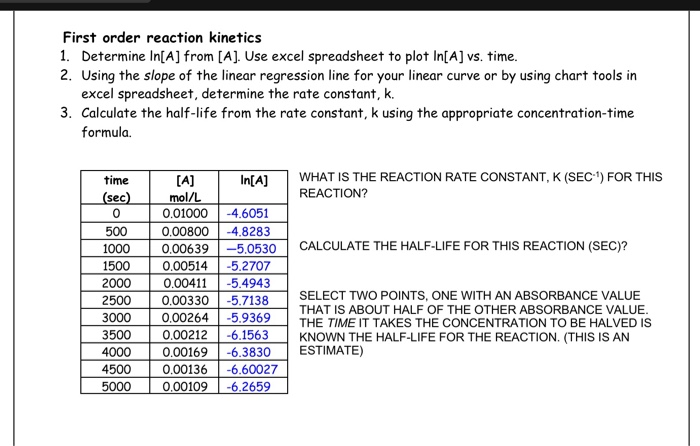
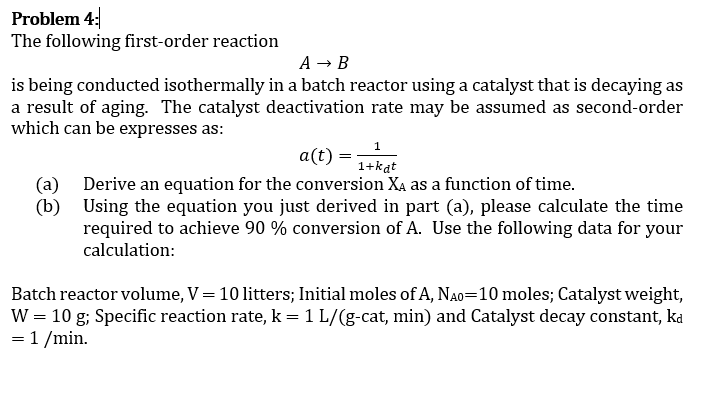
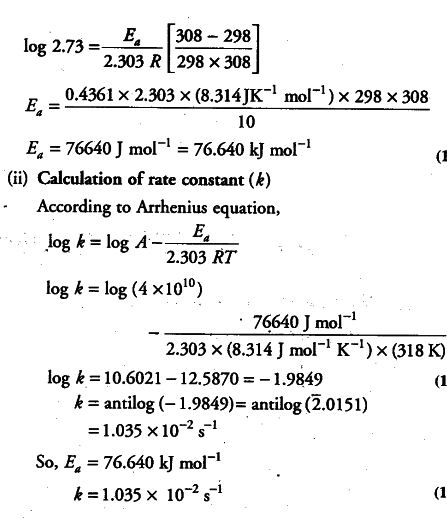
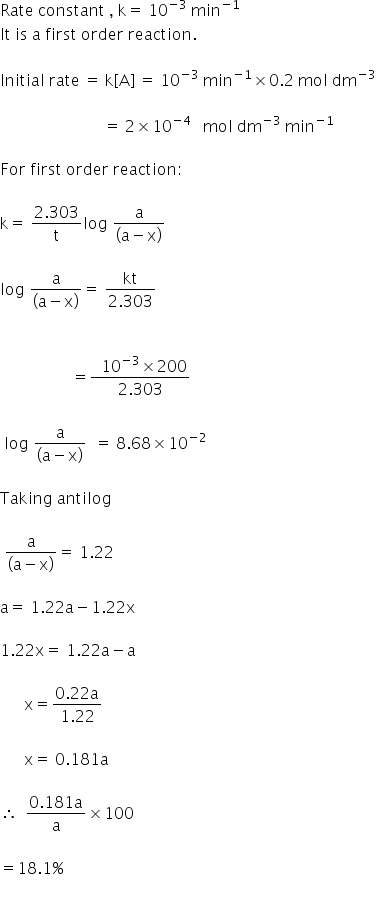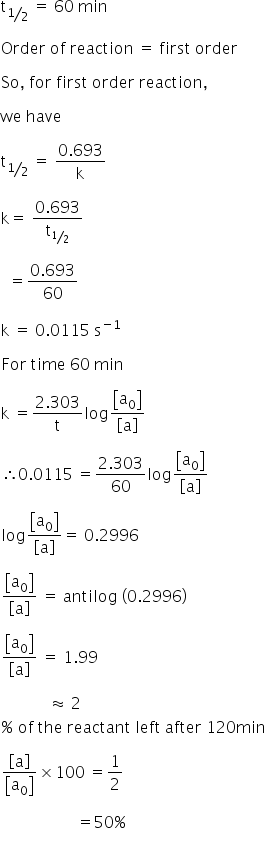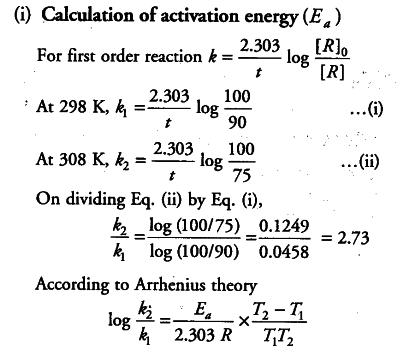K Formula For First Order Reaction
This reaction is therefore a first order reaction.

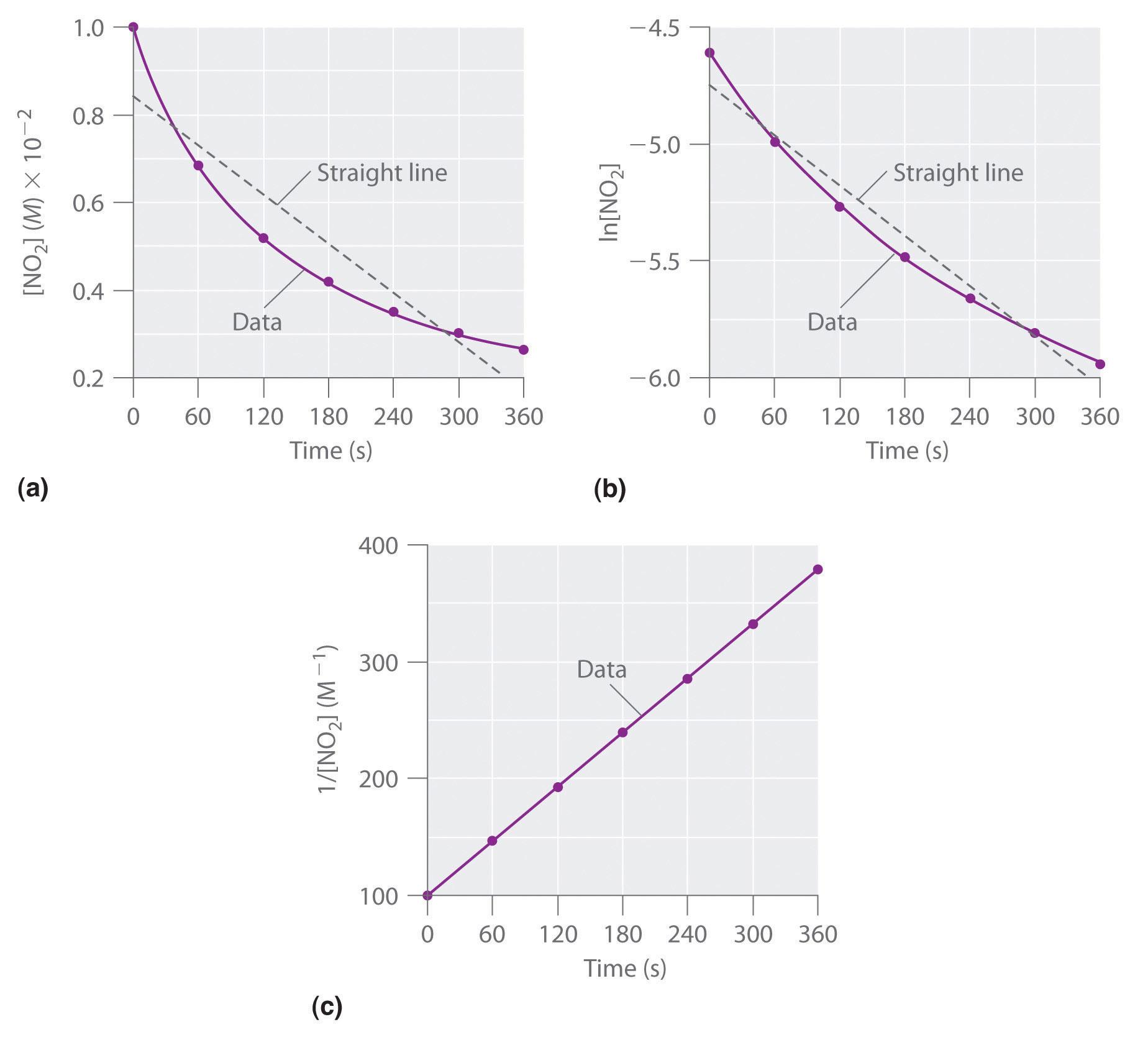
K formula for first order reaction. For first order reaction we know that. For more complicated rate laws the overall reaction order and the orders with respect to each component are used. Where m stands for concentration in molarity mol l 1 t for time and k for the reaction rate constant.
Moll 1 or m k is the rate constant of the reaction unit. Key takeaways key points. In fractional order reactions the order is a non integer which often indicates a chemical chain reaction or other complex reaction mechanism.
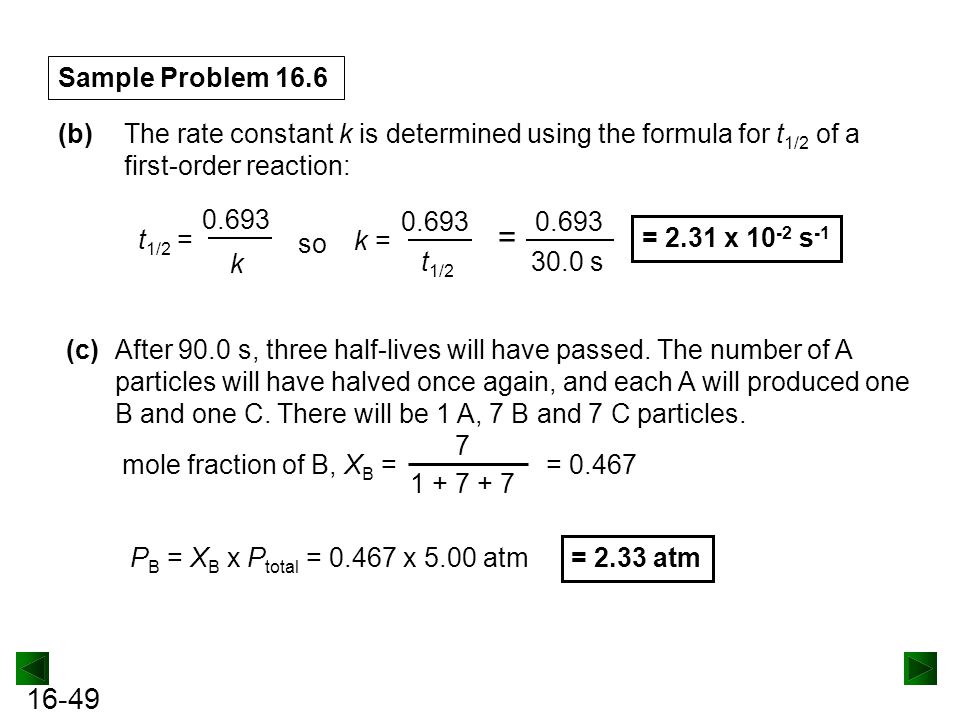
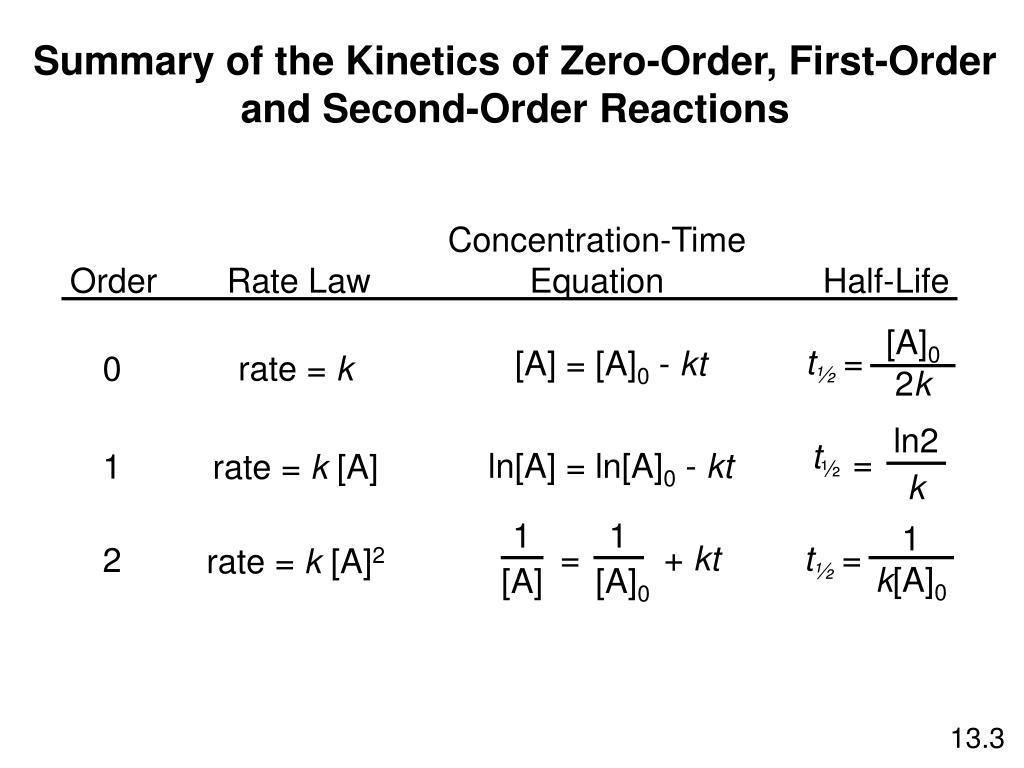
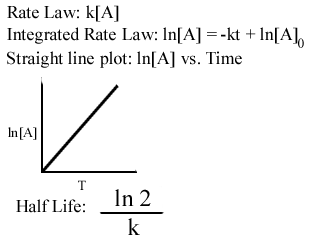
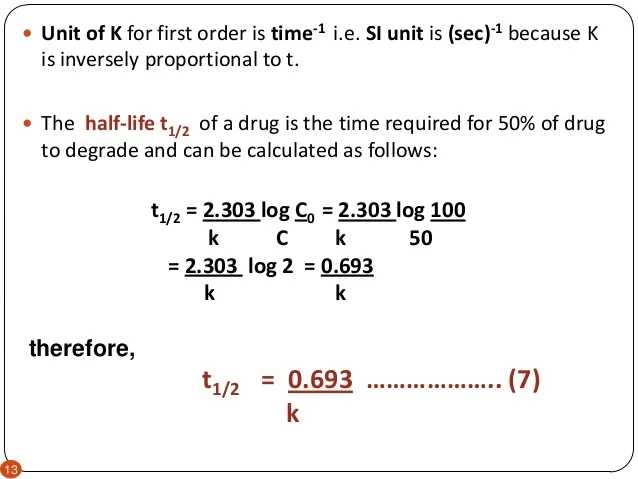
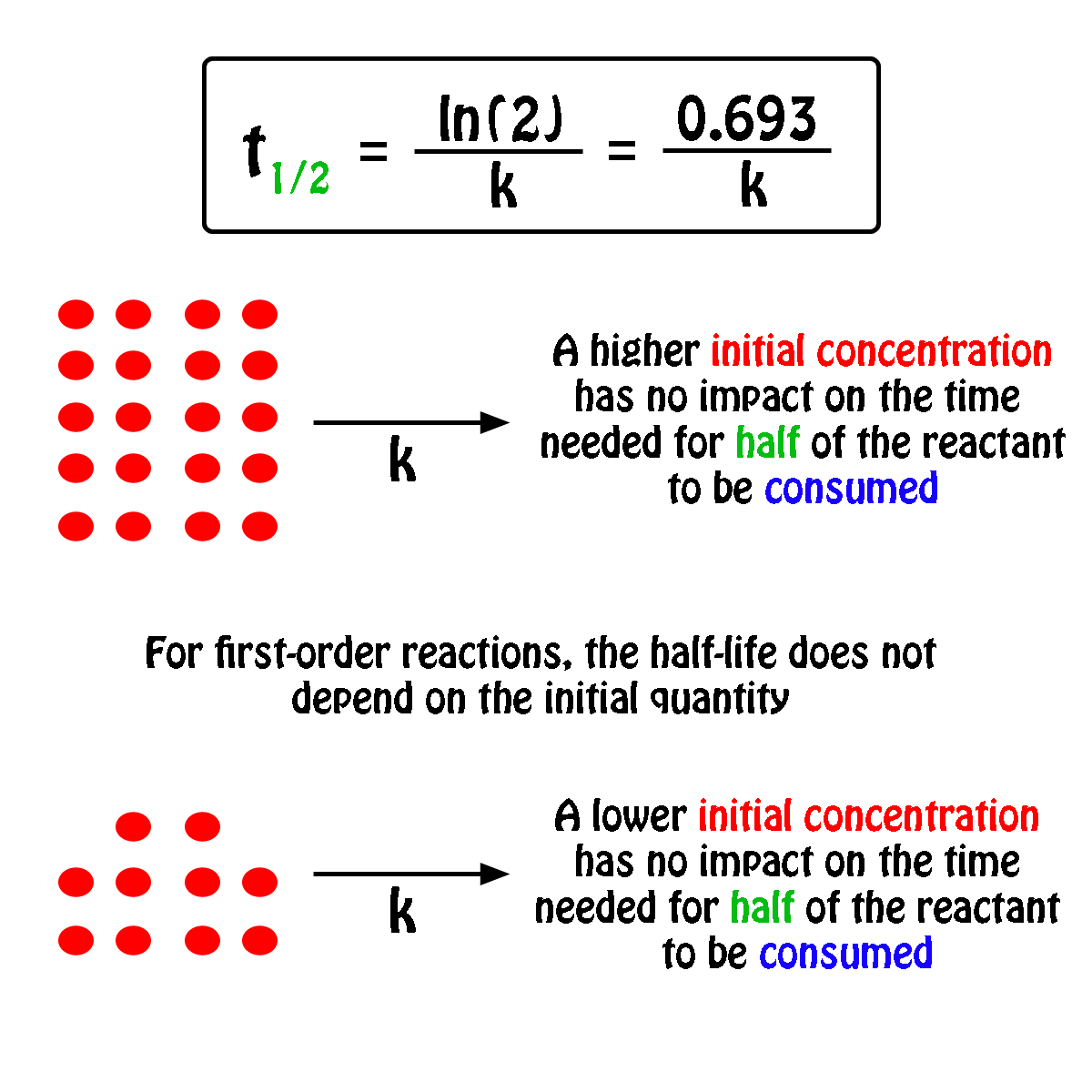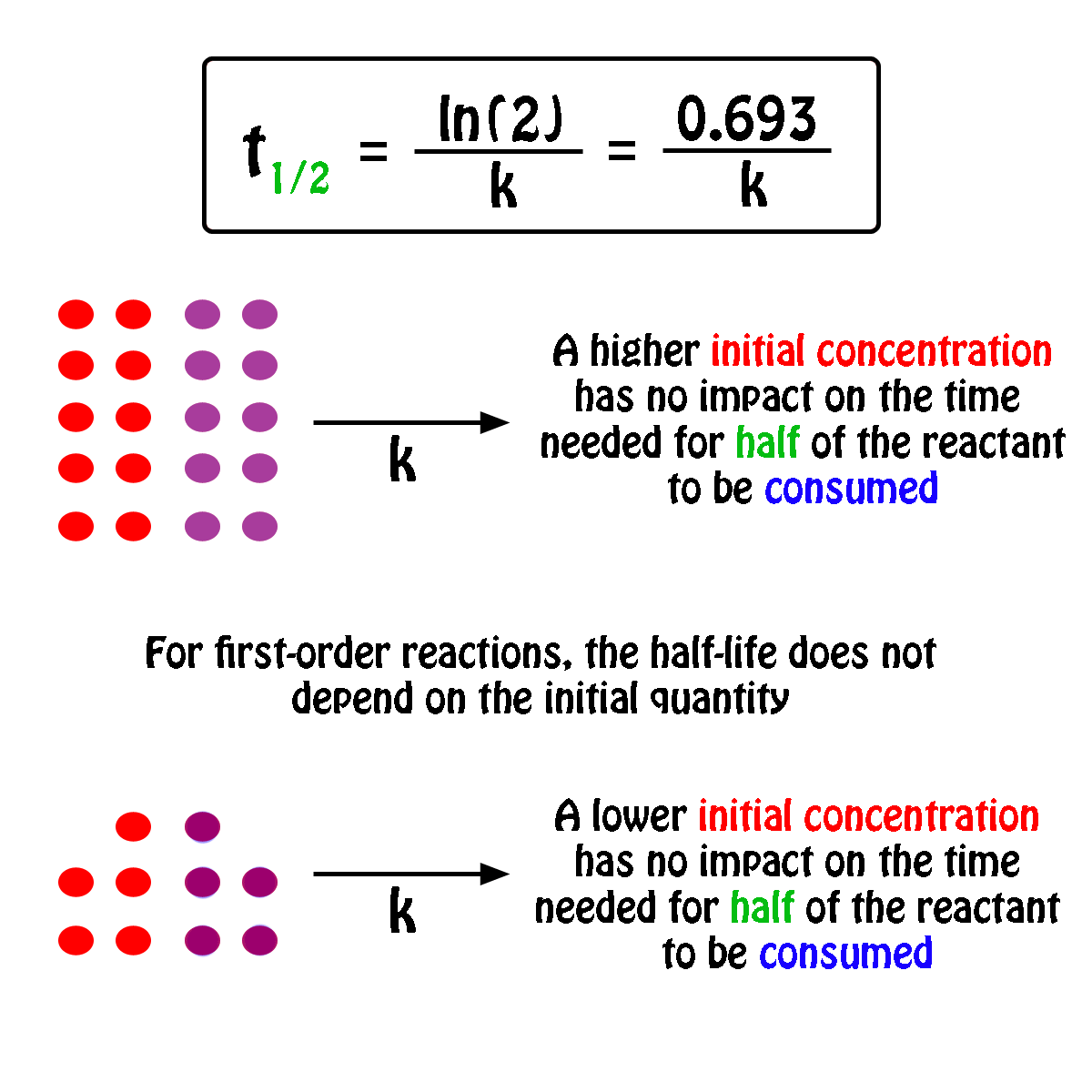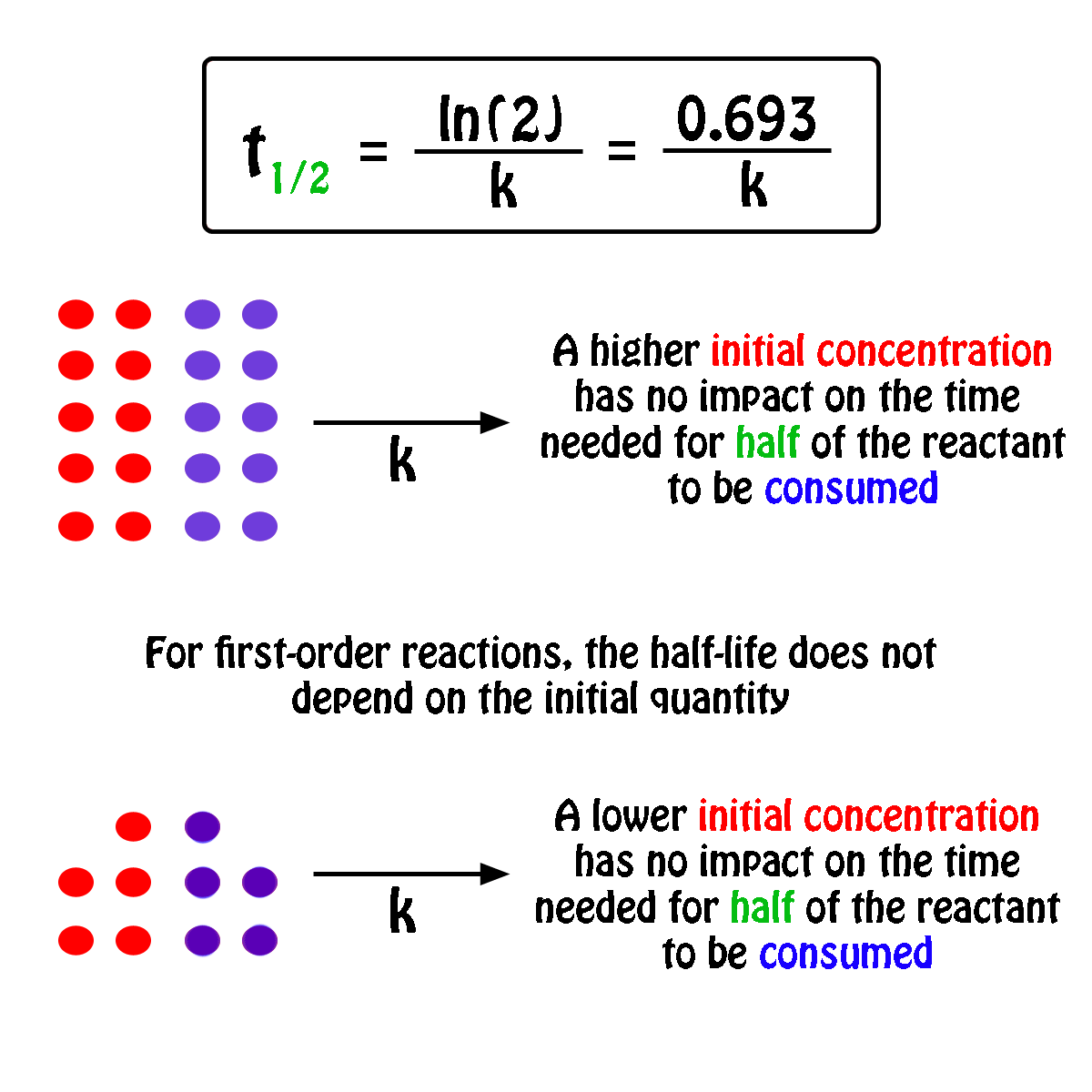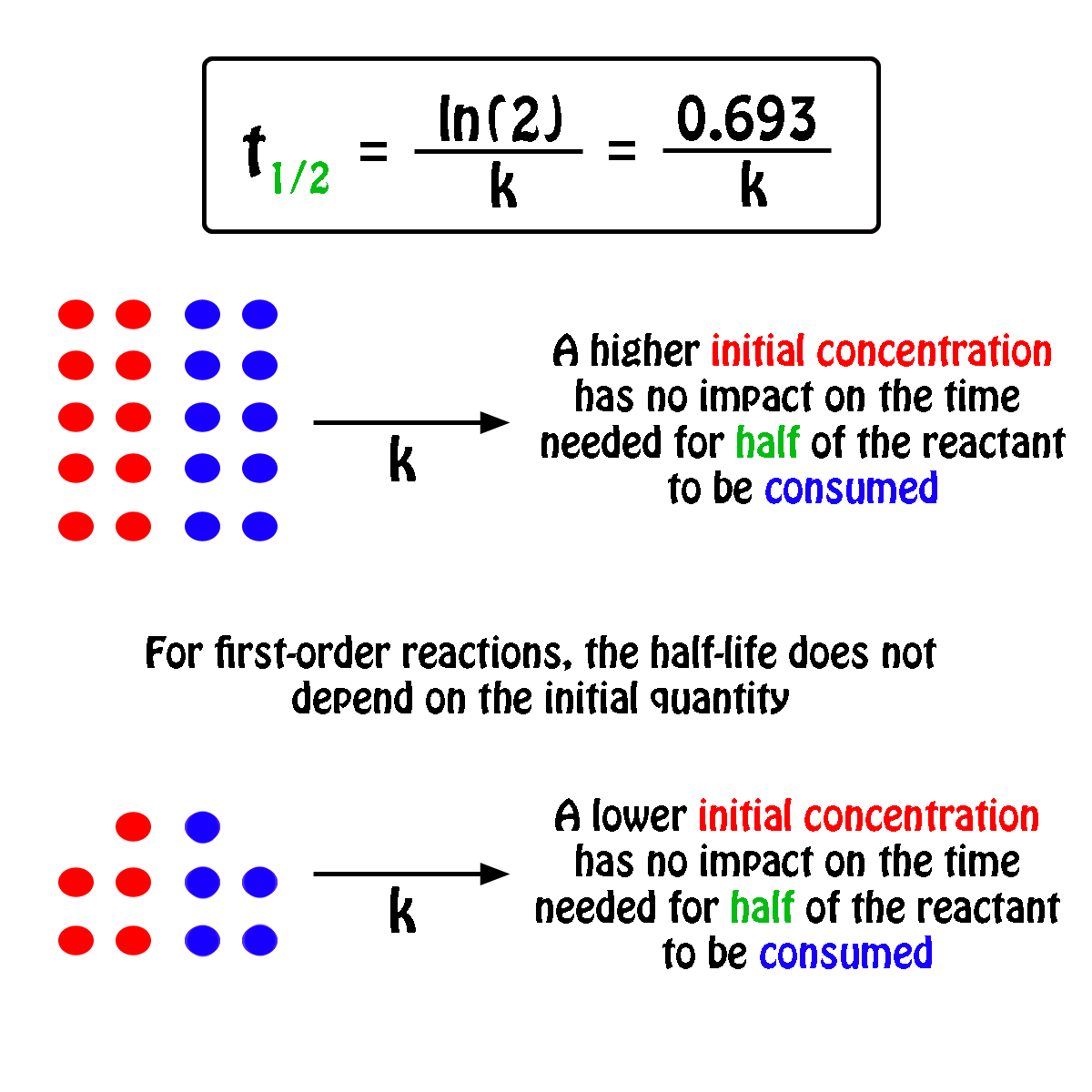
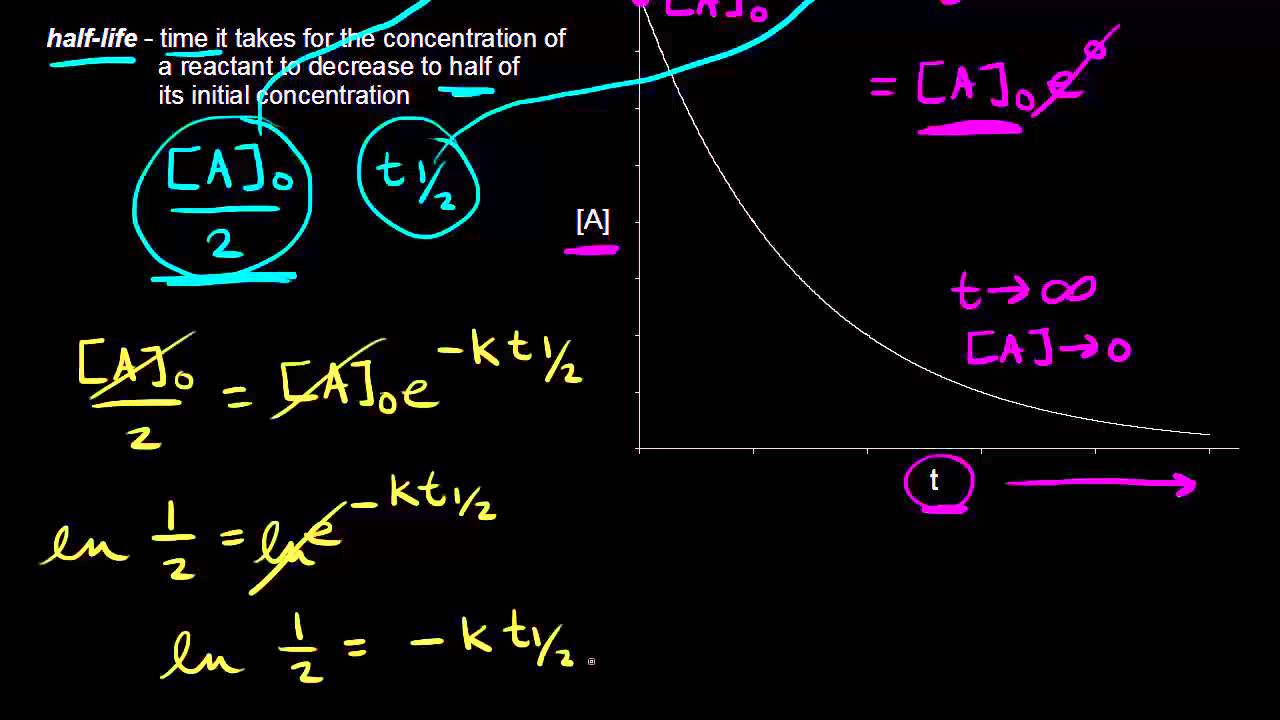
K is the first order rate constant which has units of 1s. Therefore the rate of reaction for the above is k c 2 h 4. The half life of a first order reaction is often expressed as t 12 0693k as ln20693.
This means if we start with 4 mole l 1 of a reactant reacting by first order. So for a first order reaction so for first order a first order reaction rate law is rate is equal to our rate constant k times the concentration of our reactant raised to the first power. At half life of reaction t t a a o 2.
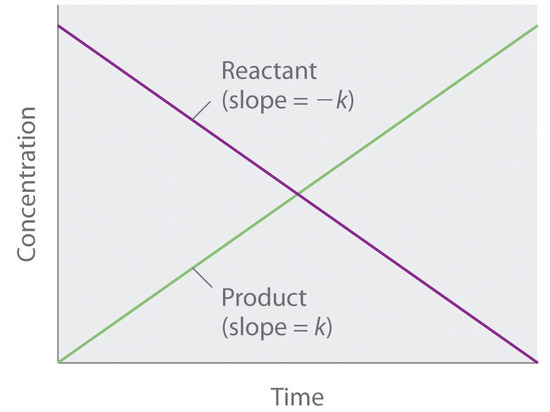
For a reaction between reactants a and b to form product c a a b b c c. In chemical kinetics a reaction rate constant or reaction rate coefficient k quantifies the rate and direction of a chemical reaction. For the n 2 o 5 decomposition with a rate law of kn 2 o 5 this exponent is 1 and thus is not explicitly shown.
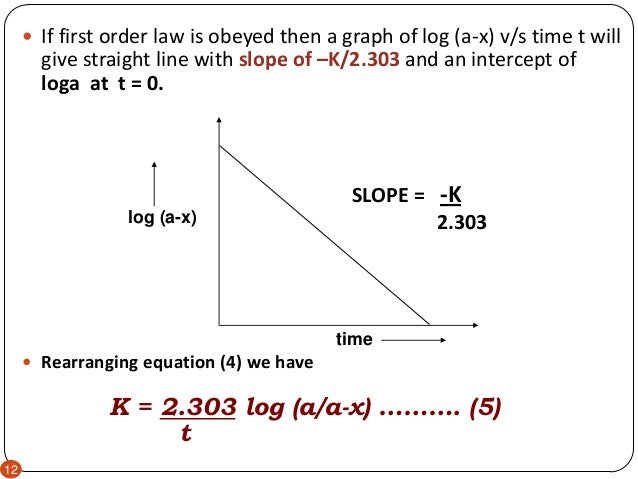
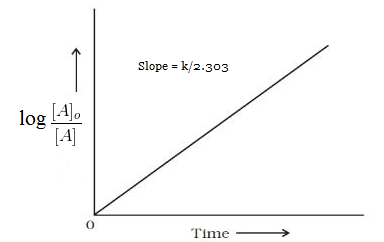
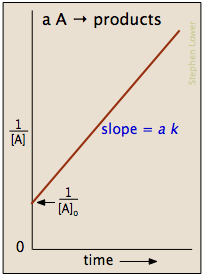
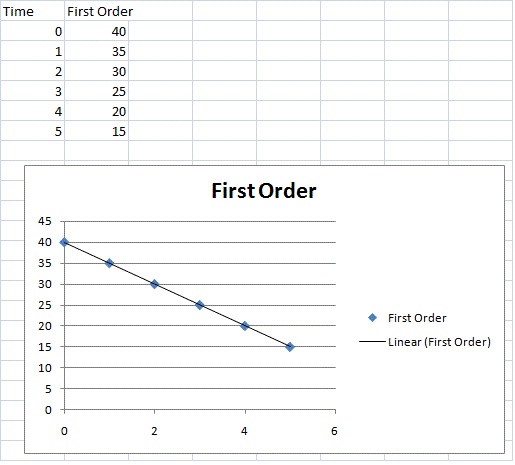
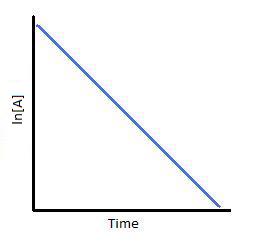
Example of first order reaction. If we plot a graph of logr 0 r against t we get slope k2303. Thus the equation of a straight line is.
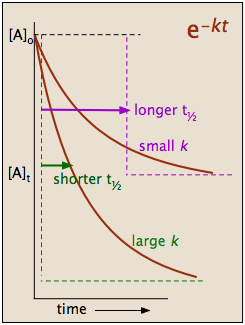
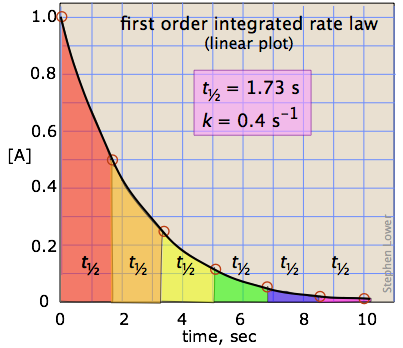
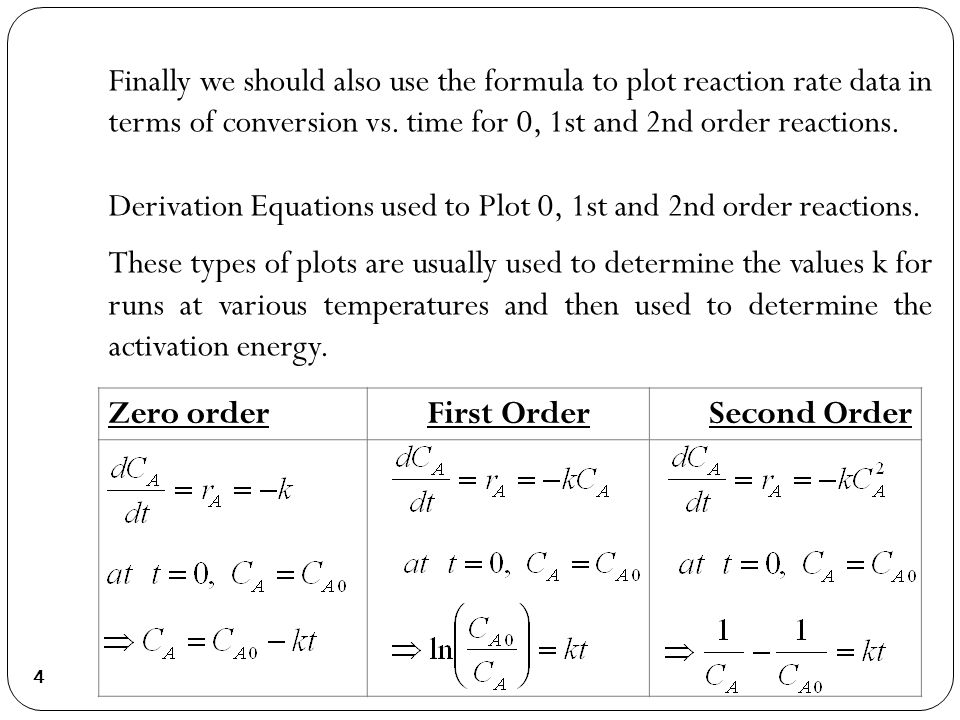
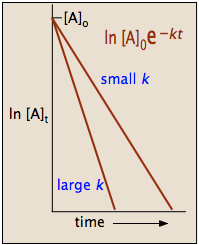
Hence equations iii and vii are the equations of rate constants of zero and first. M 1 n s 1. Decay profiles for first order reactions with large and small rate constants.
This concludes that unit of k in a first order of reaction must be time 1. Here kt is the reaction rate constant that depends on temperature and a and b are the molar concentrations of. The method of determining the order of a reaction is known as the method of initial rates.
T 12 0693k. The reaction rate is often found to have the form. C 2 h 4 h 2 c 2 h 6.
Because the logarithms of numbers do not have any units the product kt also lacks units. Examples of time 1 include s 1 or min 1. The overall order of a reaction is the sum of all the exponents of the concentration terms in the rate equation.
For a first order reaction the half life is given by. It can also be said that the reaction is first order in n 2 o 5. Where t 12 is the half life of the reaction unit.
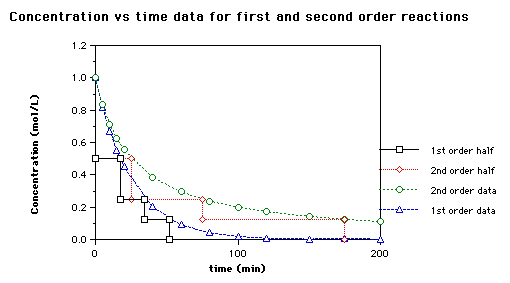
So now we know that the units of k times molar equals molar. For a second order reaction the formula for the half life of the reaction is. An example of a first order reaction is the hydrogenation of ethene.

Rate Laws Example Determine The Rate Law For The Following Reaction Given The Data Below H 2 O 2 Aq 3 I Aq 2h Aq I 3 Aq H 2 O L Ppt Download
slideplayer.com

What Is Half Life Period Of A Reaction Calculate The Half Life Period Of A First Order Reaction
www.toppr.com

E Plot Of The Pseudo First Order Reaction Rate Constant K P As A Download Scientific Diagram
www.researchgate.net