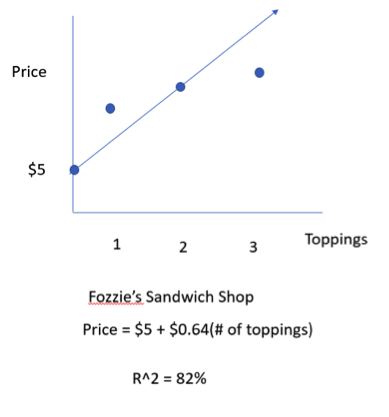
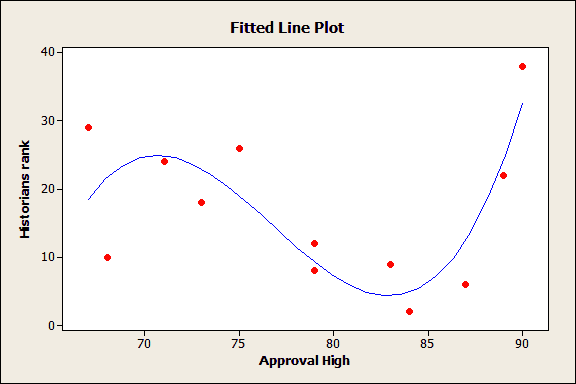
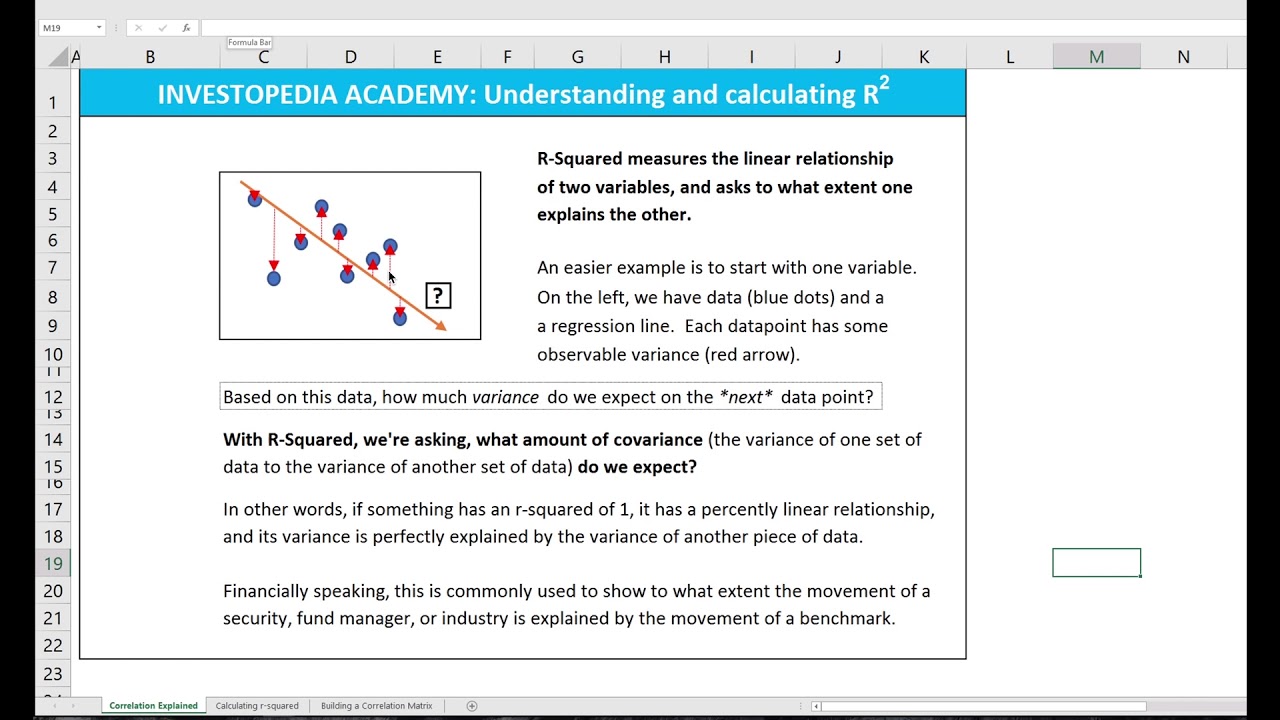
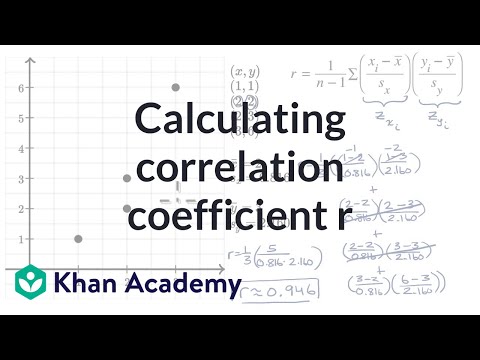
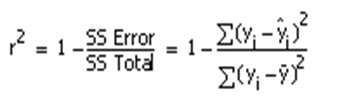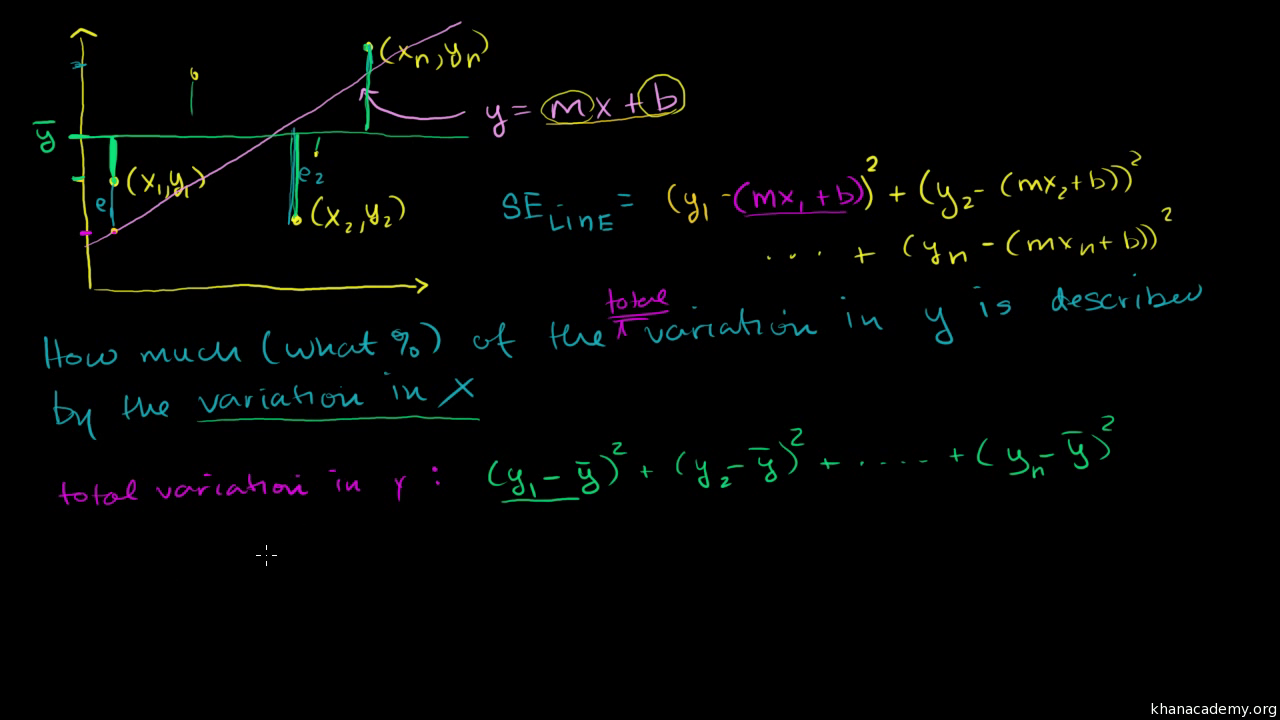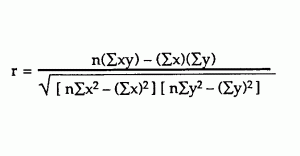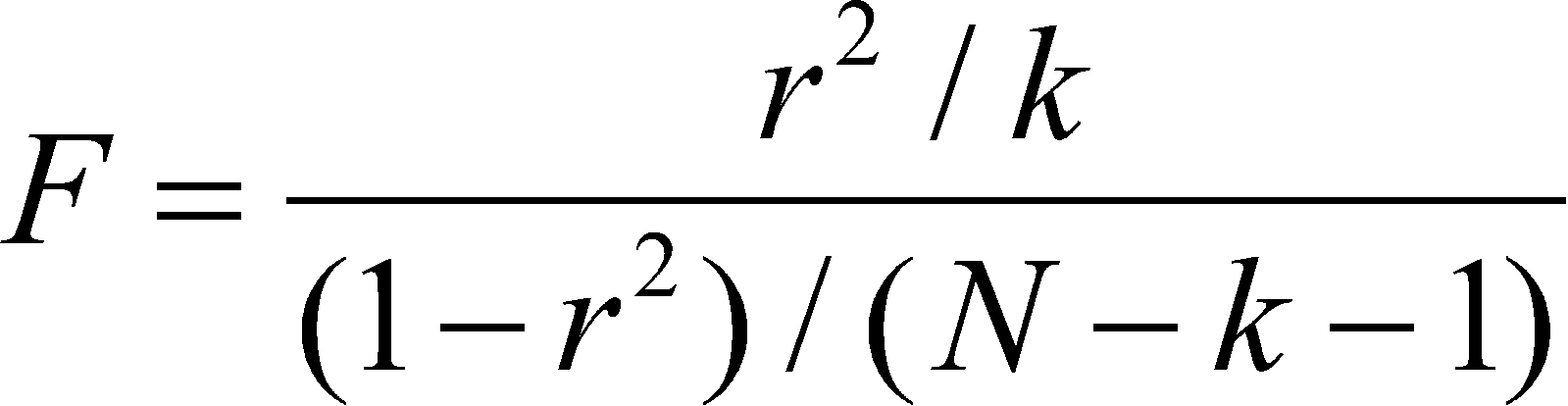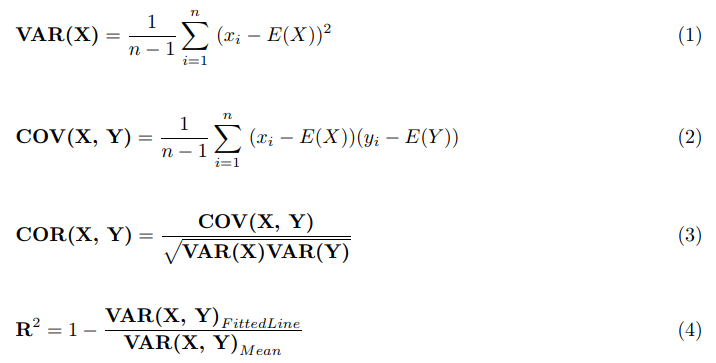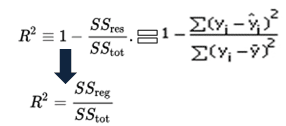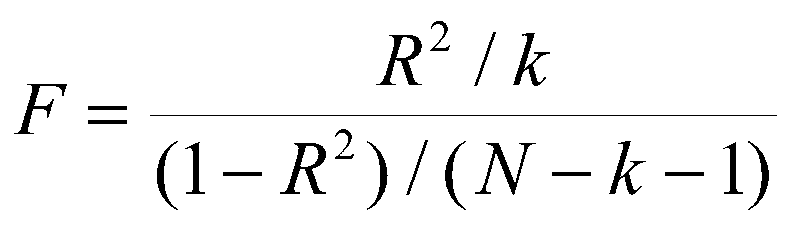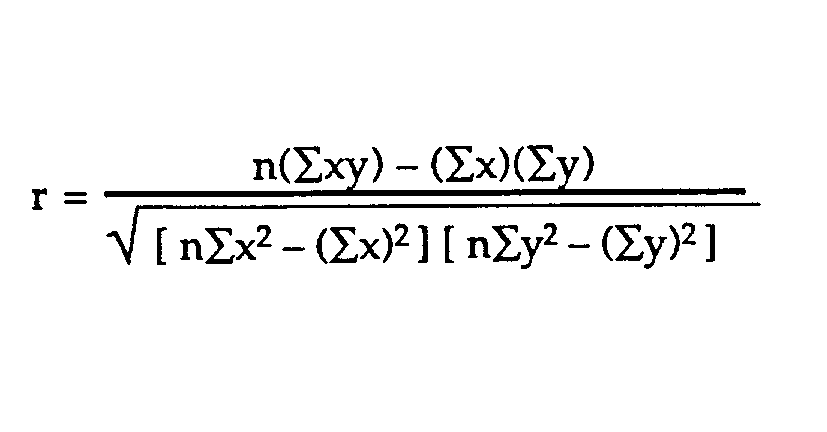R2 Formula Stats
R squared r 2 is a statistical measure that represents the proportion of the variance for a dependent variable thats explained by an independent variable or variables in a regression model.

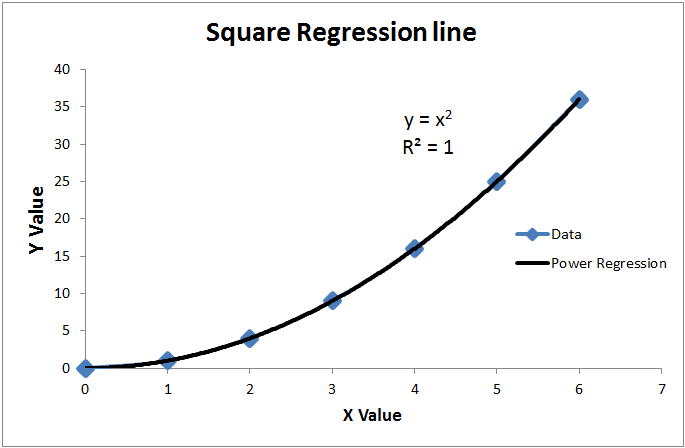
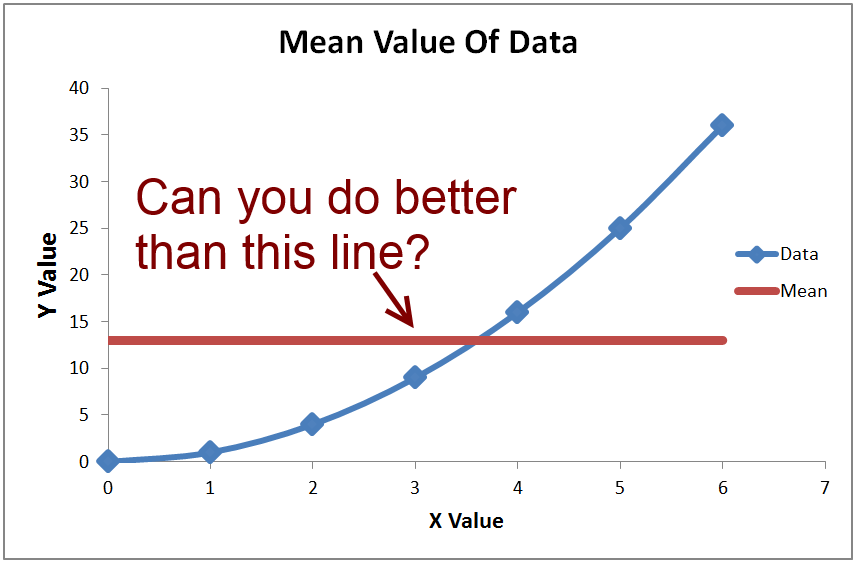
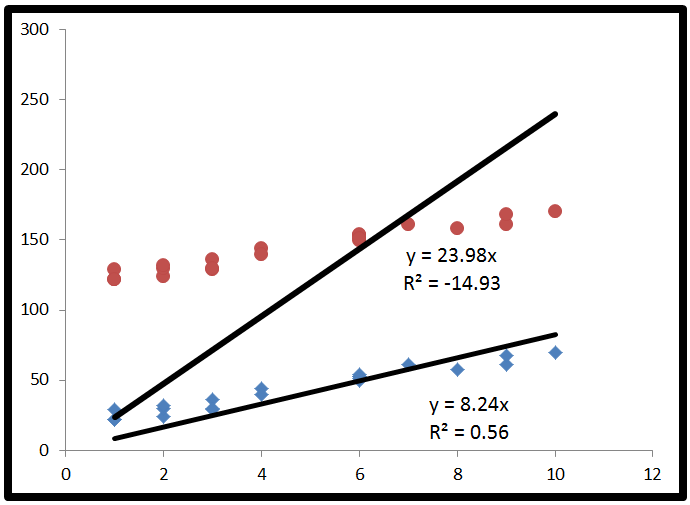
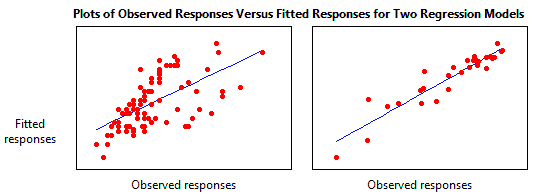
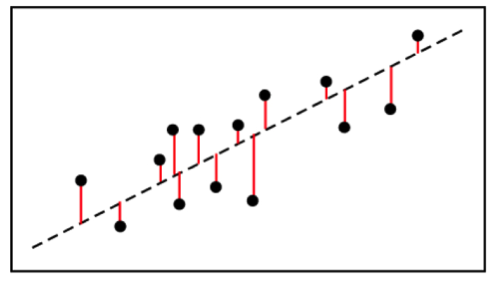
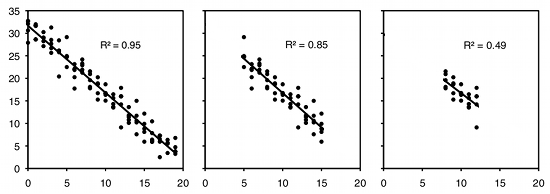
R2 formula stats. Data sets with values of r close to zero show little to no straight line relationship. Facetgrid to specify the rows and columns that needs to be plotted with or without faceting. The closer that the absolute value of r is to one the better that the data are described by a linear equation.
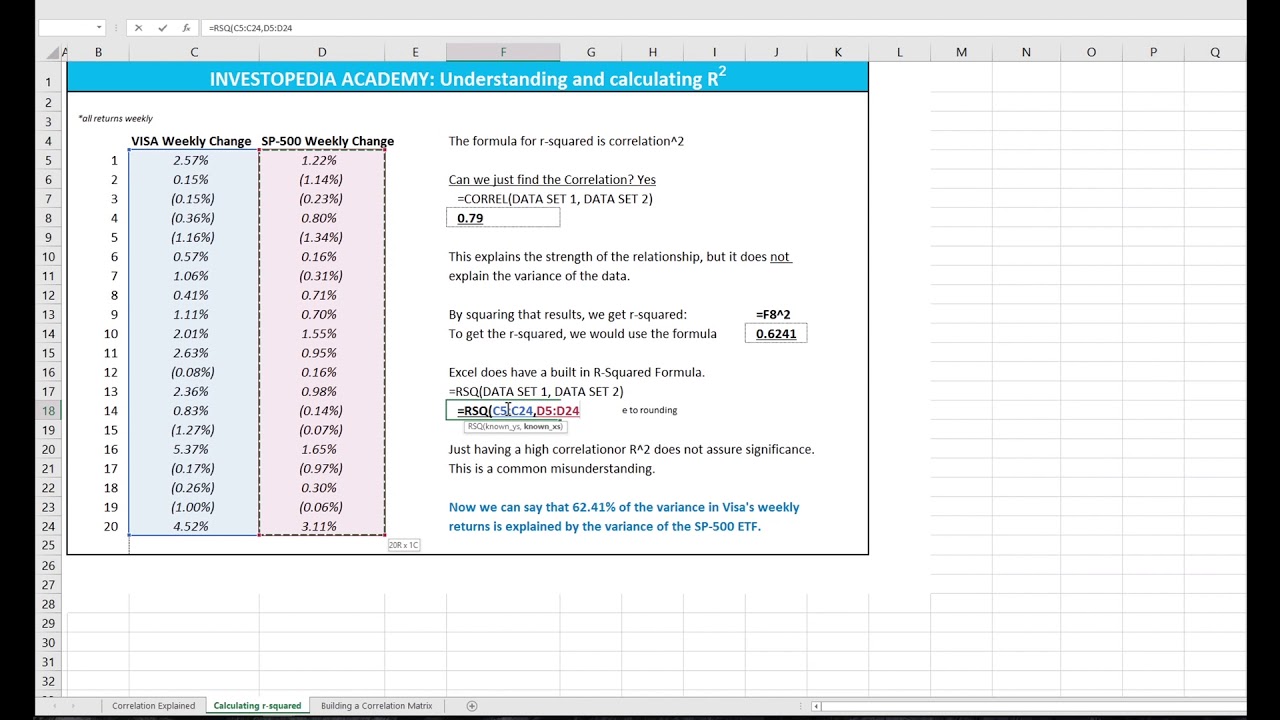
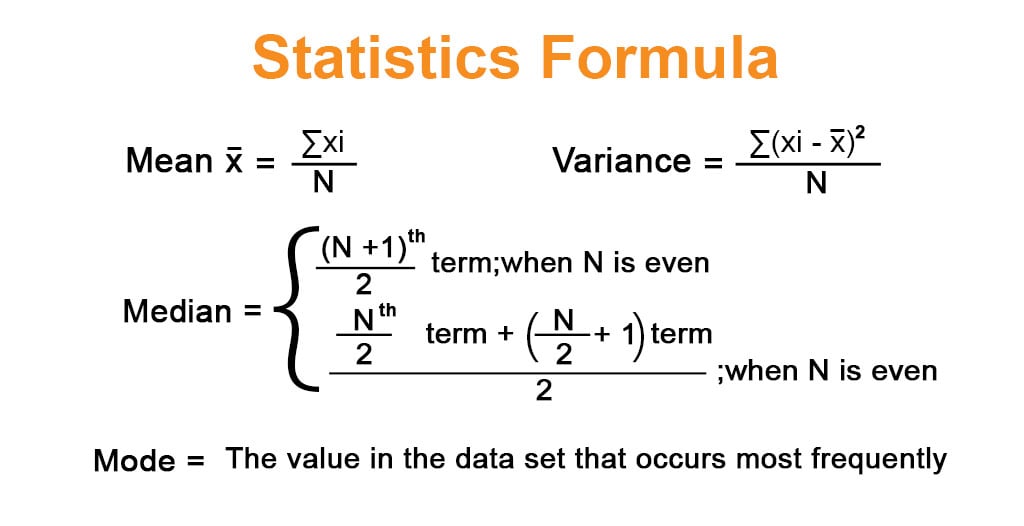
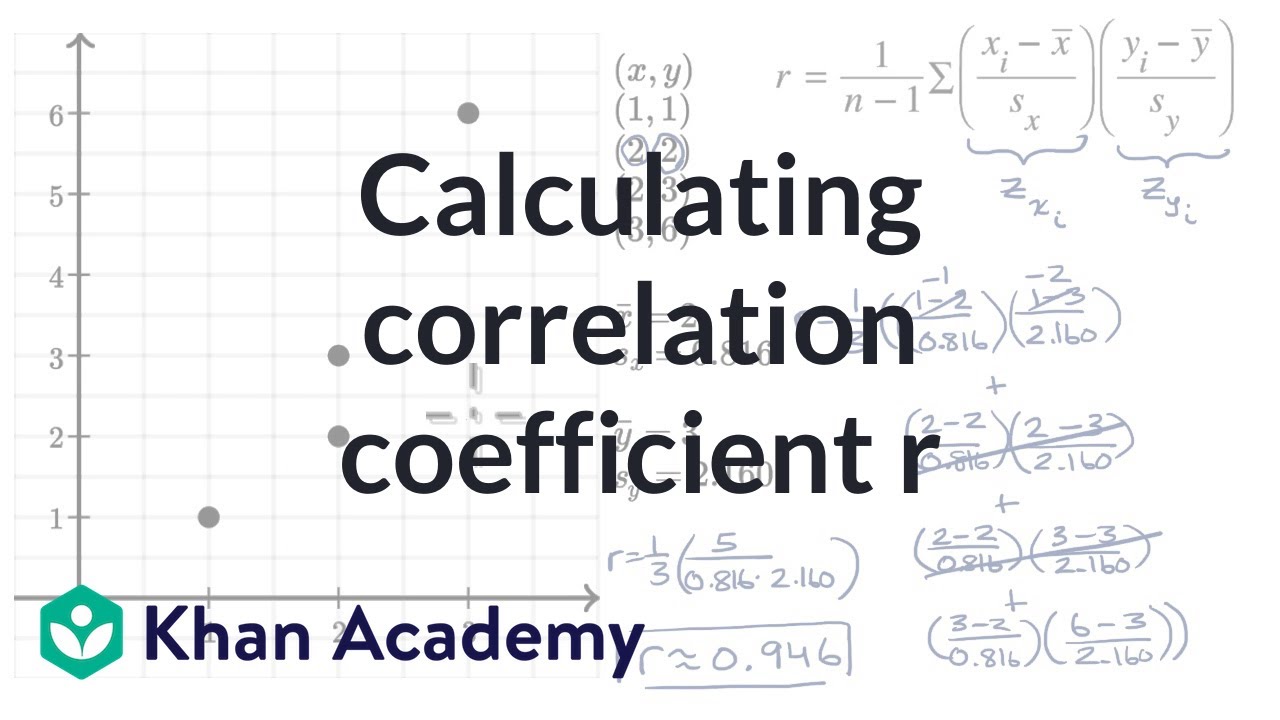
R the correlation coefficient n number in the given dataset x first variable in the context y second variable. Facetwrap to specify panels for plotting. The most common descriptive statistics are in the following table along with their formulas and a short description of what each one measures.
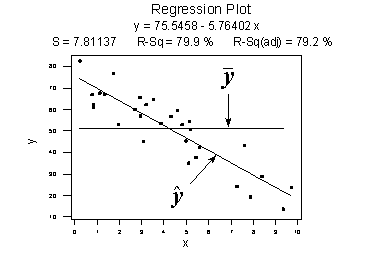
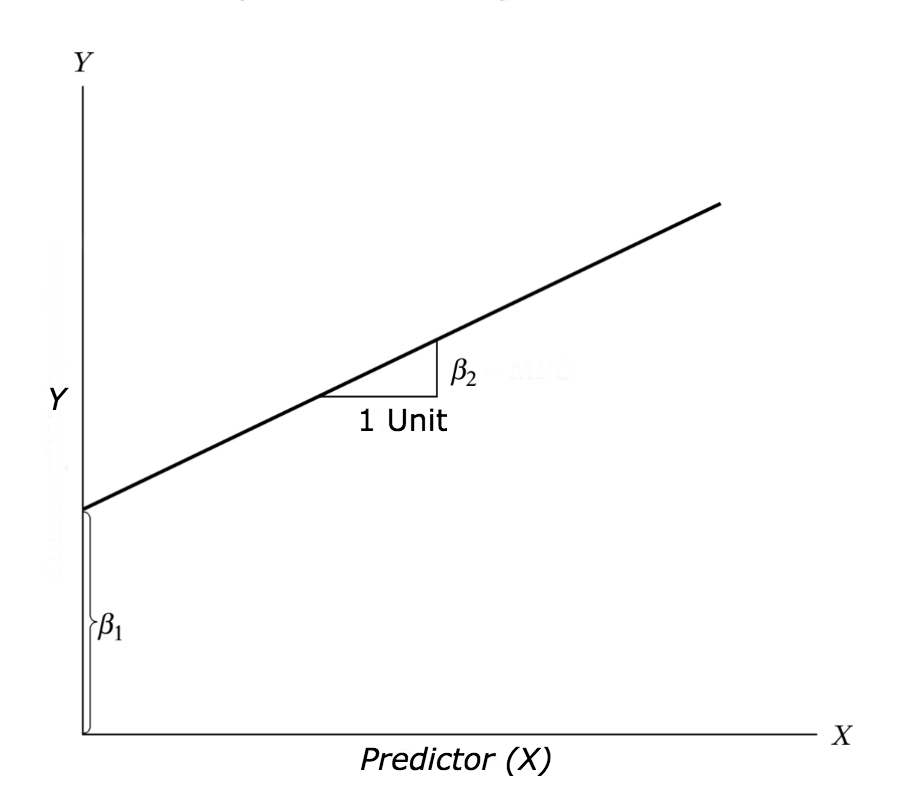
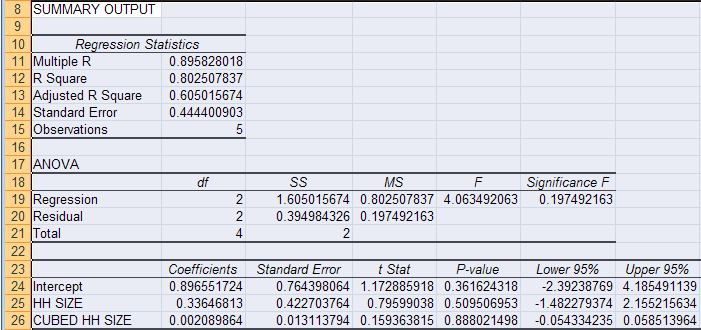
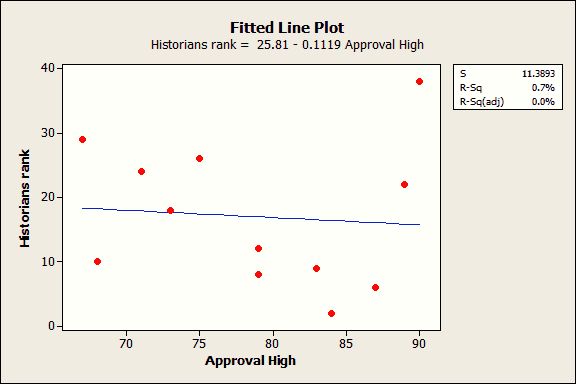
The correlation coefficient denoted by r tells us how closely data in a scatterplot fall along a straight line. There are 2 closely related quantities in statistics correlation often referred to as r and the coefficient of determination often referred to as r2. R squared 1 first sum of errors second sum of errors.
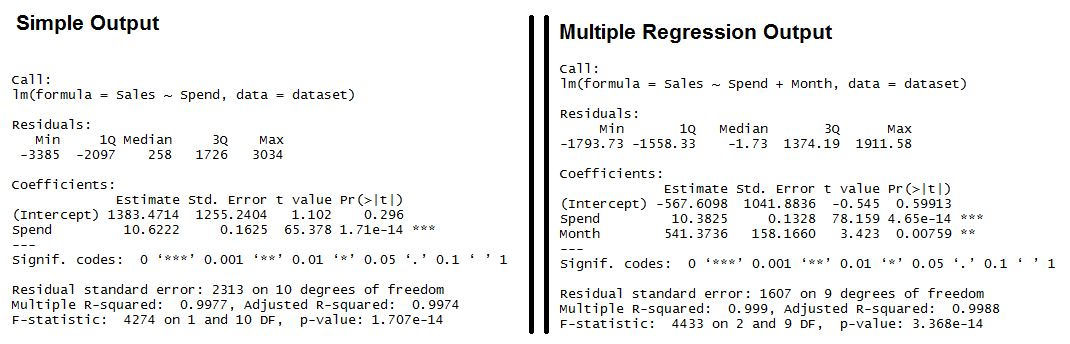
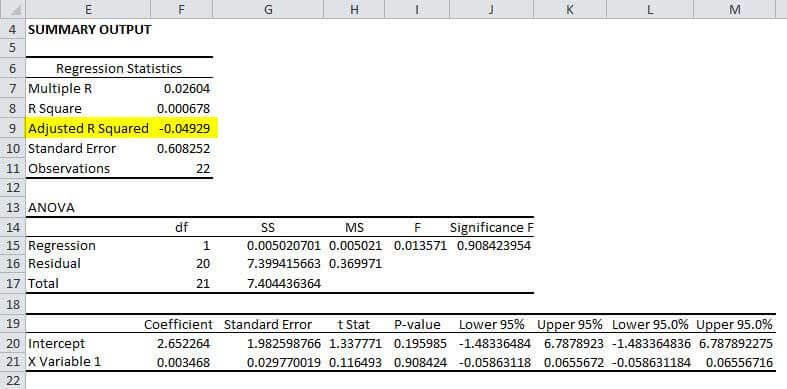
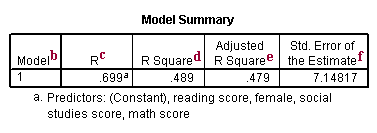
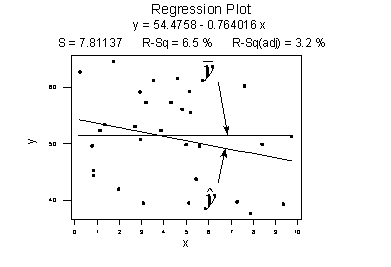
The key difference between r 2 and adjusted r 2 is that r 2 increases automatically as you add new independent variables to a regression equation even if they dont contribute any new explanatory power to the. Statistically figuring sample size when designing a study the sample size is an important consideration because the larger the sample size the more data you have and the more precise your results. The r squared formula is calculated by dividing the sum of the first errors by the sum of the second errors and subtracting the derivation from 1.
The correlation coefficient. Adjusted r 2 always takes on a value between 0 and 1. Today well explore the nature of the relationship between r and r2 go over some common use cases for each statistic and address some misconceptions.
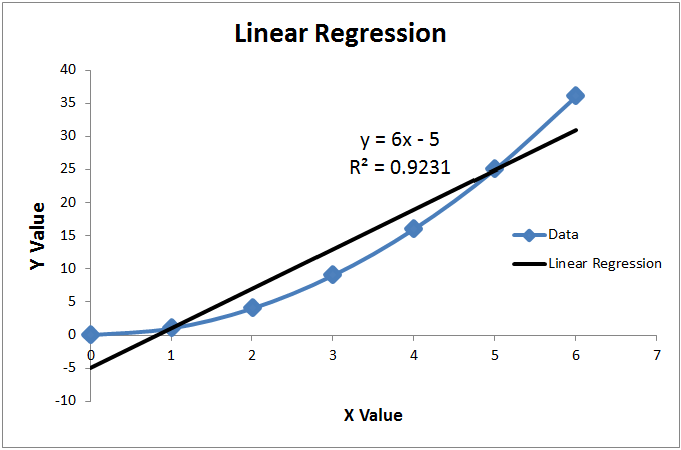
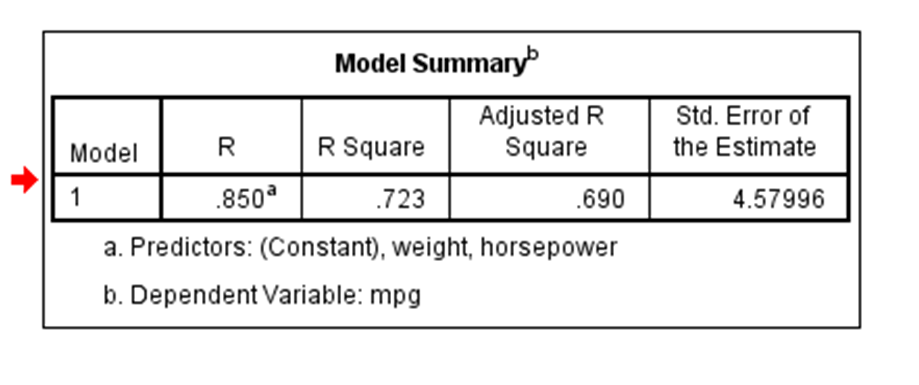
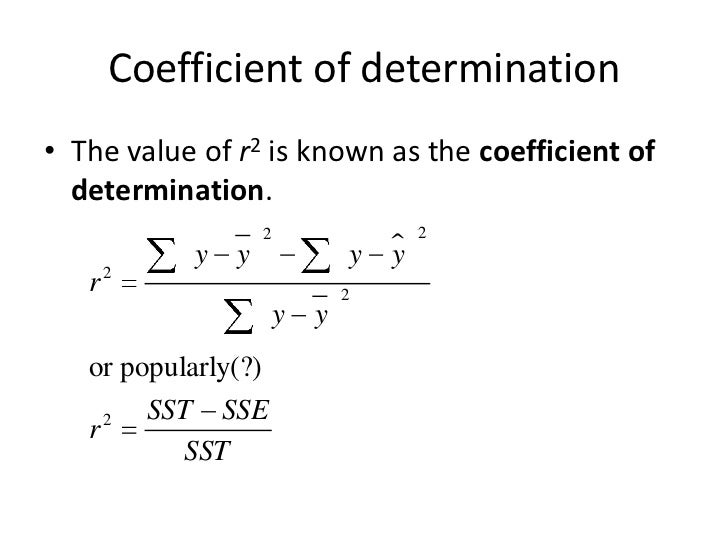
Coefficient of determination in statistics r 2 or r 2 a measure that assesses the ability of a model to predict or explain an outcome in the linear regression setting. The closer adjusted r 2 is to 1 the better the estimated regression equation fits or explains the relationship between x and y. More specifically r 2 indicates the proportion of the variance in the dependent variable y that is predicted or explained by linear regression and the predictor variable x also known as the independent variable.
In statistics the coefficient of determination denoted r 2 or r 2 and pronounced r squared is the proportion of the variance in the dependent variable that is predictable from the independent variables. You can use formulas in various ggplot2 functions. This will influence the form of the fit.
Geomsmooth or statssmooth to specify the formula to use in the smoothing function.
R Squared Interpretation R Squared Linear Regression By Cory Maklin Towards Data Science
towardsdatascience.com