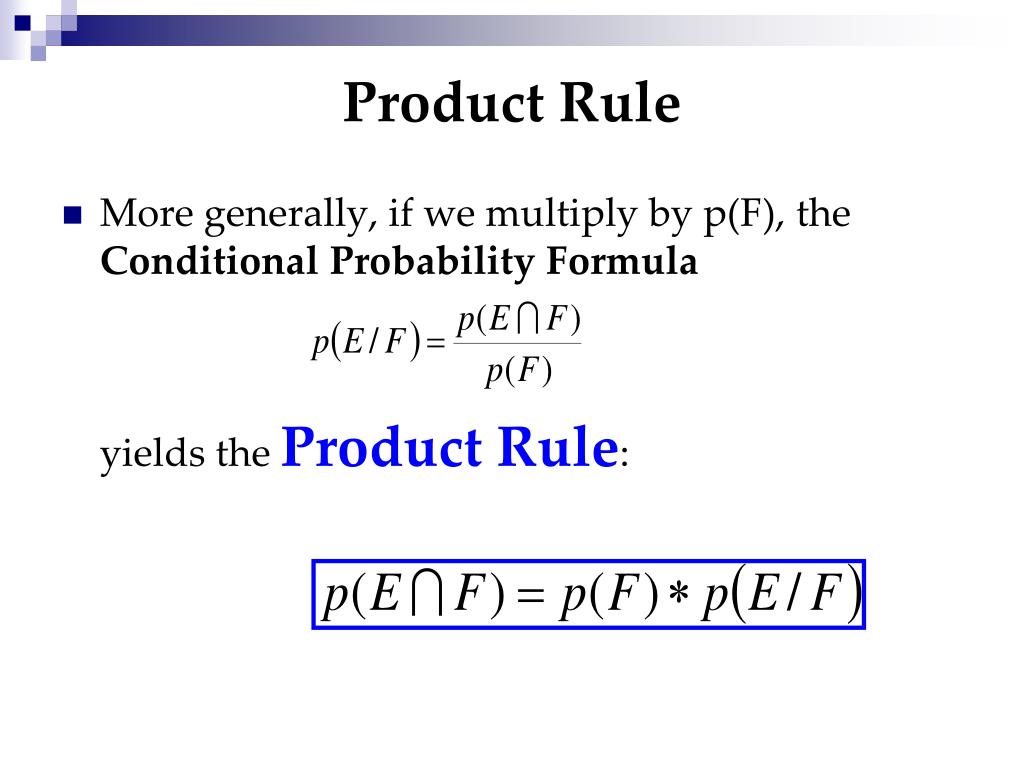
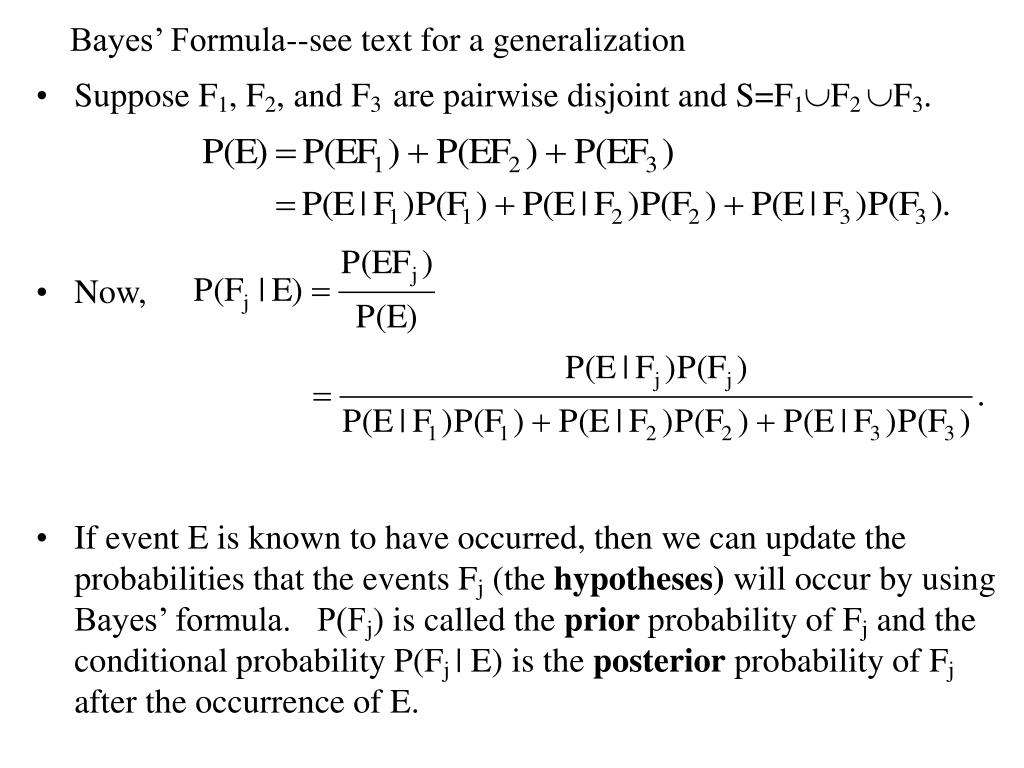
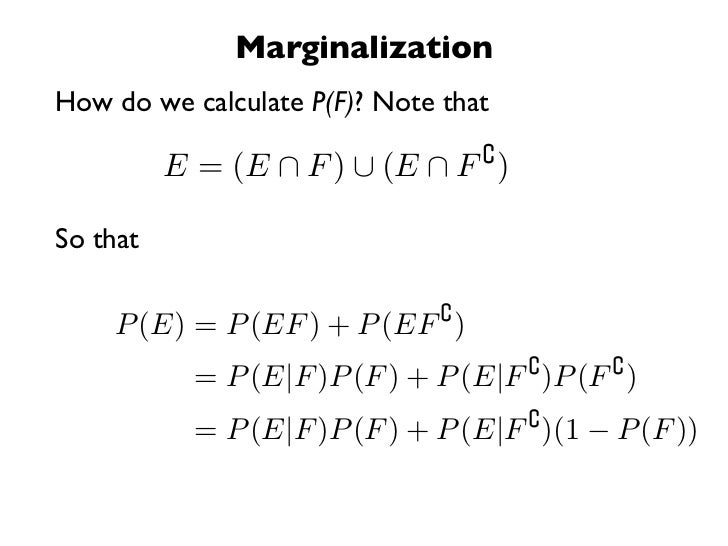
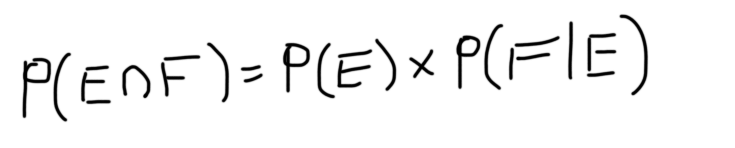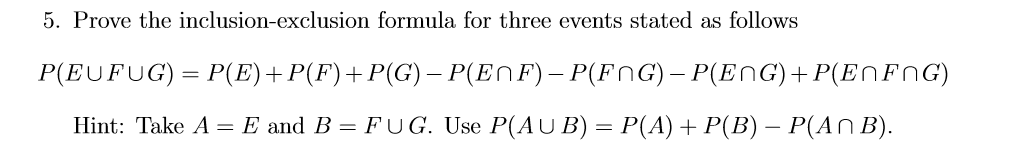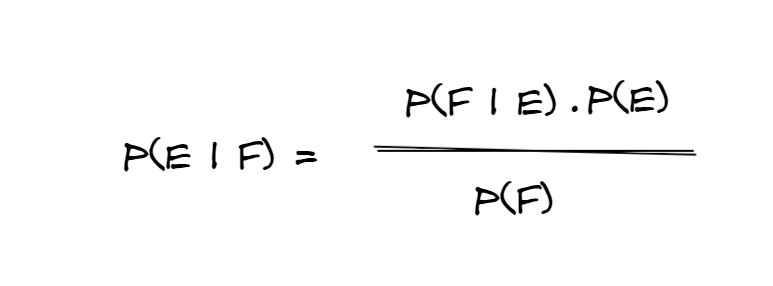Pef Formula
P not e and not f p e f p e f 1 p e f 1 58 8 58 demorgans law if a b a b ator a b a b.

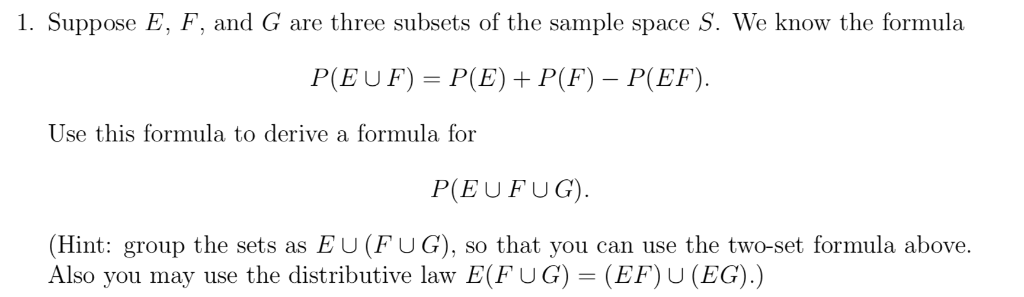
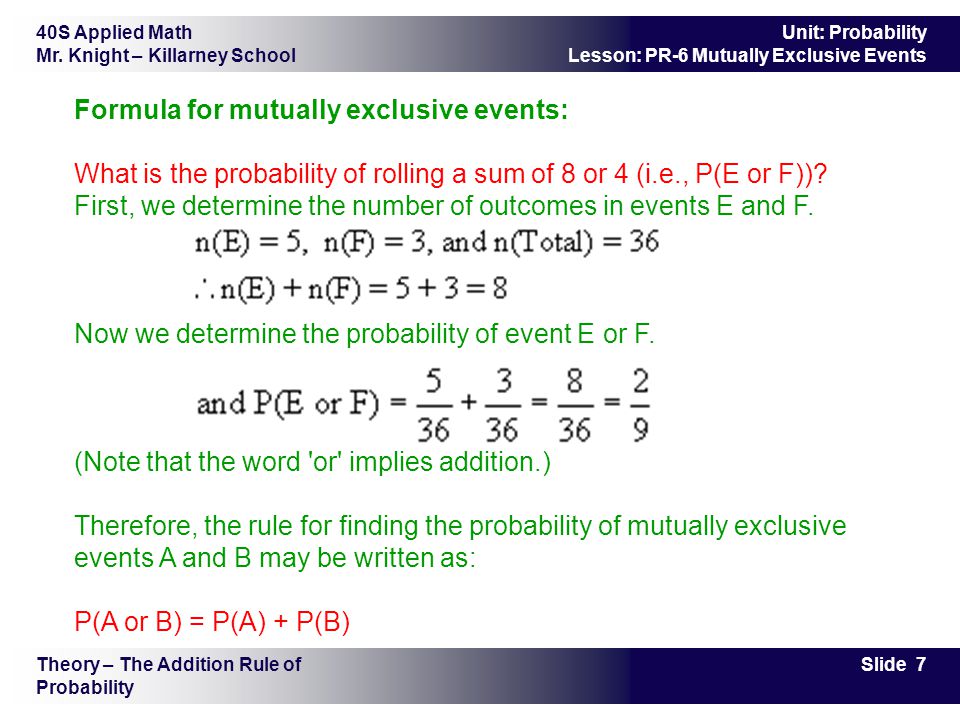
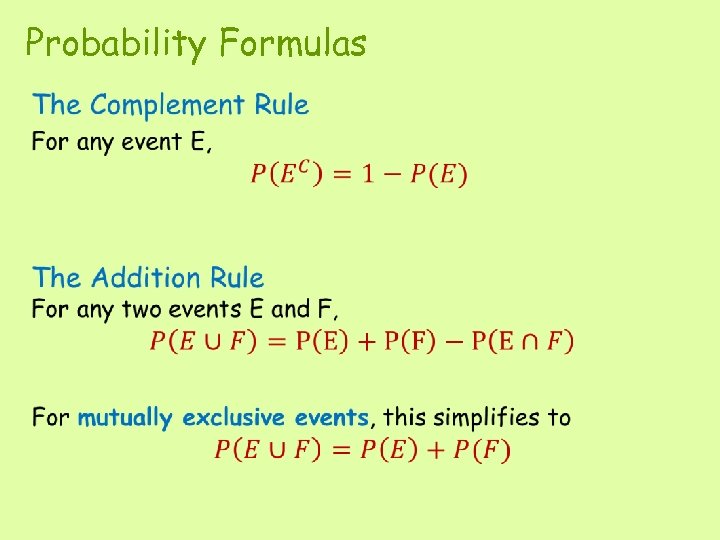
Pef formula. The empirical probability of an event is the relative frequency of a frequency distribution based upon observation. P e or f p e p f p e and f where p e and f is the set of outcomes in both e and f. Empirical probability is based on observation.
This rule is true both for disjoint events and for non disjoint events for if two events are indeed disjoint then p e and f 0 and the general addition formula simply reduces to the basic addition formula for disjoint events. The pe ratio can help us determine from a valuation perspective which of the two is cheaper. If southland industries has 60000 of 16 annual interest bonds outsanding 1500 shares of preferred stock paying an annual dividend of 500 per share and 4000 shares of common stock outsanding.
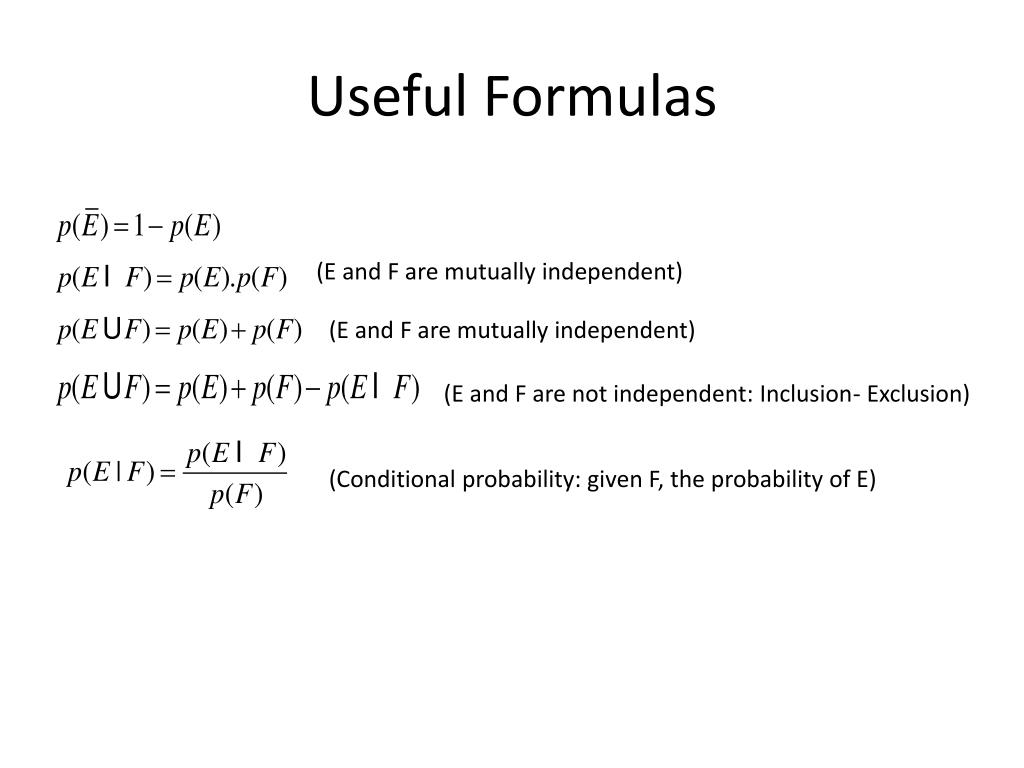
The formula gives pe or f 14 313 352 2252 42. Pe 14 and pf 313 jack queen or king out of 13 choices pe and f 352. Pe f pe 1 we say that e and f are independent if pe f pe pf 2 note.
Also 2 is properly dened when pf 0. Pe ne ns empirical probability. If the sectors average pe is 15 stock a has a pe 15 and stock b has a pe 30 stock a is cheaper despite having a higher absolute price than stock b because you pay less for every 1 of current earnings.
2 is usually better to do the math. Price earnings ratio pe ratio. P divided by f pf ratio.
How to calculate the pf ratio. Compute earnings 1 answers. All probabilities are between 0 and 1 inclusive 0 pe 1.
Pe f n probability rules. 90 040 pf ratio 225. F represents the fio 2 the fraction percent of inspired oxygen that the patient is receiving expressed as a decimal 40 oxygen fio 2 of 040.
Pao2 fio2 p represents pao 2 arterial po2 from the abg. In short the pe ratio shows what the market is willing to pay today for a stock based. The price earnings ratio pe ratio is the ratio for valuing a company that measures its current share price relative to its per share earnings.
2 is a rearrangement of 1. Compute pef and pfe given pe4 pf6 and pe and f 23. 1 is a useful way to think about independence.
The pe ratio helps investors determine the market value of a stock as compared to the companys earnings.
Solution Let E And F Be Two Mutually Exclusive Events And Suppose P E 0 4 And P F 0 2 Compute The Probabilities Below A P E Intersection F B P E Union F C
www.algebra.com