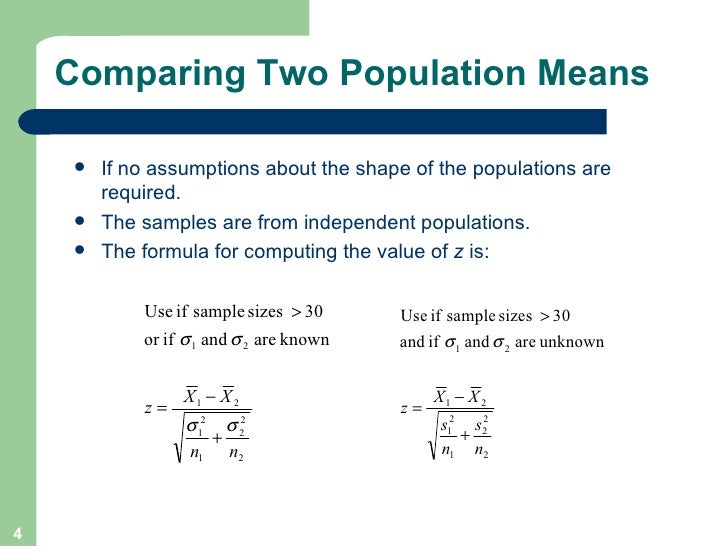
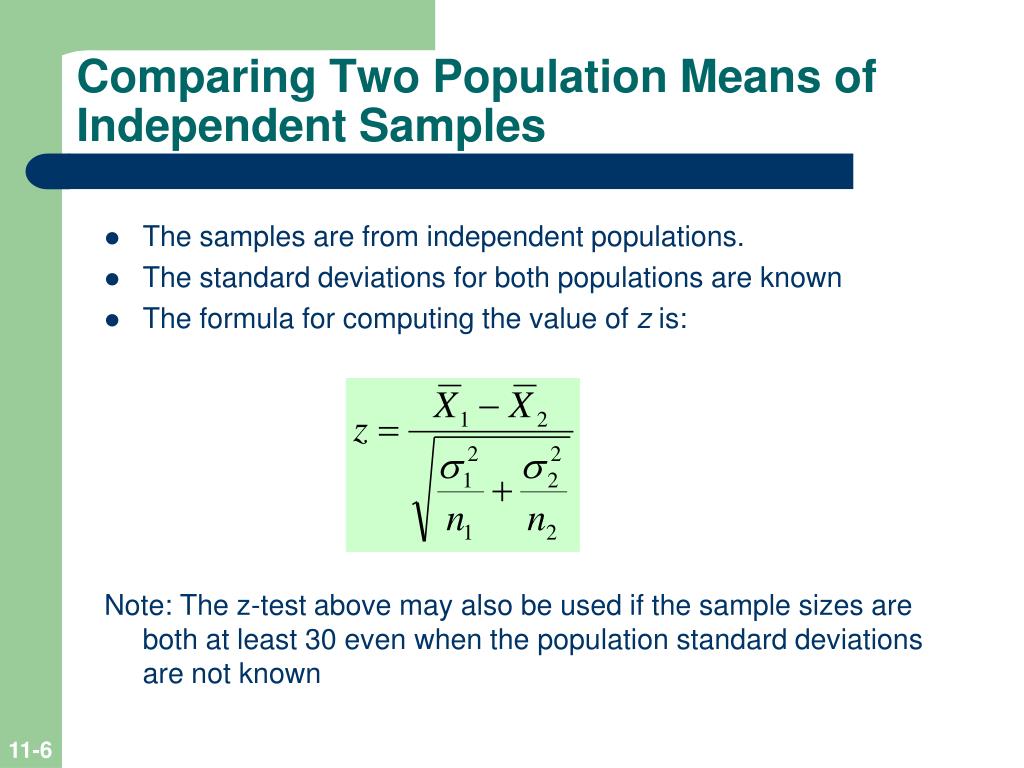
The z test uses a normal distribution. While using the z test we test a null hypothesis which states that the mean of the two population is equal. A z test is a statistical test to determine whether two population means are different when the variances are known and the sample size is large.
Two sample z test. A z test for two means is a hypothesis test that attempts to make a claim about the population means mu1 and mu2. Lets take an example to understand the usage of two sample z test.
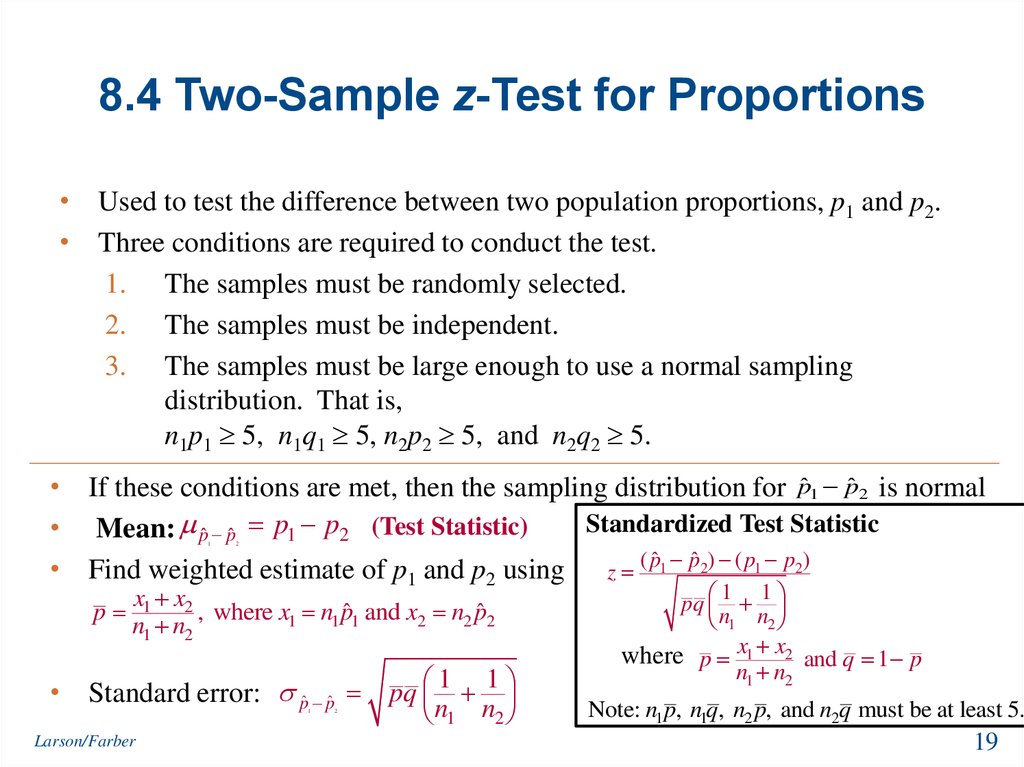
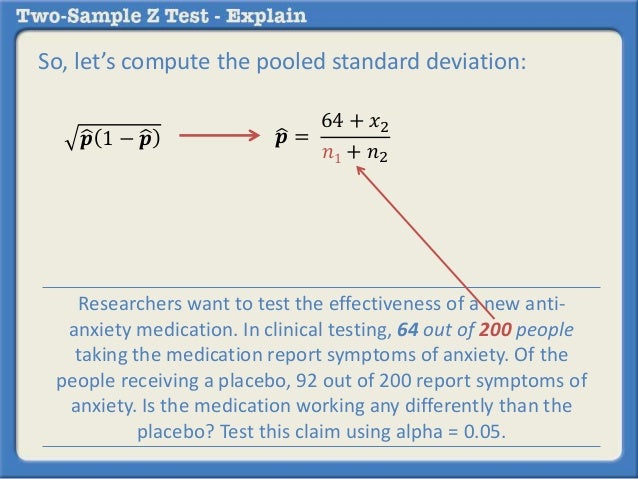
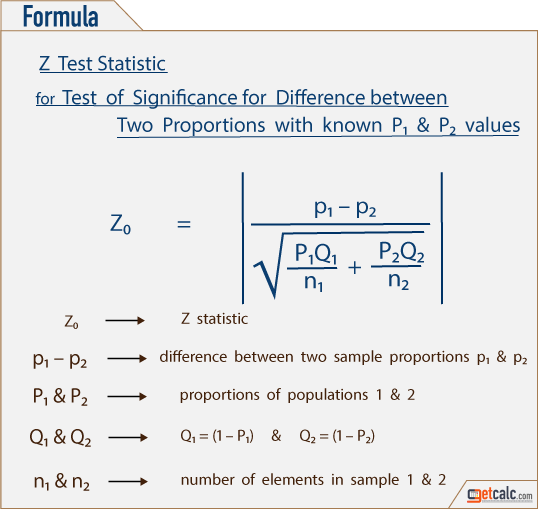
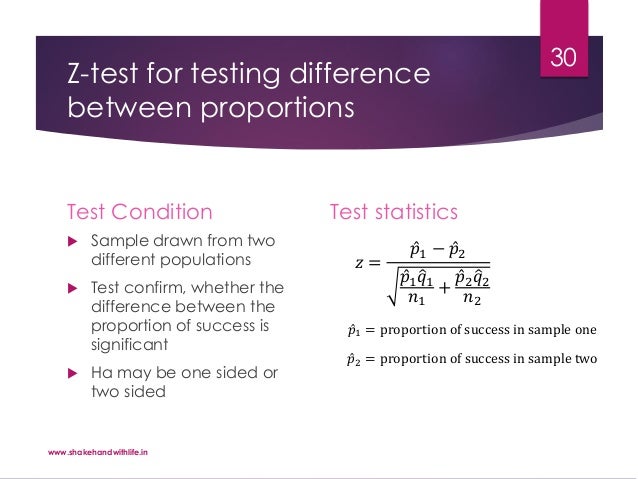
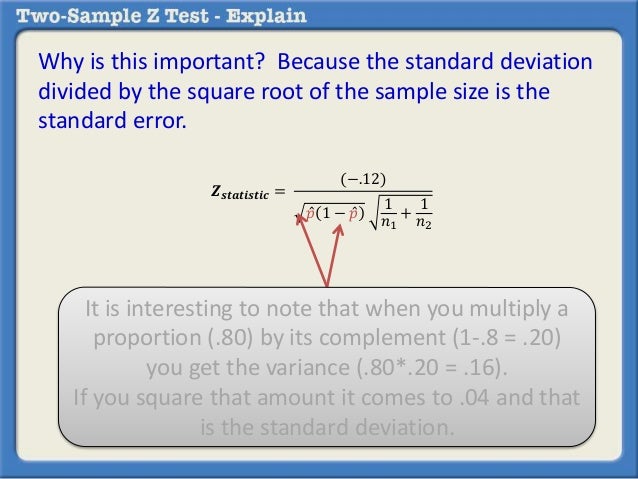
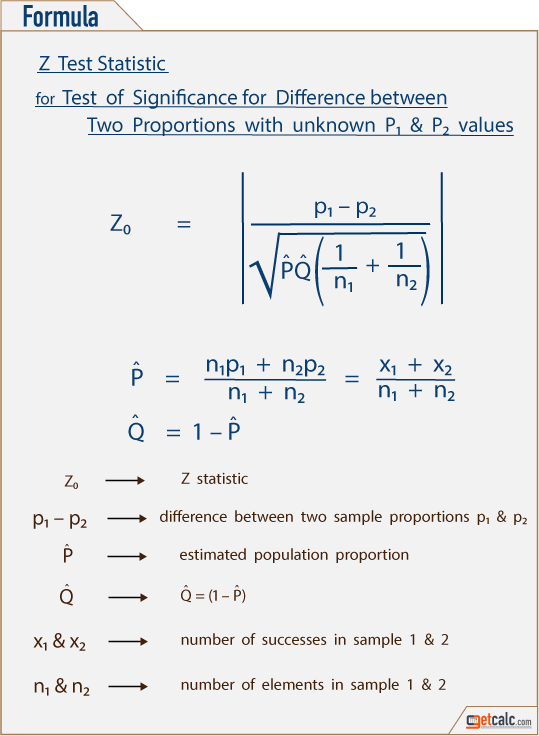
In that case he can use a z test statistics method to obtain the results by taking a sample size say 500 from the city out of which suppose 280 are tea drinkers. U 1 u 2 0. Where p 1 and p 2 are the sample proportions n 1 and n 2 are the sample sizes and where p is the total pooled proportion calculated as.
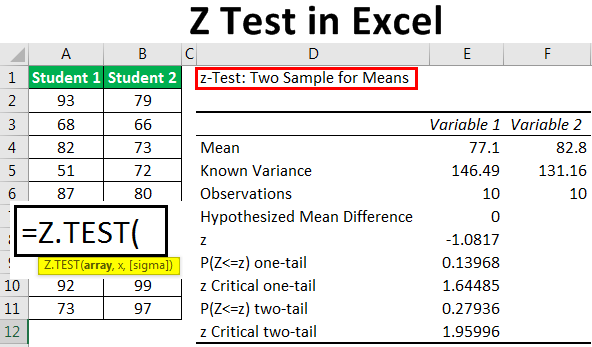
It can be used to test hypotheses in which the z. U 1 u 2 0. As part of the test the tool also validate the tests assumptions compares the sample data to the standard deviation checks data for normality and draws a histogram and a distribution chart.
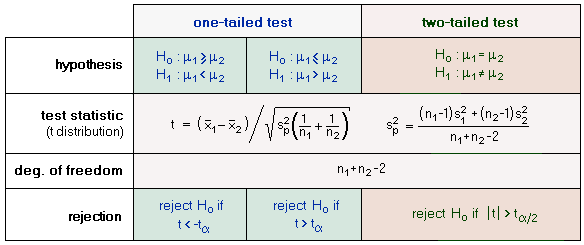
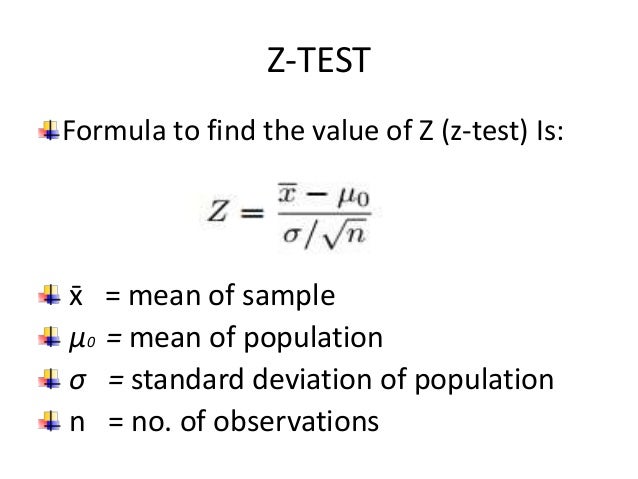
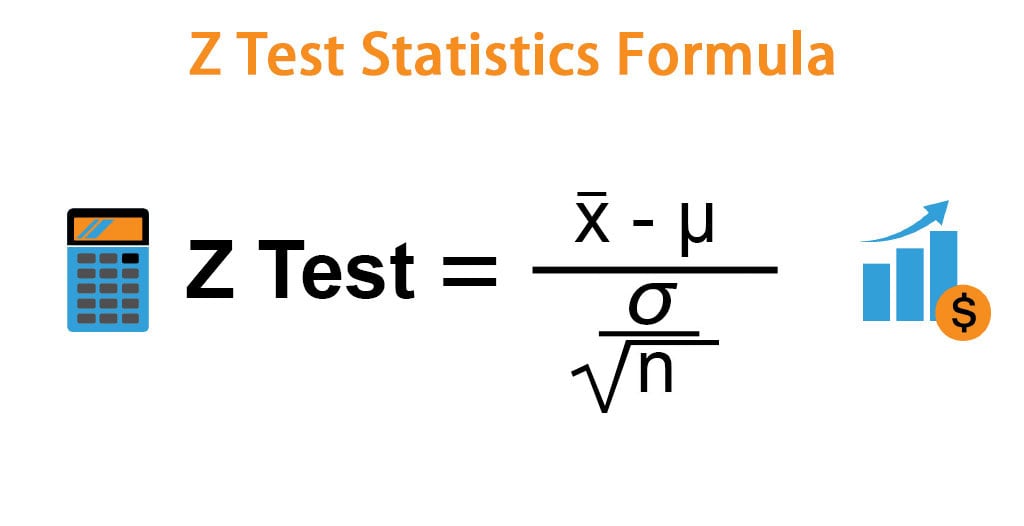
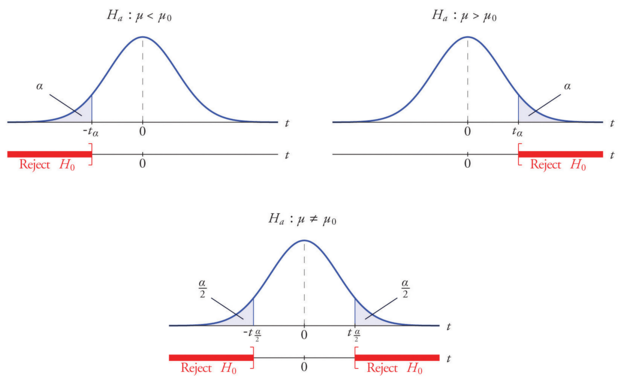
Z x m o the formula for z test statistics for a sample is derived by using the following steps. And a z statistic is generated using the formula. Where h1 is called an alternative hypothesis the mean of two populations is not equal.
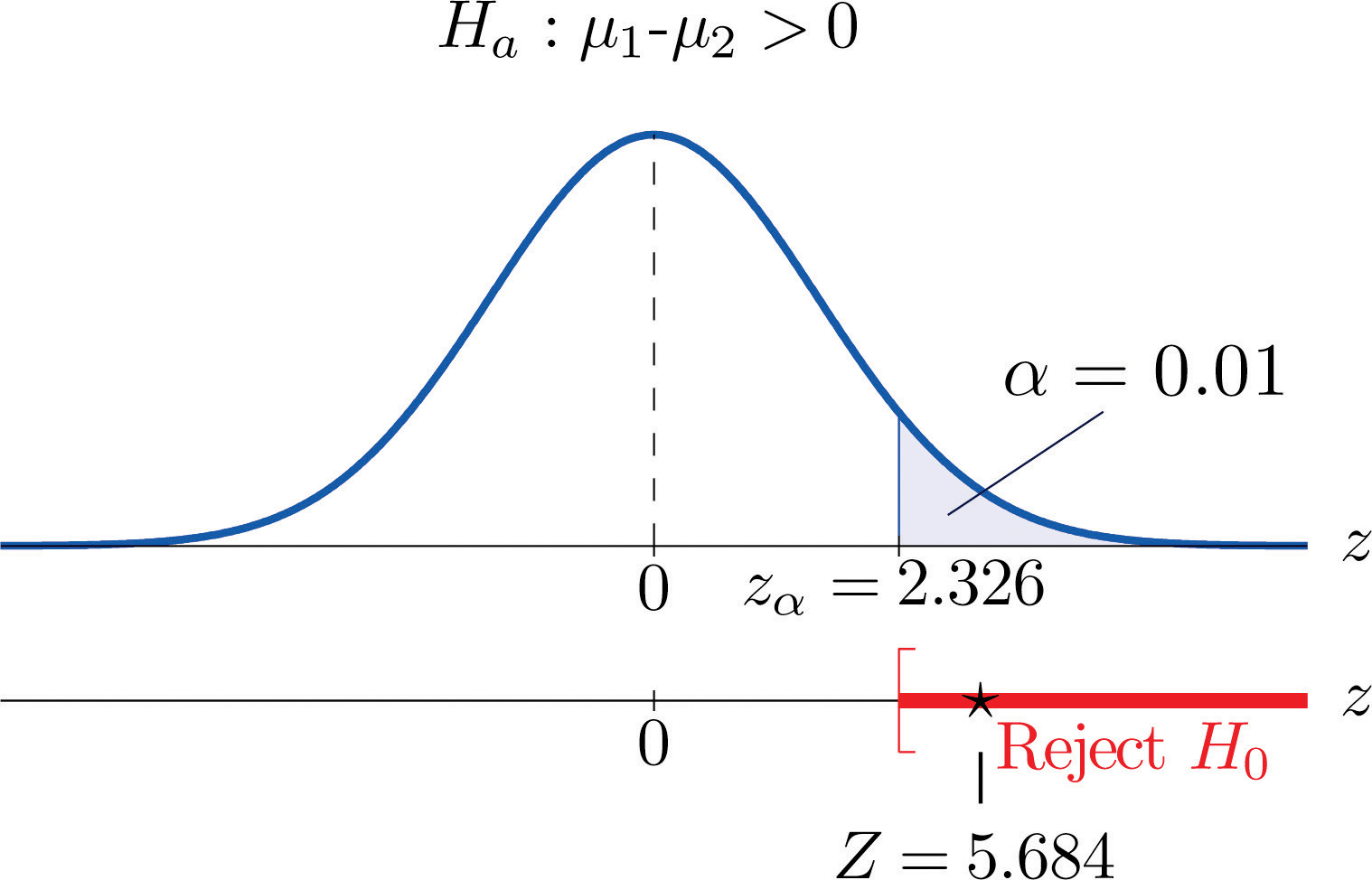
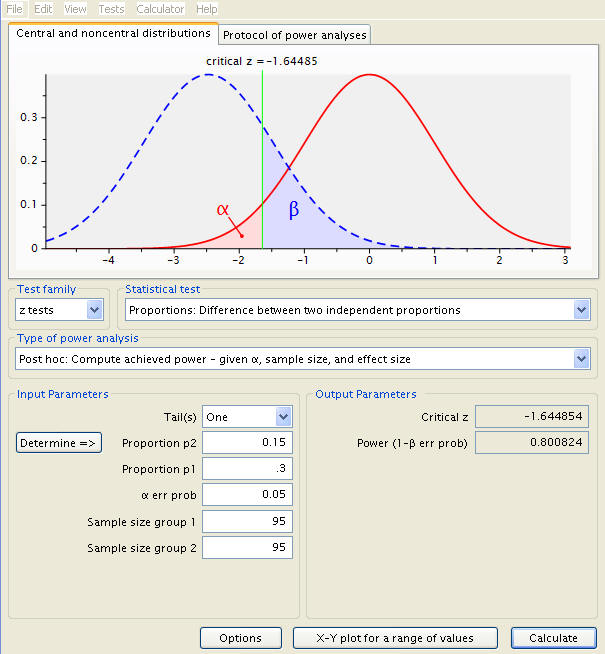
The z test for two means. Population standard deviation step 2. For each significance level in the confidence interval the z test has a single critical value for example 196 for 5 two tailed which makes it more convenient than the students t test whose critical values are defined by the sample size through the corresponding degrees of freedom.
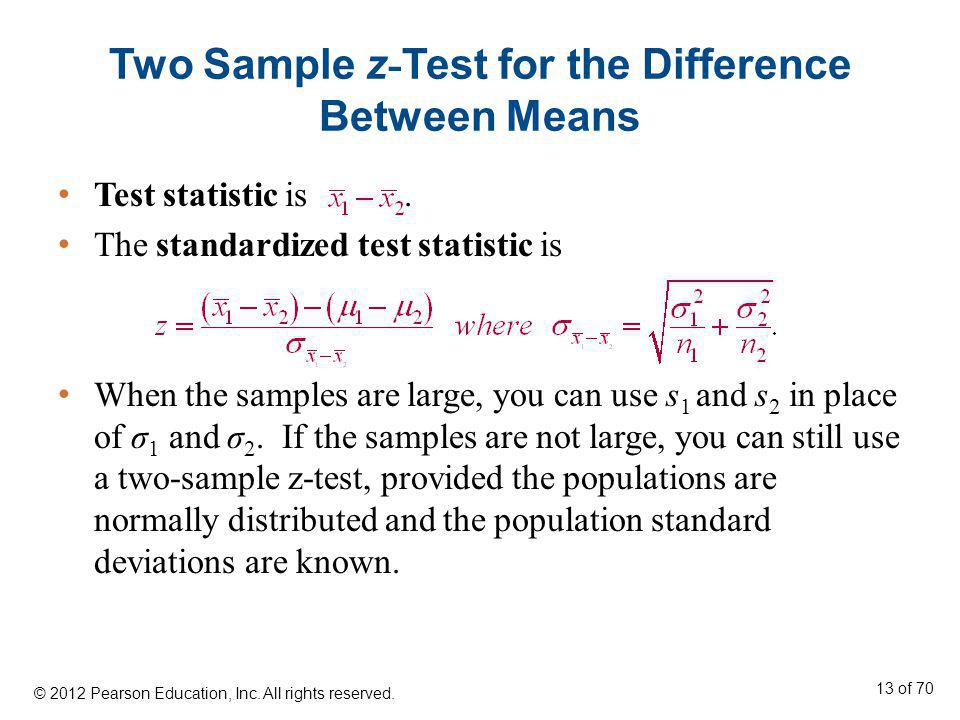
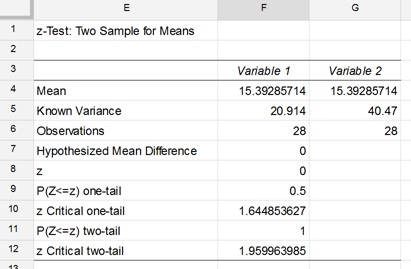
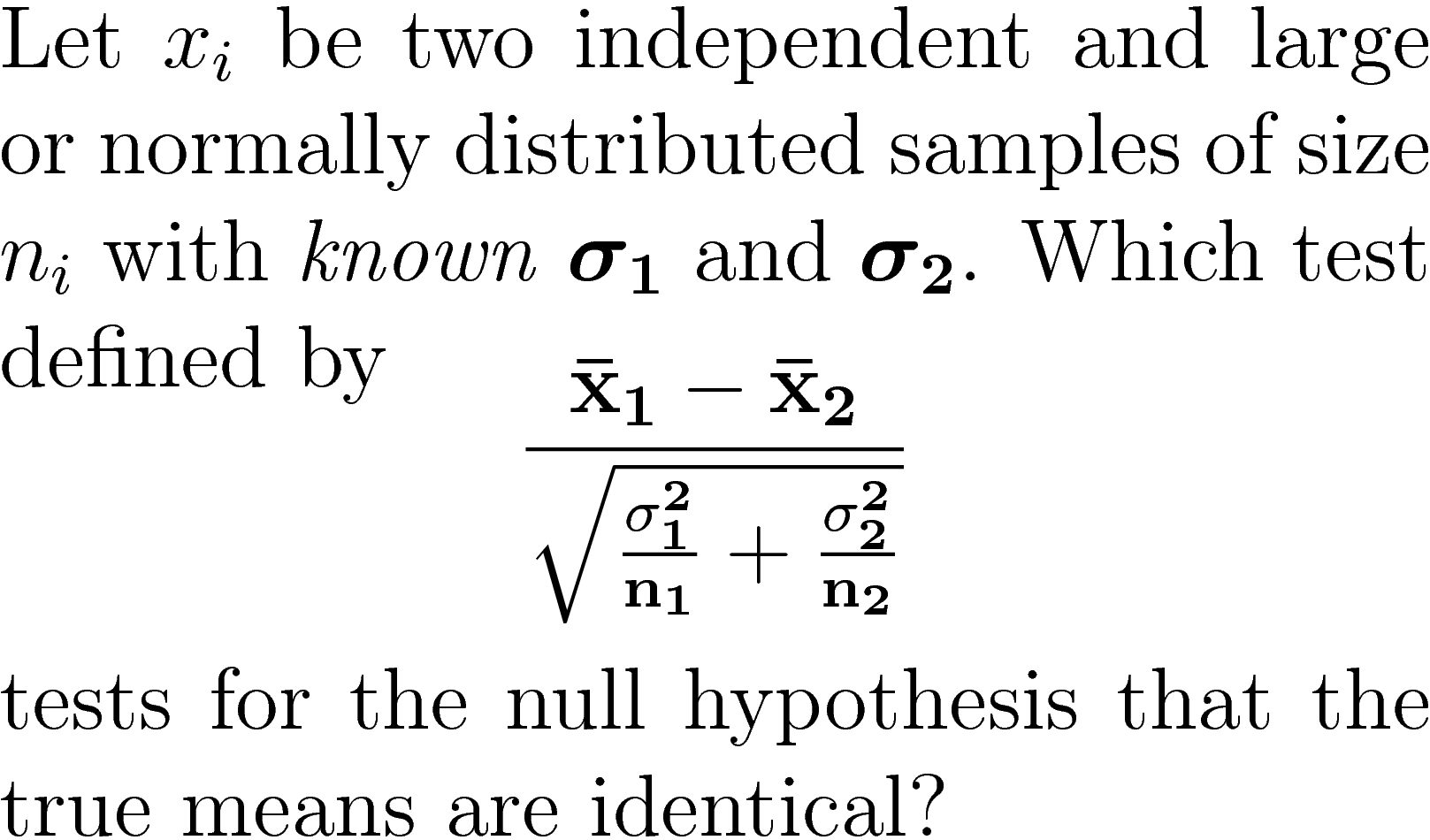
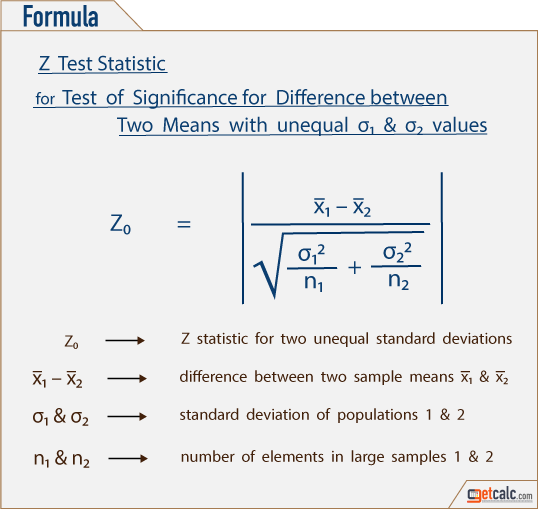
Where and are the means of the two samples d is the hypothesized difference between the population means 0 if testing for equal means s 1 and s 2 are the standard deviations of the two populations and n 1 and n 2 are the sizes of the two samples. Two sample z tests assuming equal variance introduction this procedure provides sample size and power calculations for one or two sided two sample z tests when the. 1 2 1 2 1 1 n n x x z.
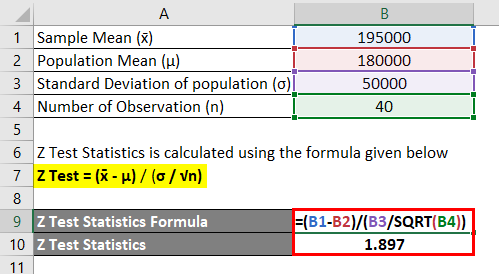
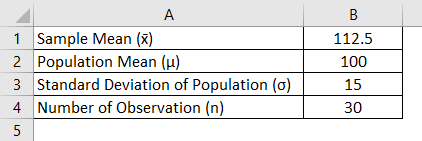
Finally the z test statistics is computed by deducting population mean from the variable and then the result is divided by the population standard deviation as shown below. Suppose a person wants to check or test if tea and coffee both are equally popular in the city. Firstly calculate the sample mean and sample standard deviation.
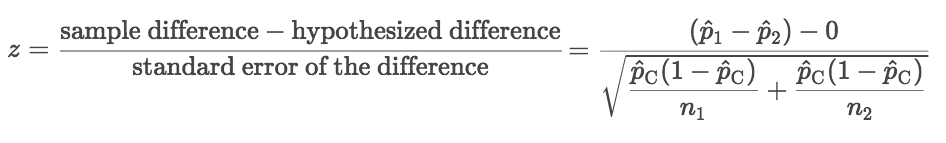



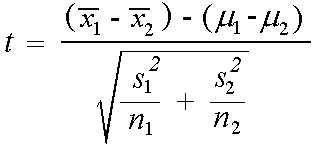


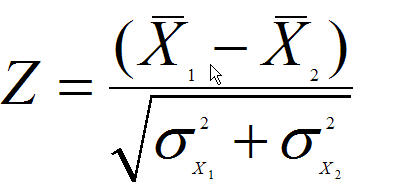
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Clipboard01-5c94e6b446e0fb00010ae8ed.jpg)


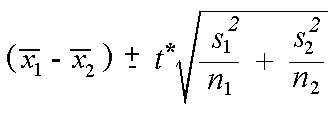












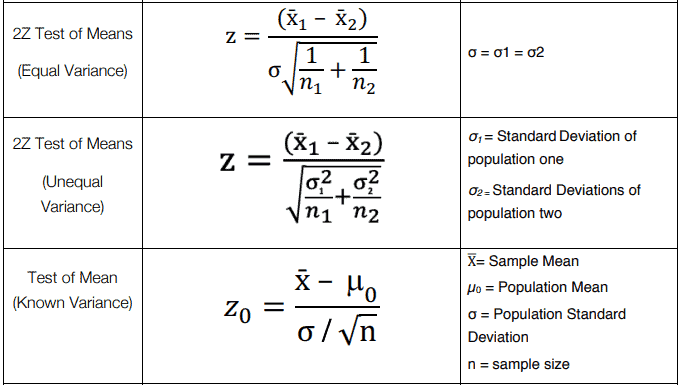


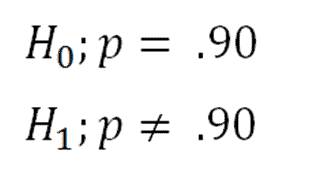




/ttest22-0afd4aefe9cc42628f603dc2c7c5f69a.png)


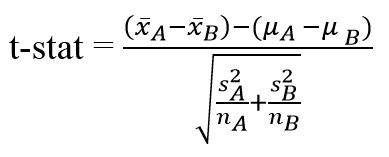



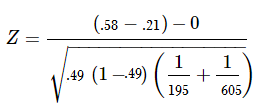



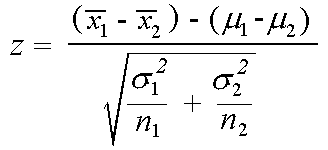



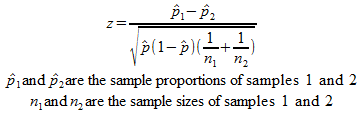



/comparing-two-proportions-57b5a4e33df78cd39c67380b.jpg)