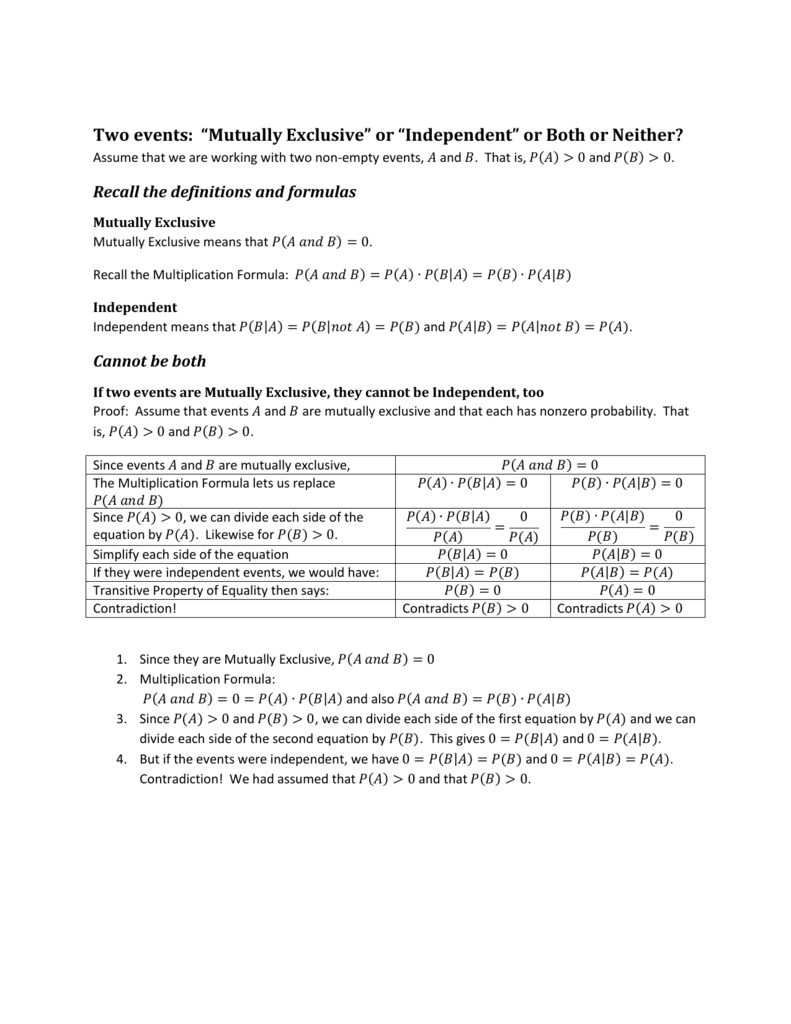
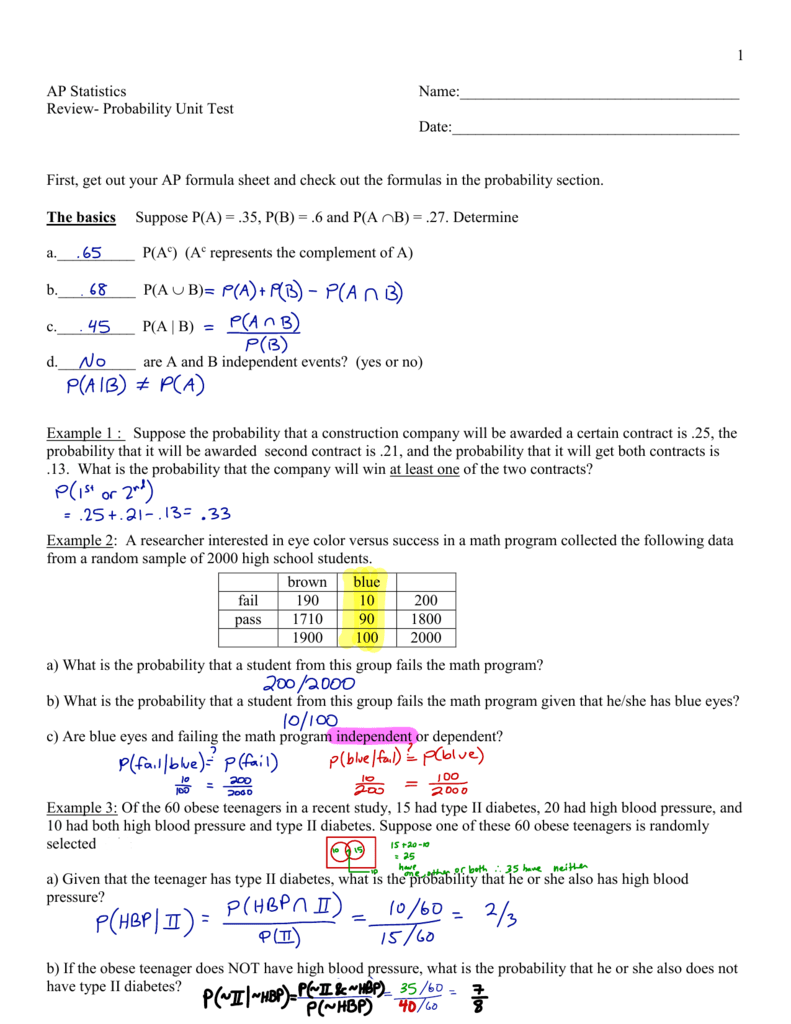
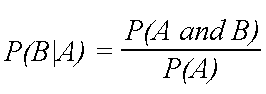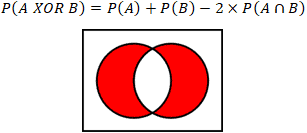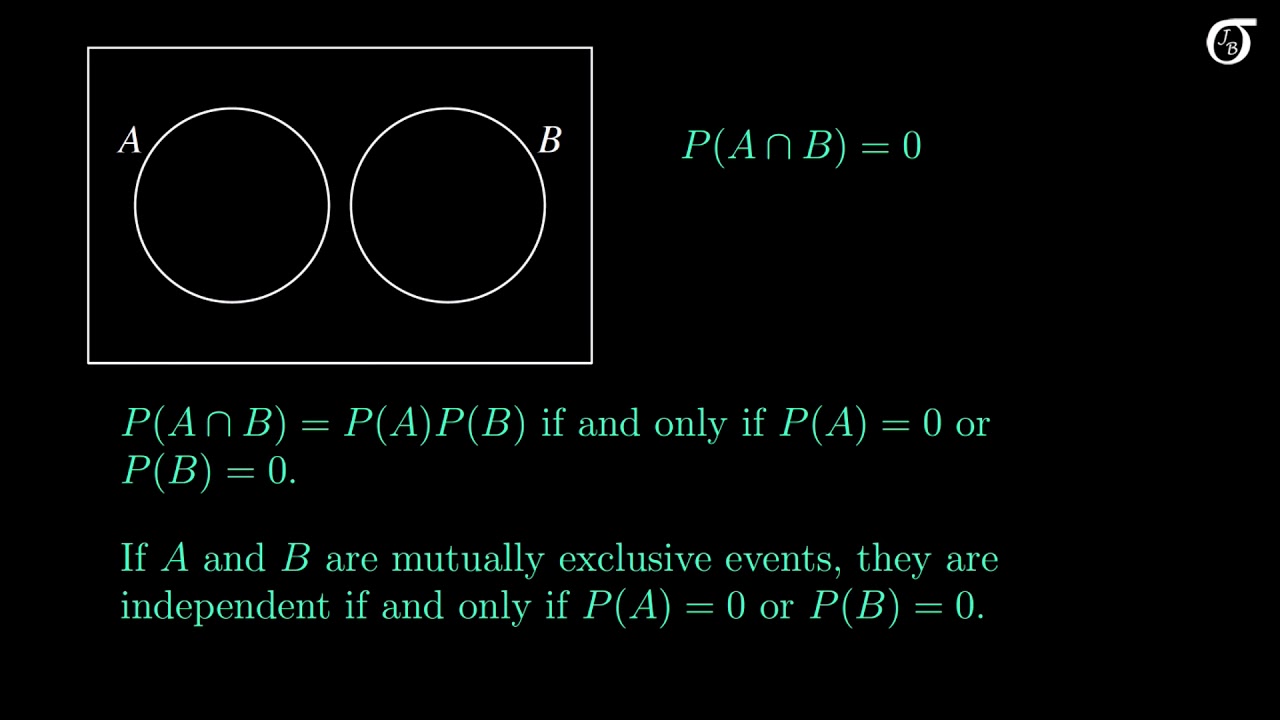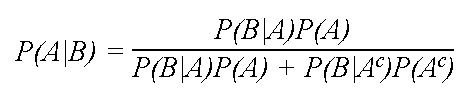Pa B Formula Independent
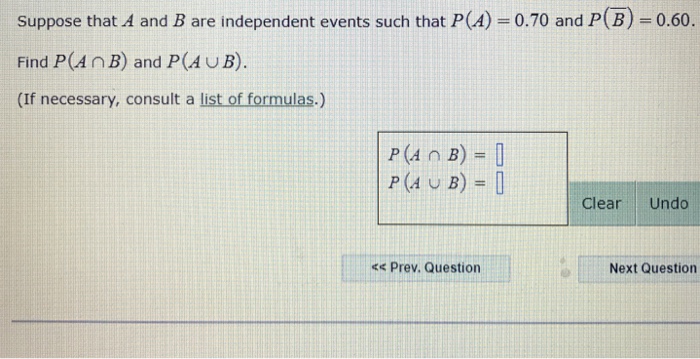
Find pa and b pa or b pb not a and pneither a nor b.
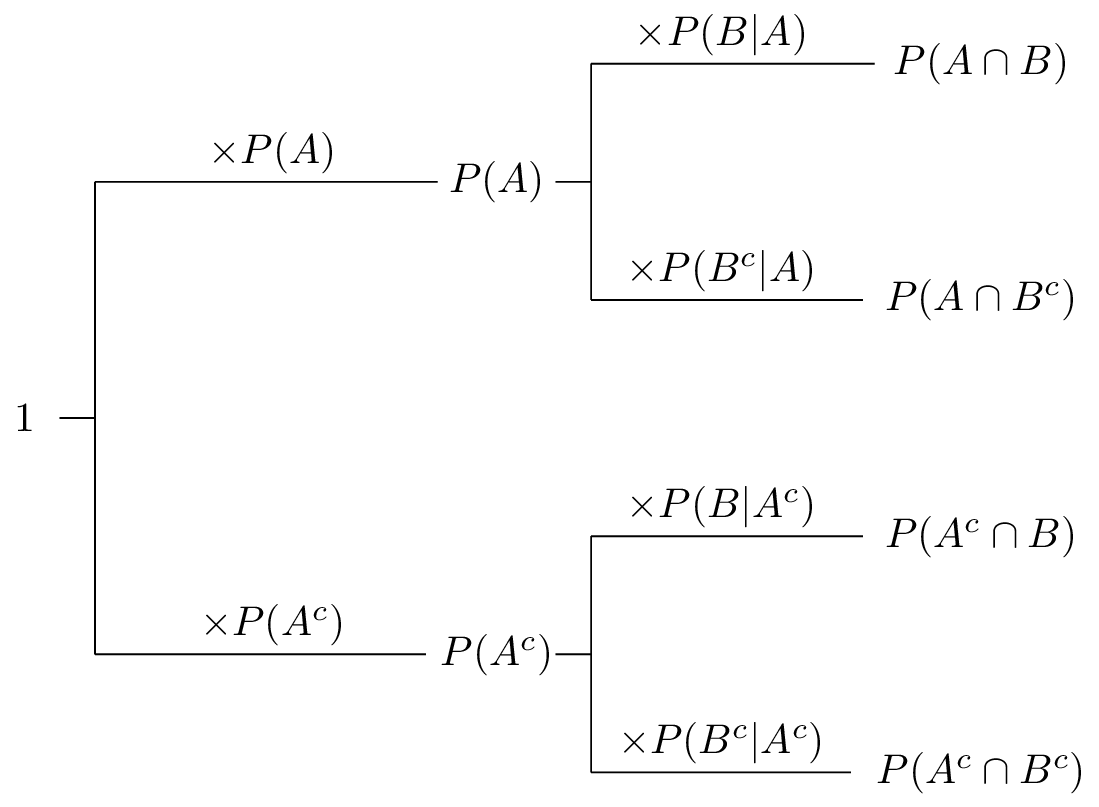
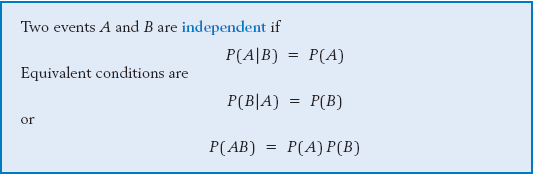
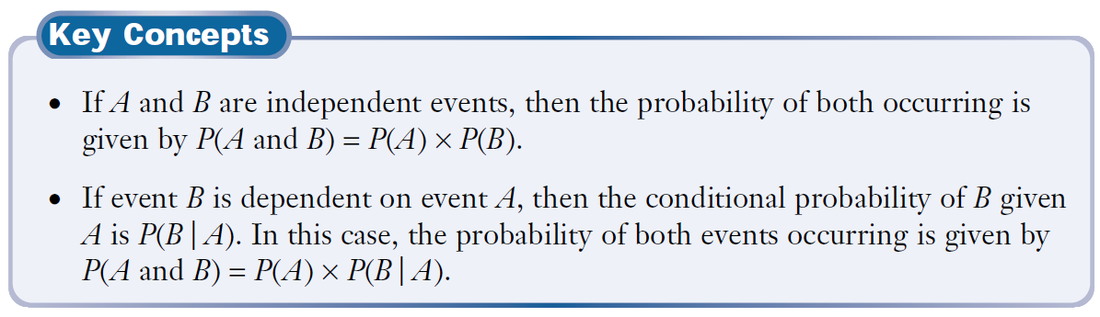
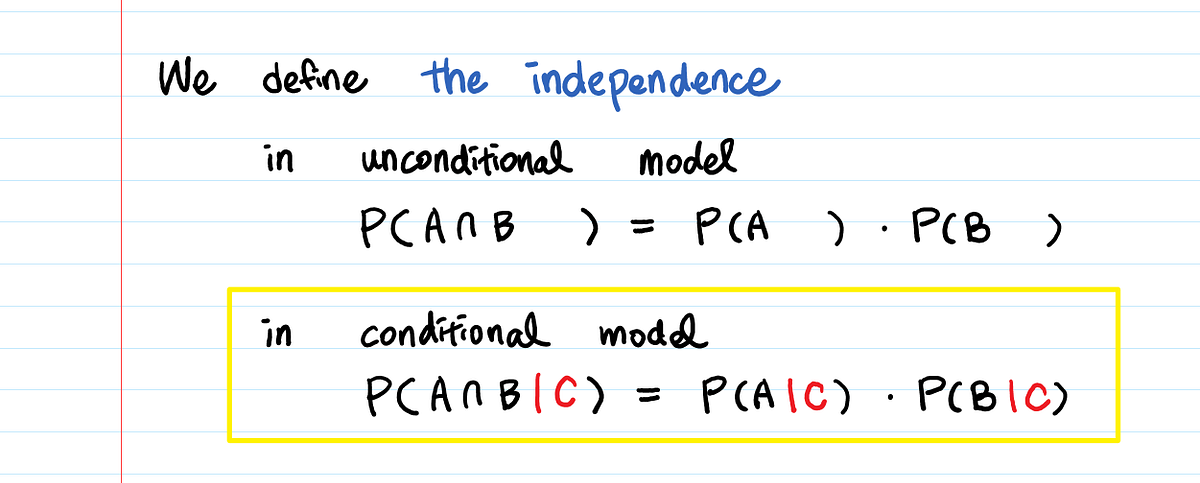
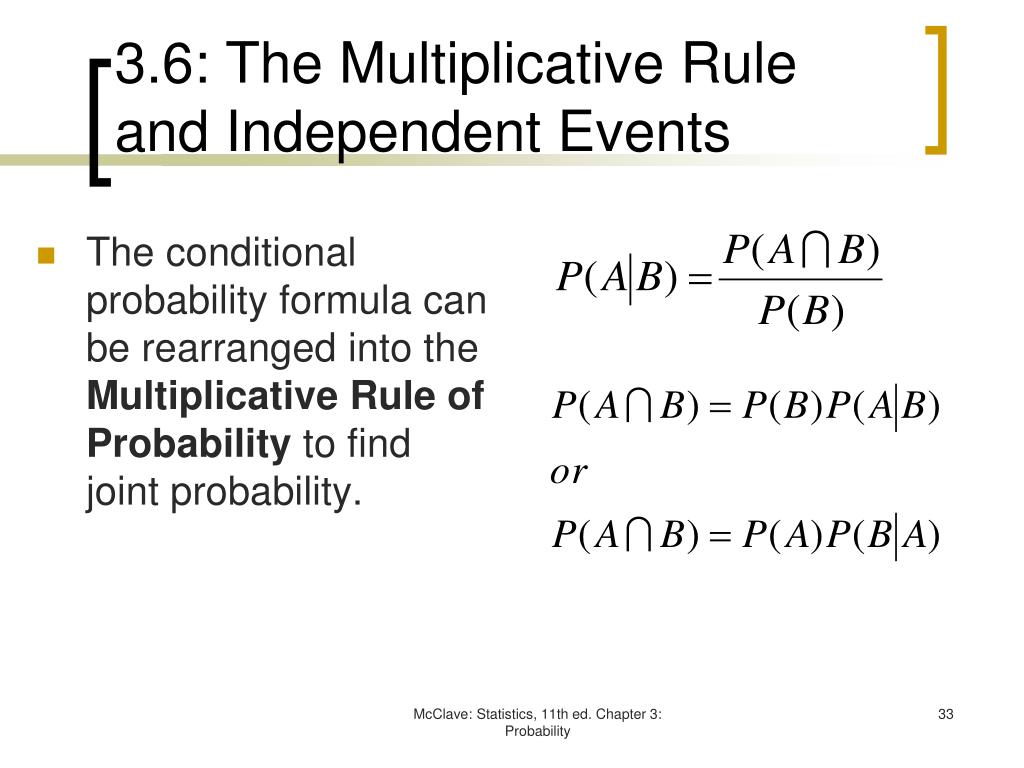
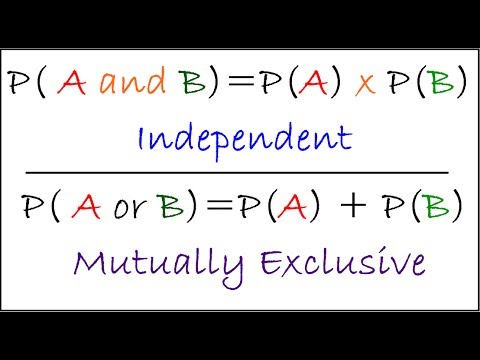
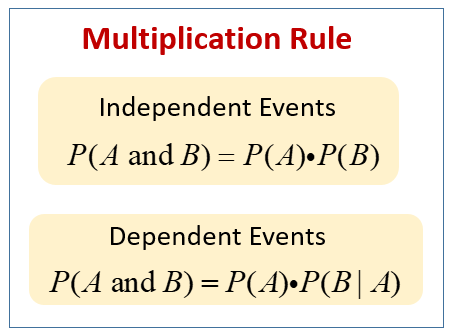
Pa b formula independent. Formula for the probability of a and b independent events. We define mathamath and mathbmath to be independent if mathpacap b papbmath. Unfortunately there isnt one.
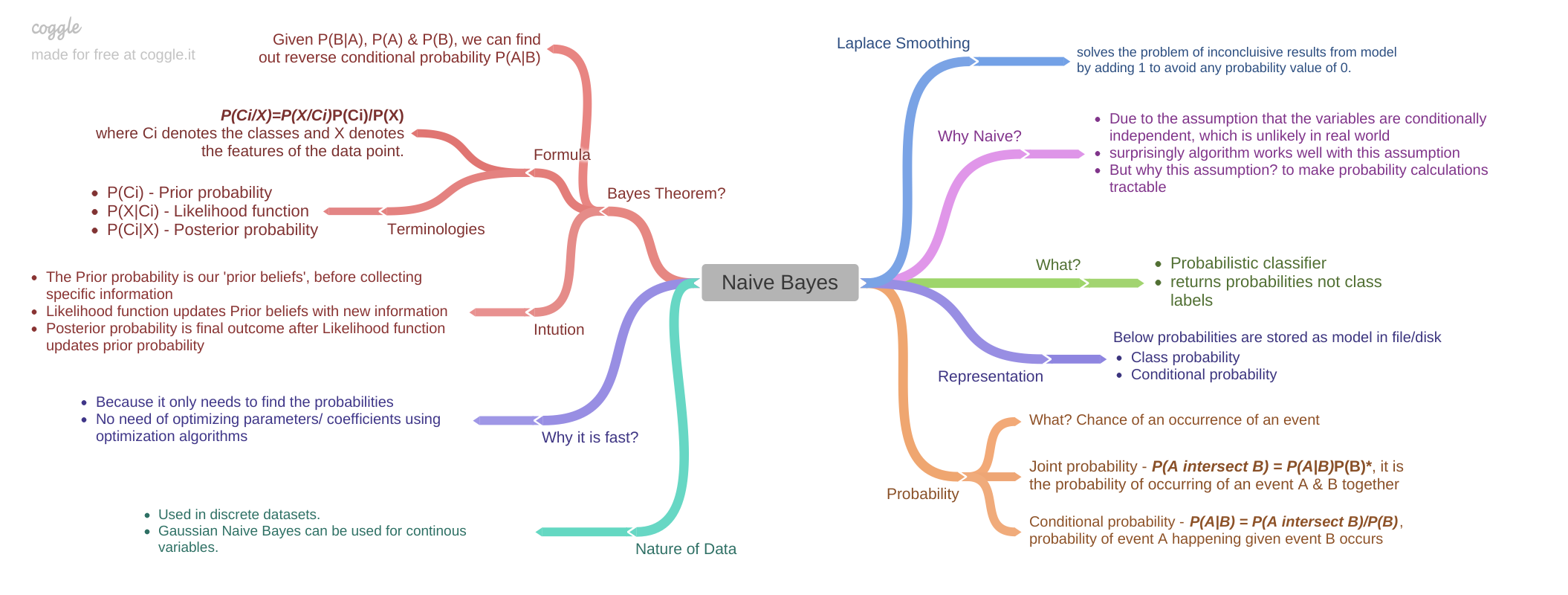
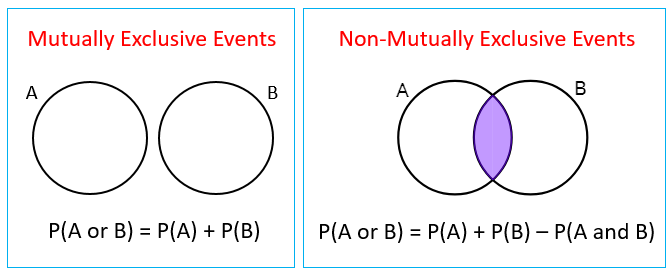
The above formula relating conditional probability and the probability of intersection gives us an easy way to tell if we are dealing with two independent events. All you do is multiply the probability of one by the probability of another. This means that the probability of b occurring whether a has happened or not is simply the probability of b occurring.
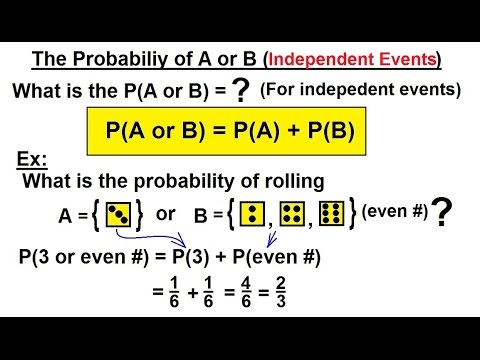
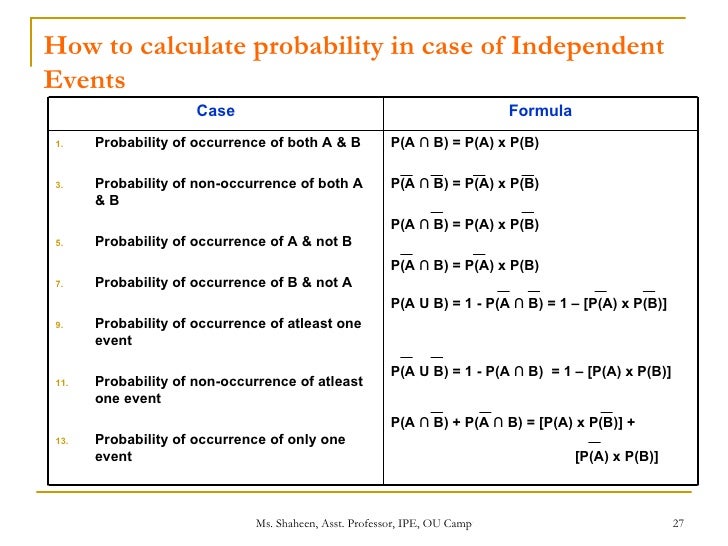
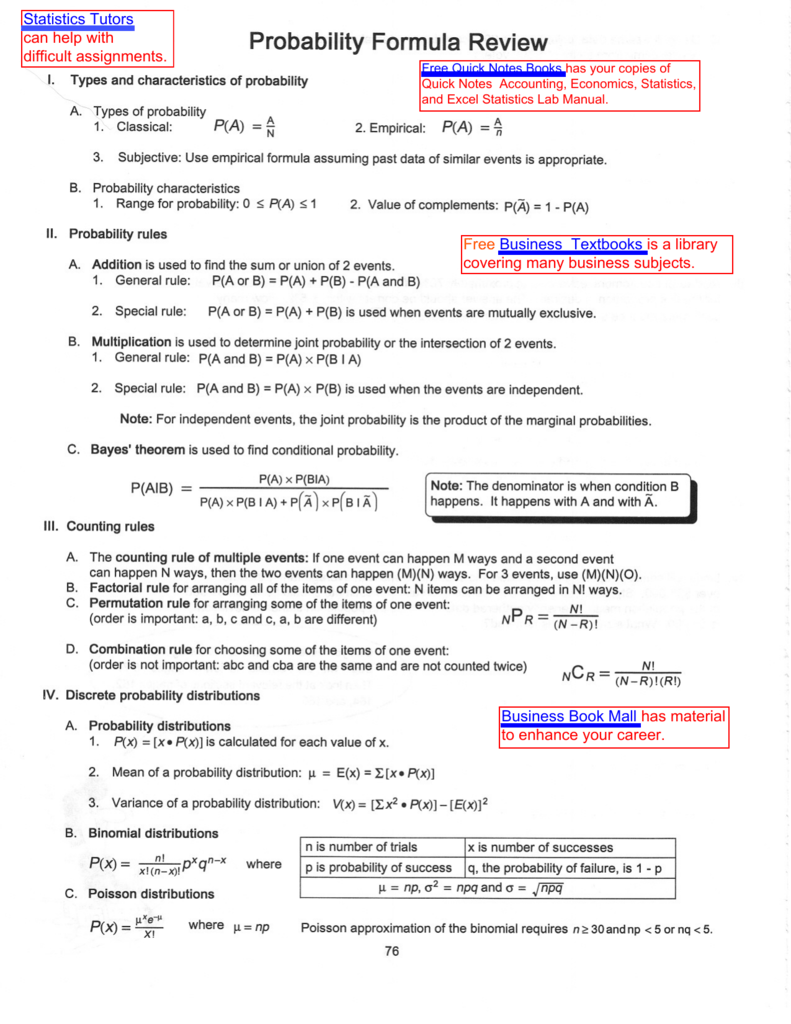
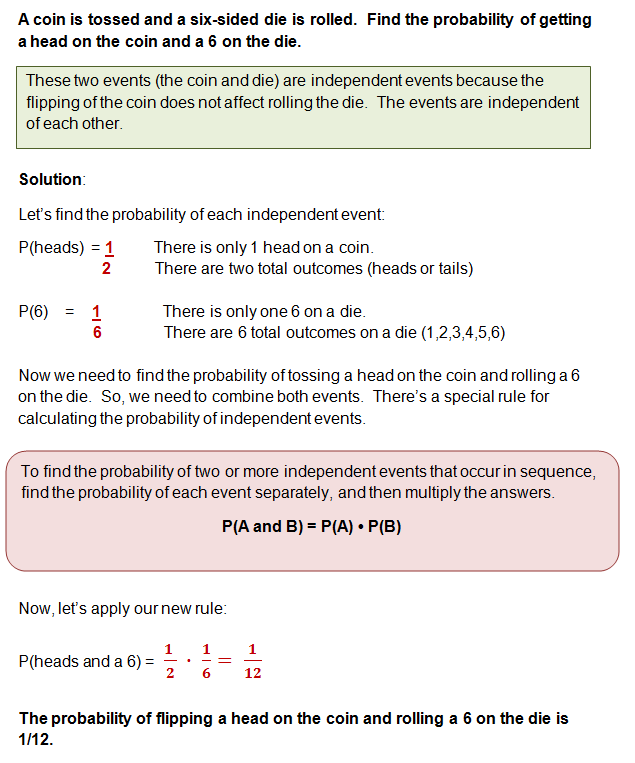
Pa and b pa pb. Three events a b and c are mutually independent if. Pa b pa pb pb c pb pc pa c pa pc pa b c pa pb pc solved example for you.
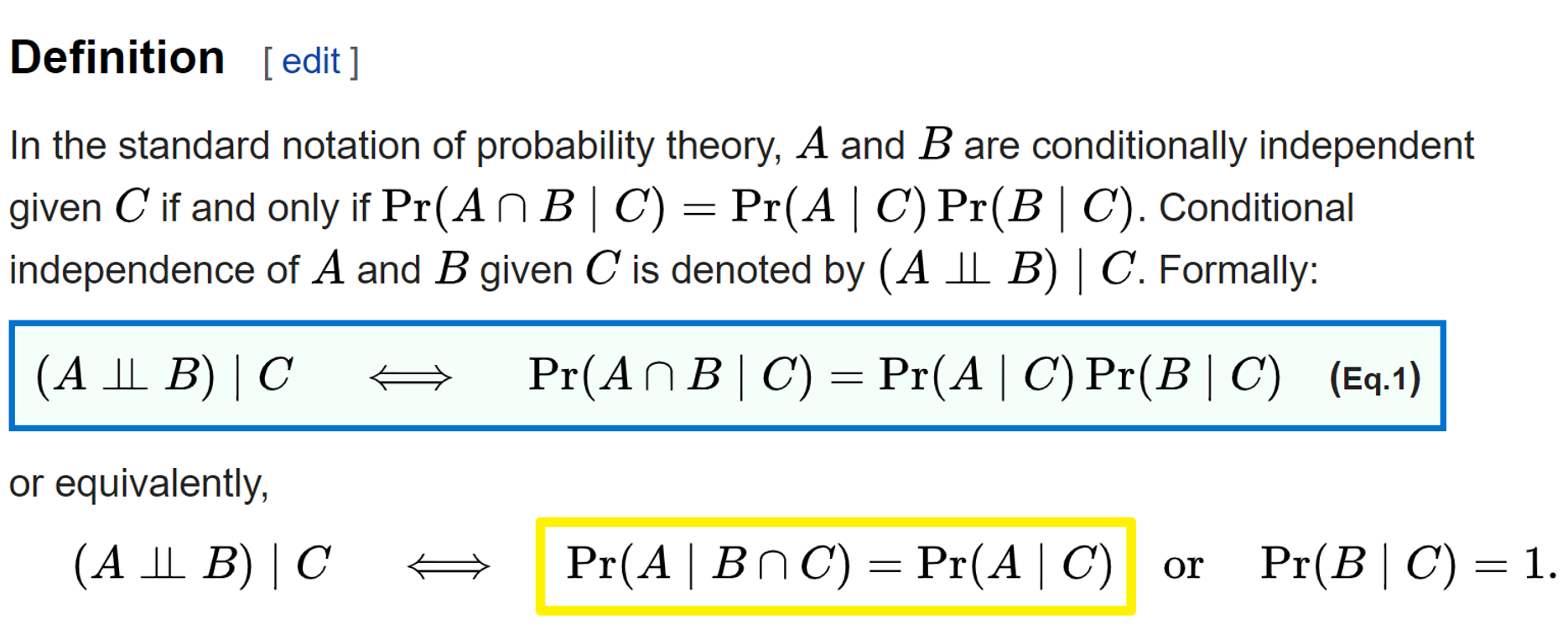
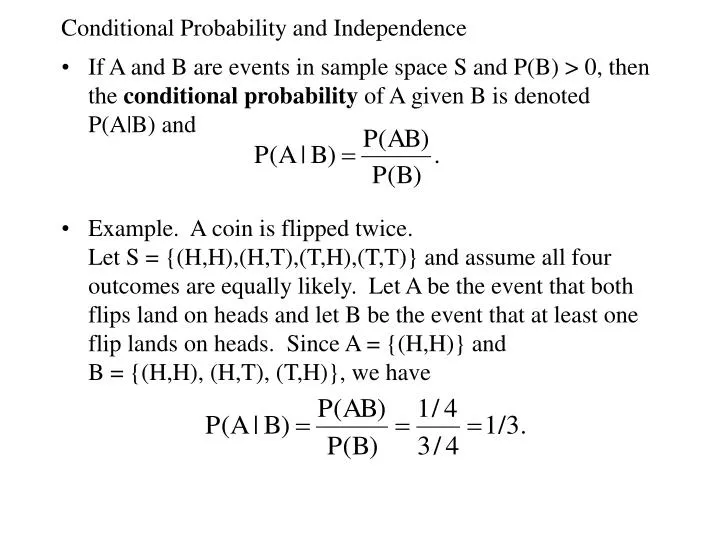
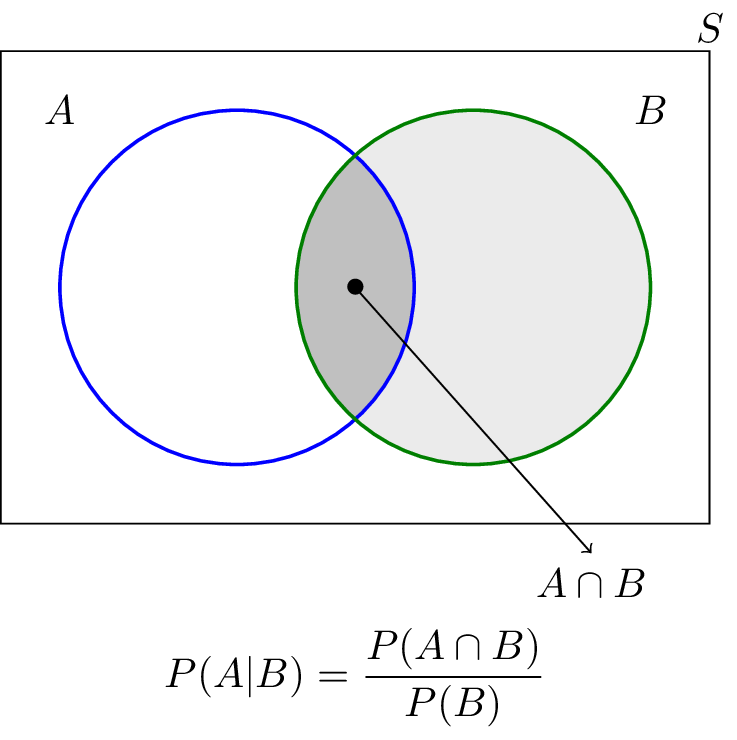
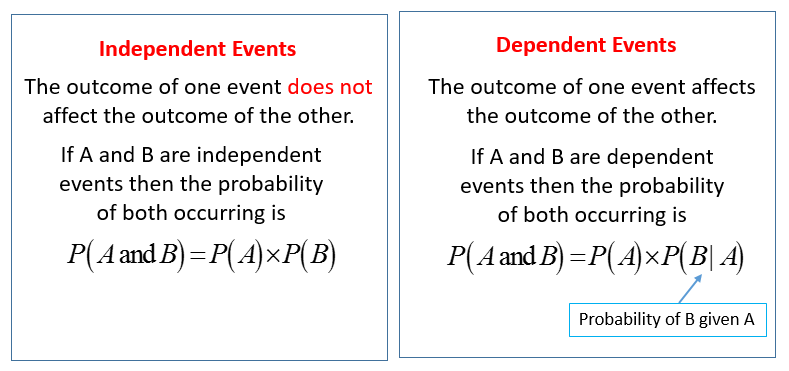
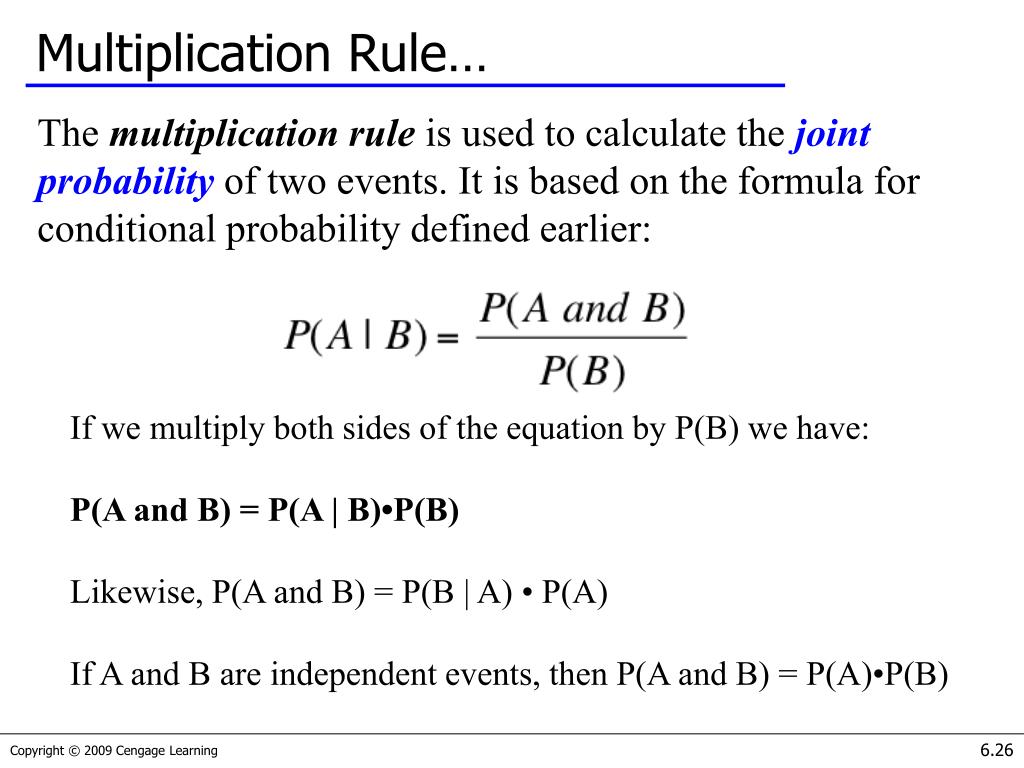
Given two events a and b from the sigma field of a probability space with the unconditional probability of b being greater than zero ie pb0 the conditional probability of a given b is defined to be the quotient of the probability of the joint of events a and b and the probability of b. P is for probability. Note that all four of the stated conditions must hold for three events to be independent.
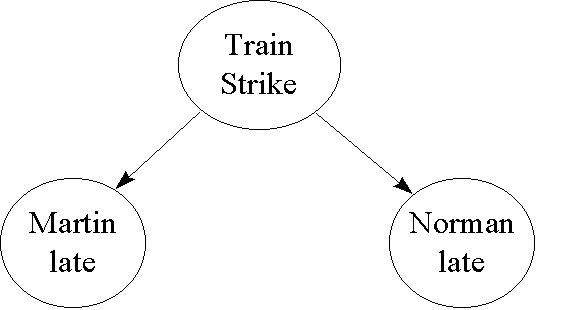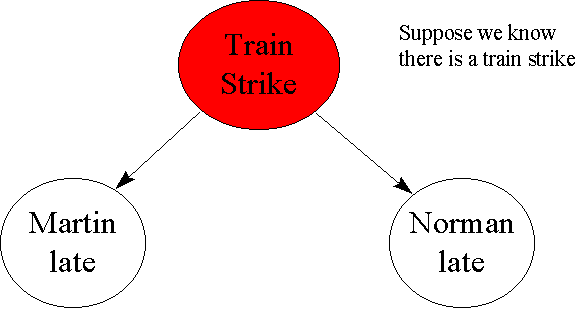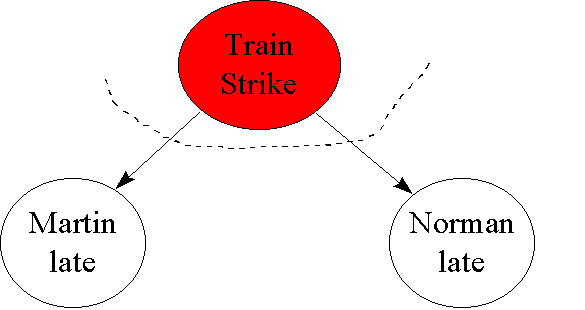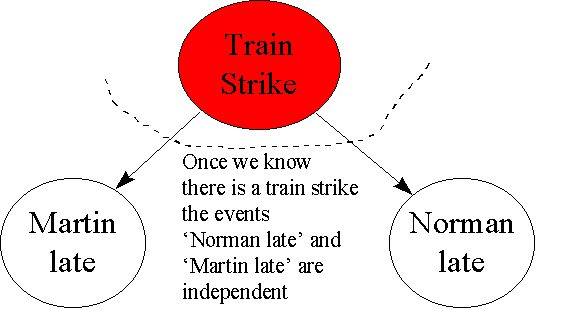
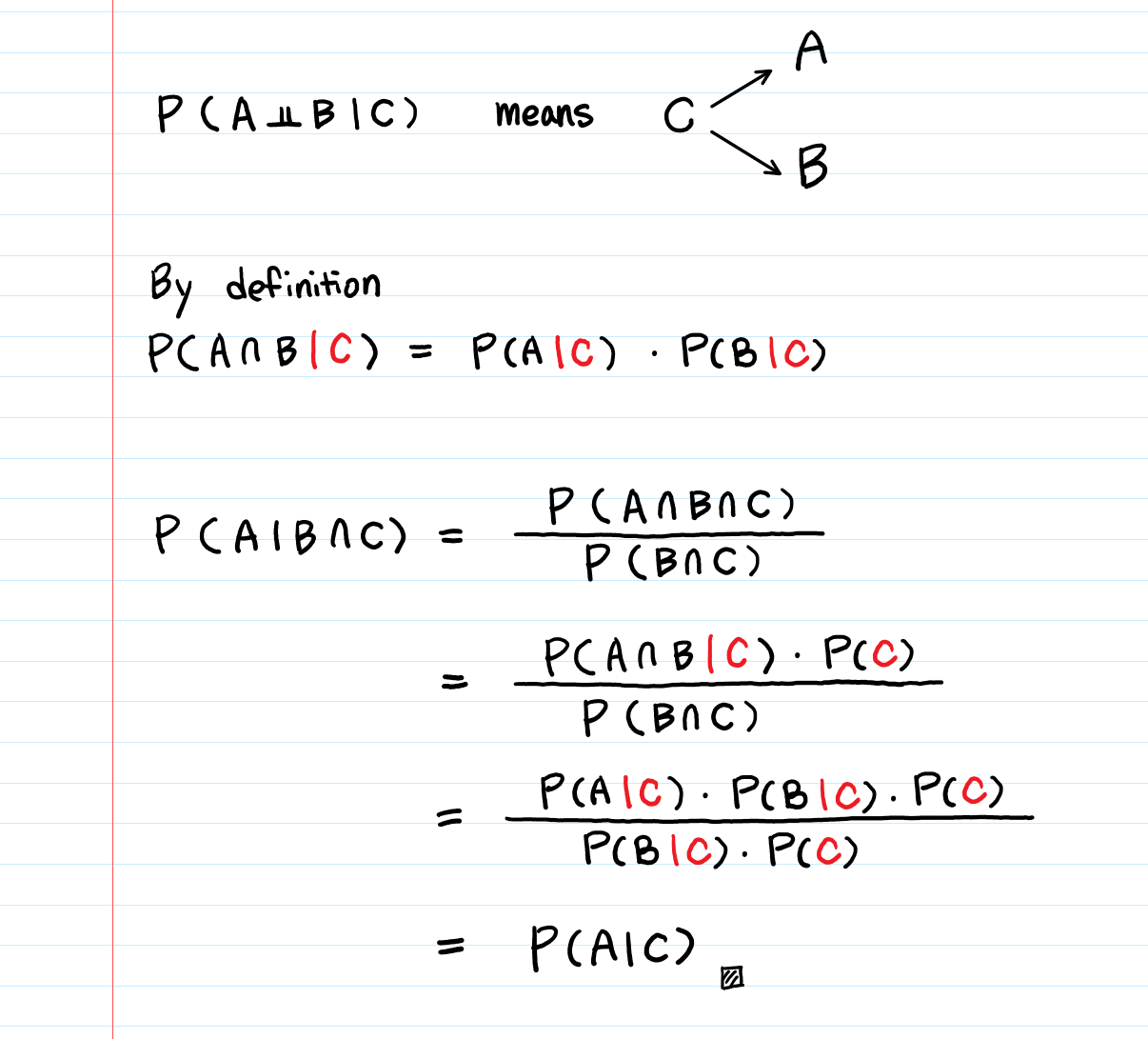
Pba is also called the conditional probability of b given a. If the probability of one event doesnt affect the other you have an independent event. Since events a and b are independent if pa b p a it follows from the above formula that events a and b are independent if and only if.
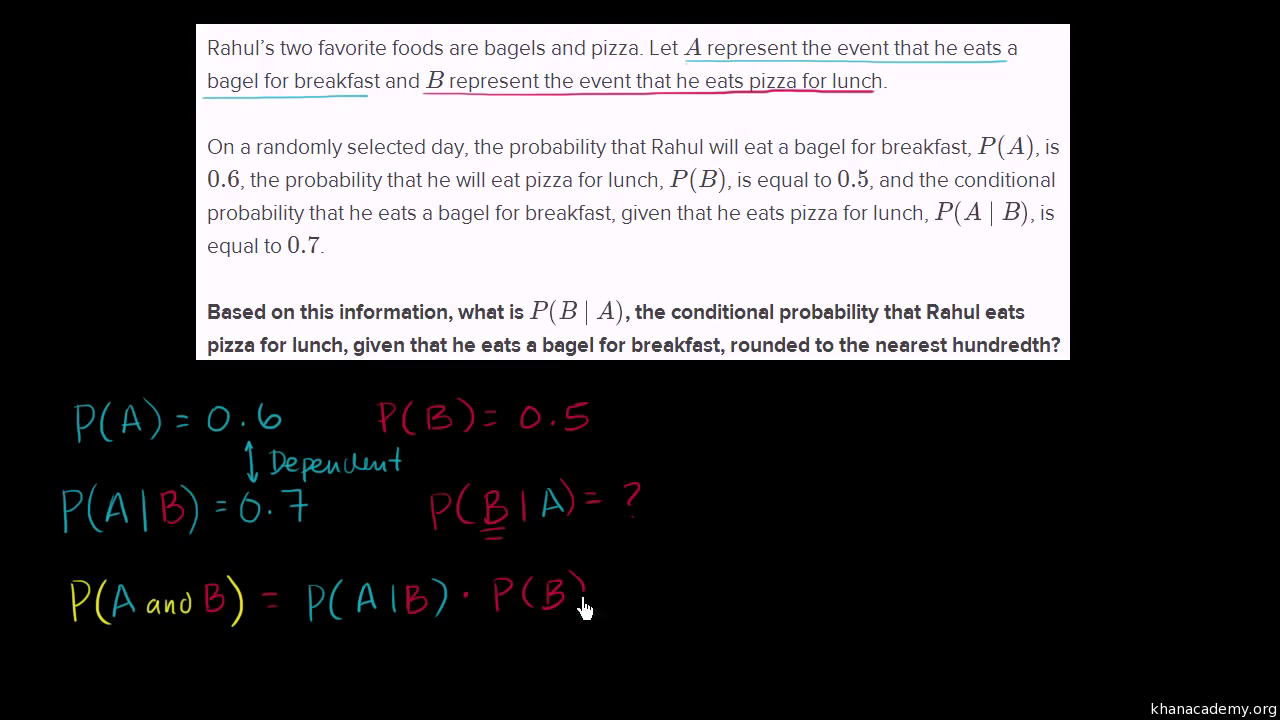
The odds of you. Let a and b are two independent events such that pa 02 and pb 08. And we write it as probability of event a and event b equals the probability of event a times the probability of event b given event a lets do the next example using only notation.
The odds of you getting promoted this year are 14. . And in our case.
This only works if they are. Conditioning on an event kolmogorov definition. So the probability of getting 2 blue marbles is.
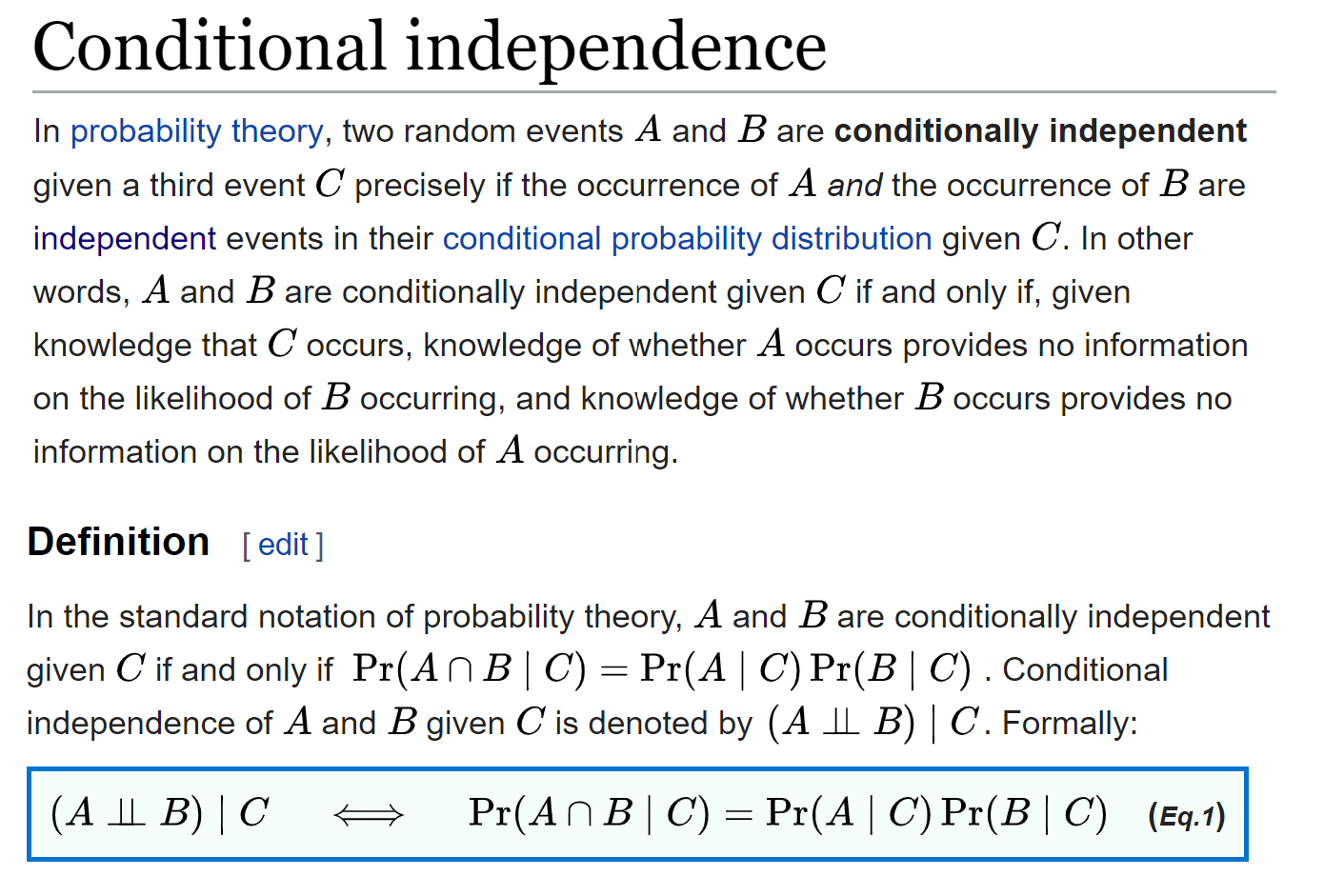
A and b are independent events. In particular you can find situations in which three of them hold but the fourth one does not. Two events are independent statistically independent or stochastically independent if the occurrence of one does not affect the probability of occurrence of the other equivalently does not affect the oddssimilarly two random variables are independent if the realization.

High School Geometry Common Corehss Cp B 8 The Multiplication Rule Of Probability Teacher Notes Patterson
www.geometrycommoncore.com











/conditional-56edf9de5f9b5867a1c1924c.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/conditional-56edf9de5f9b5867a1c1924c.jpg)





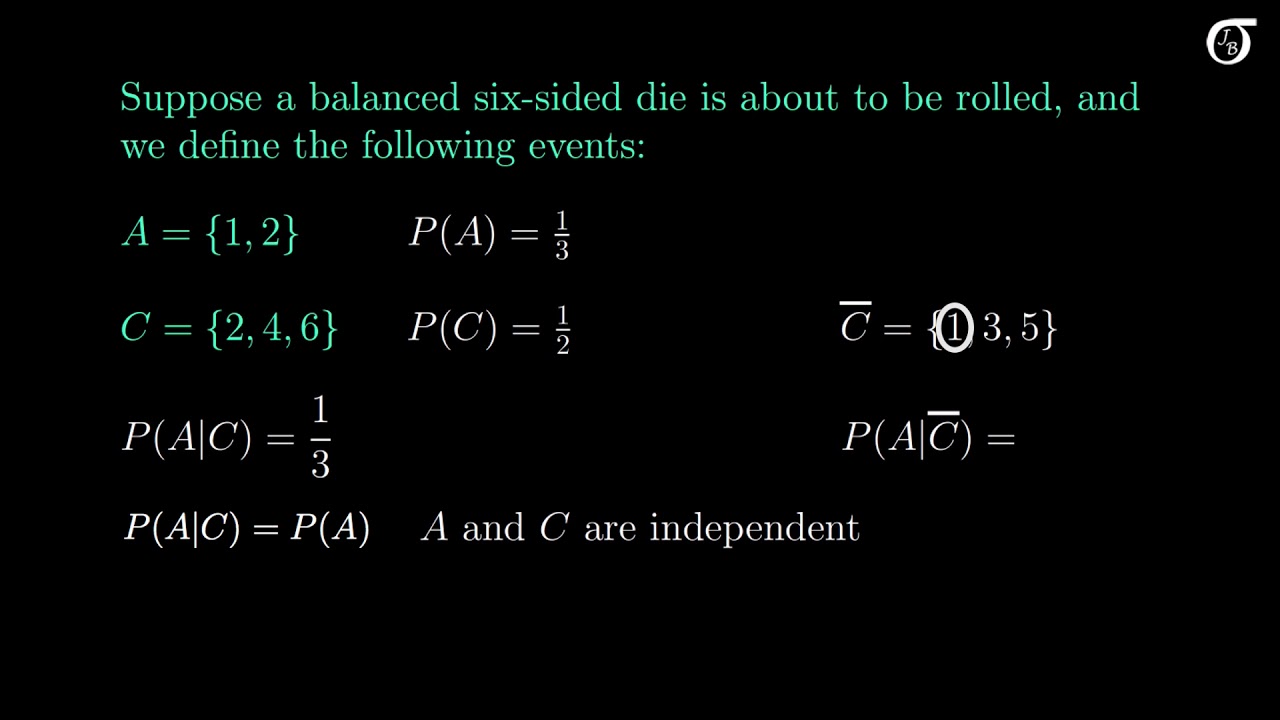
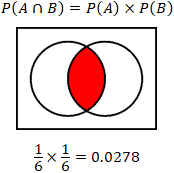

/conditional-56edf9de5f9b5867a1c1924c.jpg)
/JointProbabilityDefinition2-fb8b207be3164845b0d8706fe9c73b01.png)