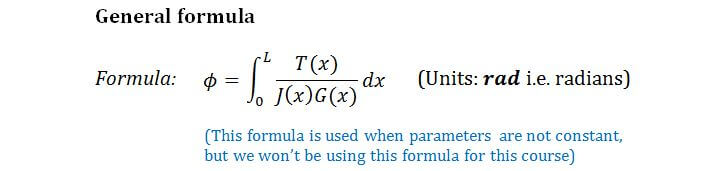J Formula Torsion
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gcrvd45gik8y Po4jsgxwiwxg7lci4veadt2ft1ssopbxozofxni Usqp Cau
encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com
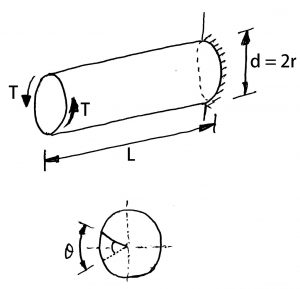
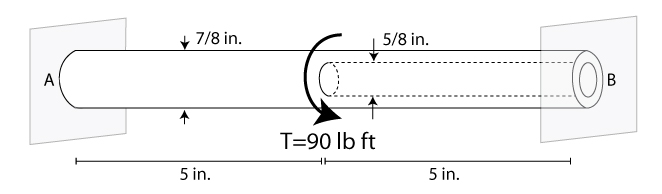
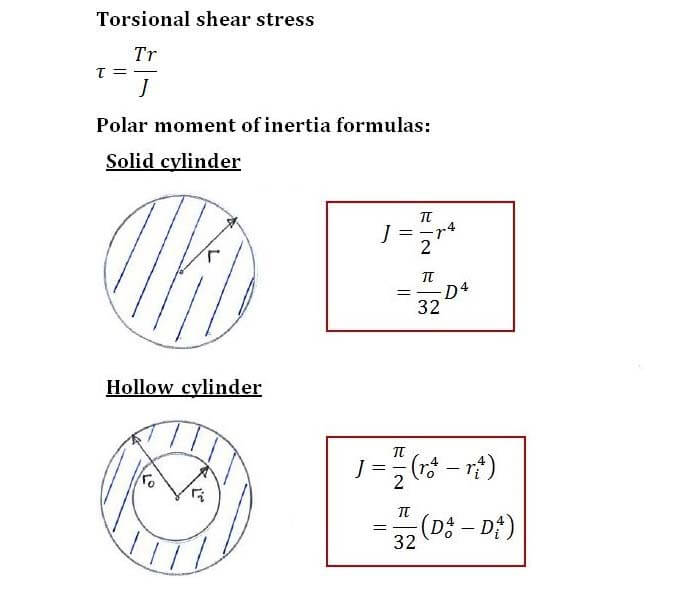
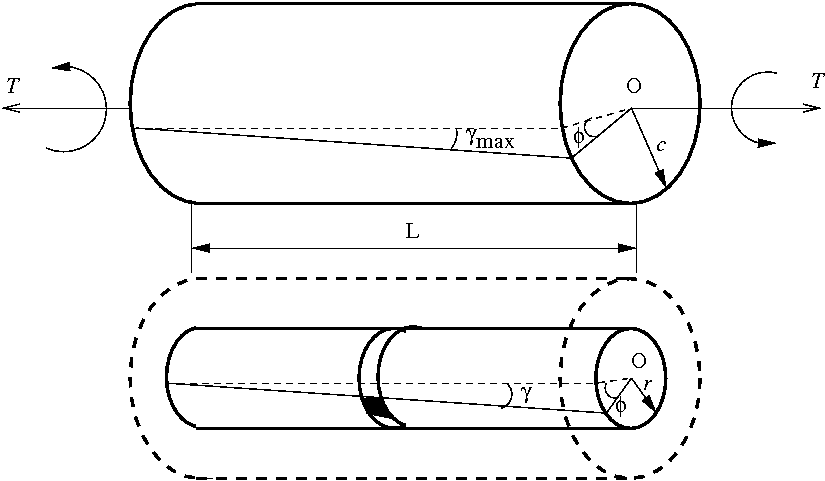
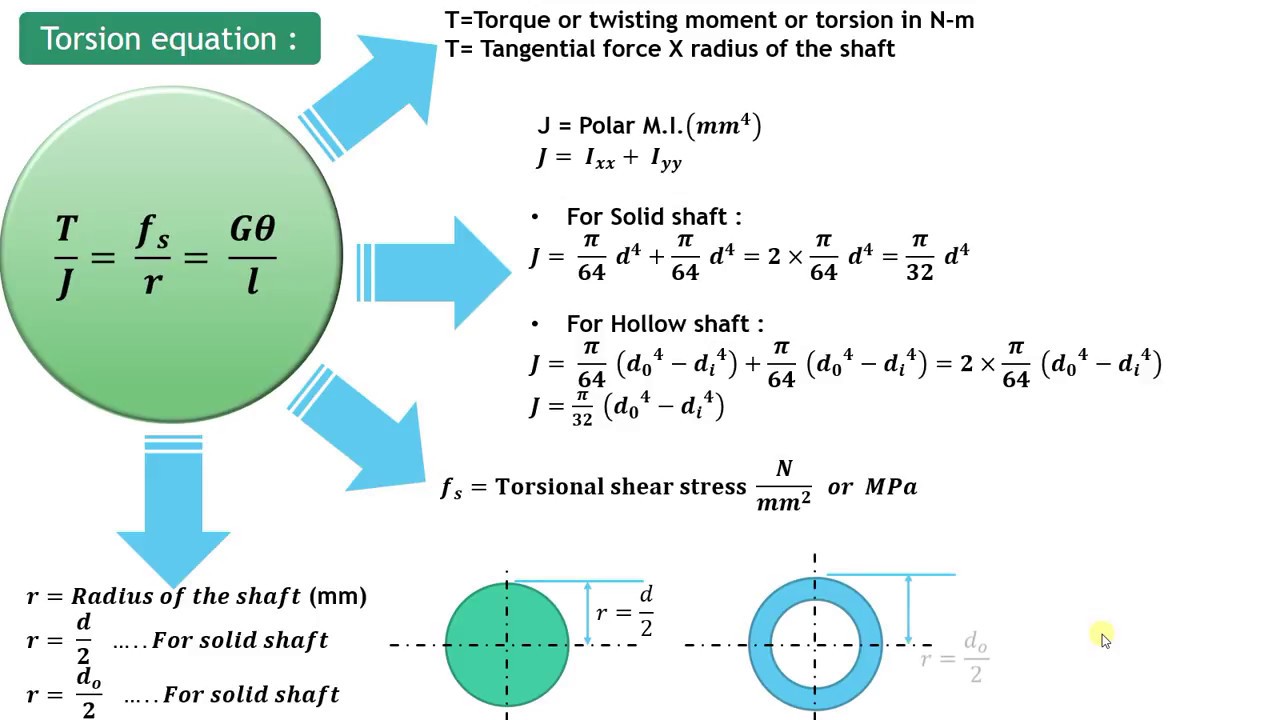
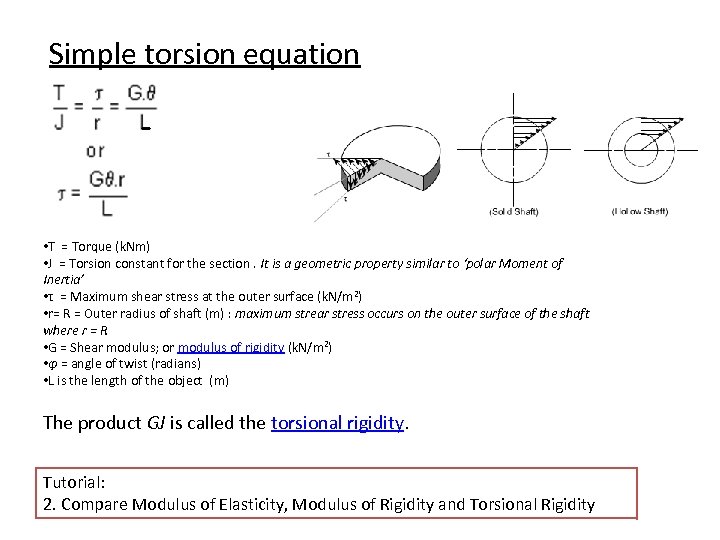
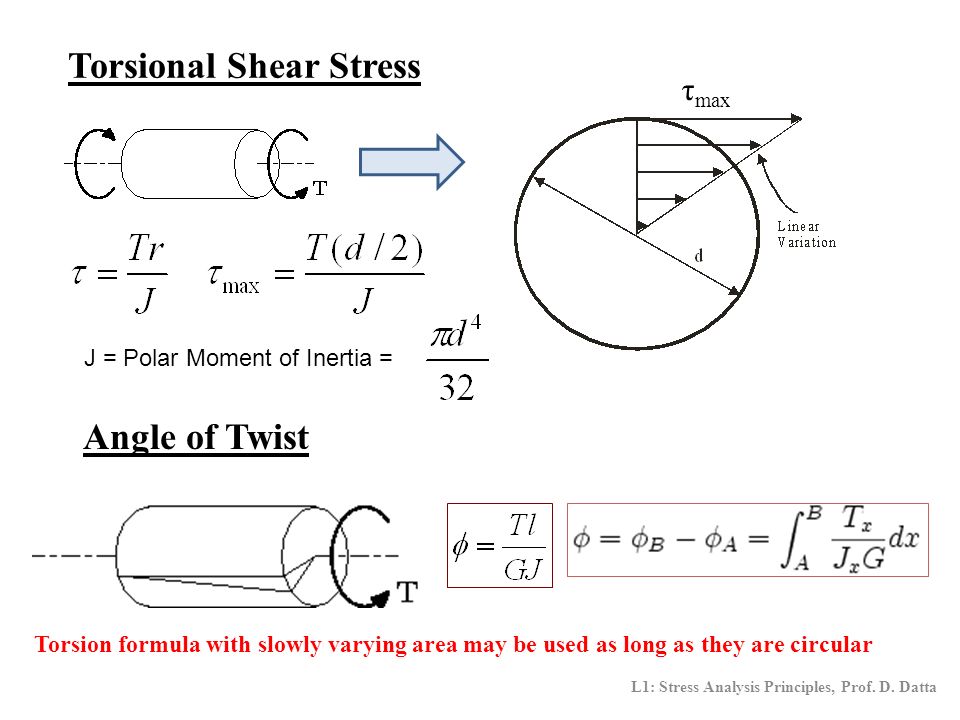
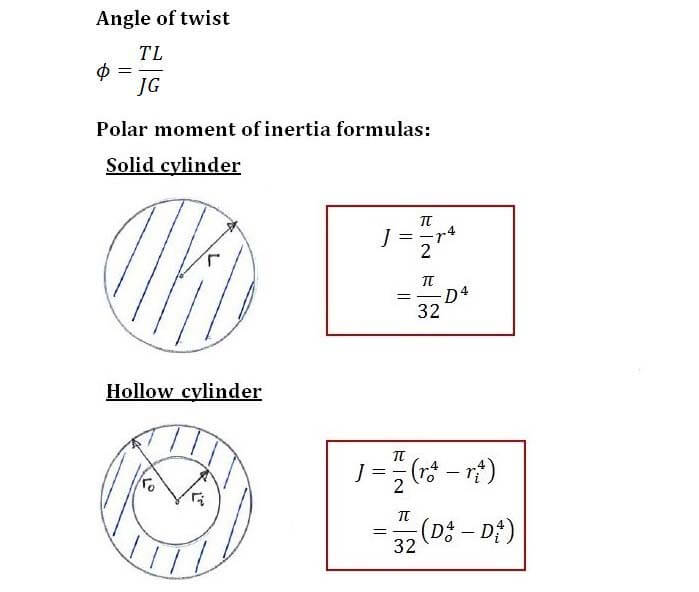
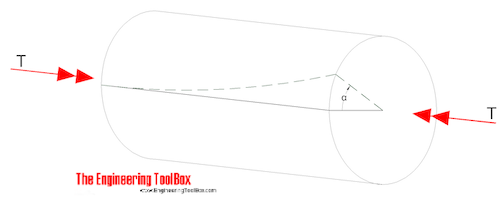
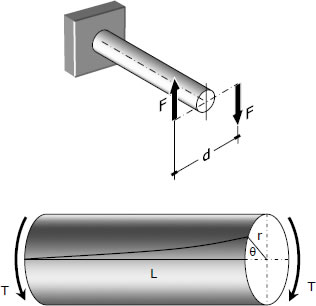
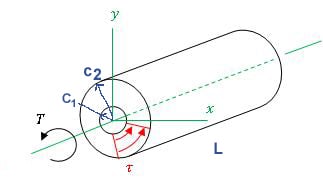
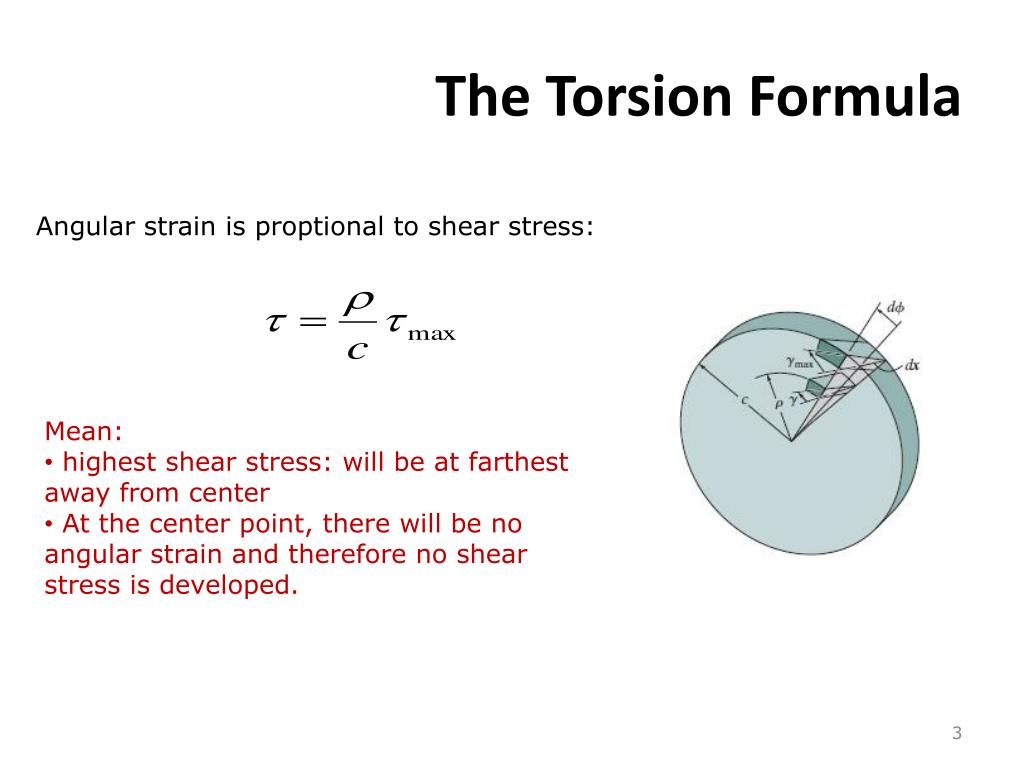
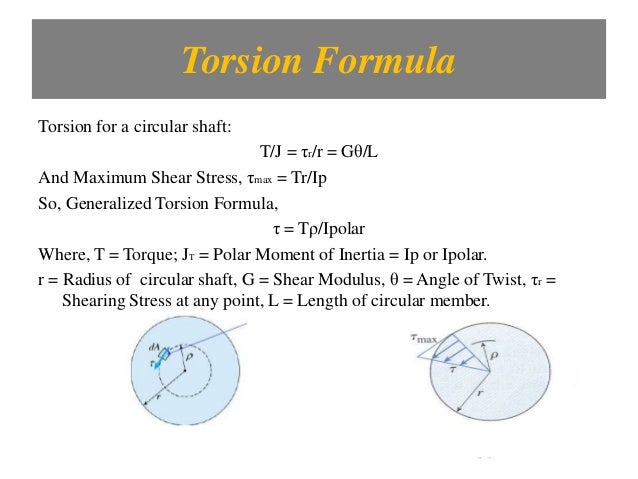
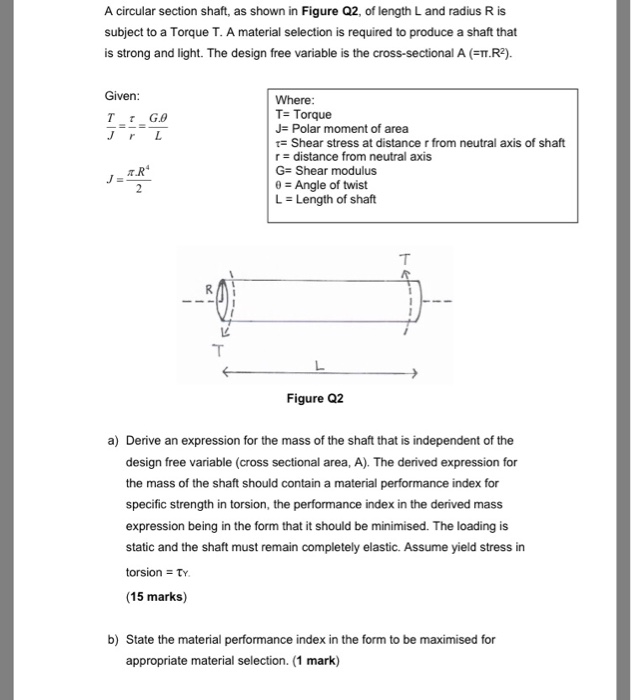
T torque or twisting moment nm lbin j polar moment of inertia or polar second moment of area about shaft axis m 4 in 4 t shear stress at outer fibre pa psi r radius of the shaft m in.
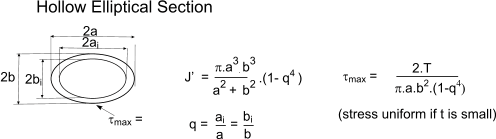
J formula torsion. The general formula of torsional stiffness of bars of non circular section are as shown below the factor j is dependent of the for the circular section j j. We can quickly understand how twist generates power just by doing a simple dimensional analysispower is measured in the unit of watts w and 1 w 1 n m s 1at the outset of this section we noted that torque was a twisting couple which means that it has units of force times. Its units are mm 4 or inches 4.
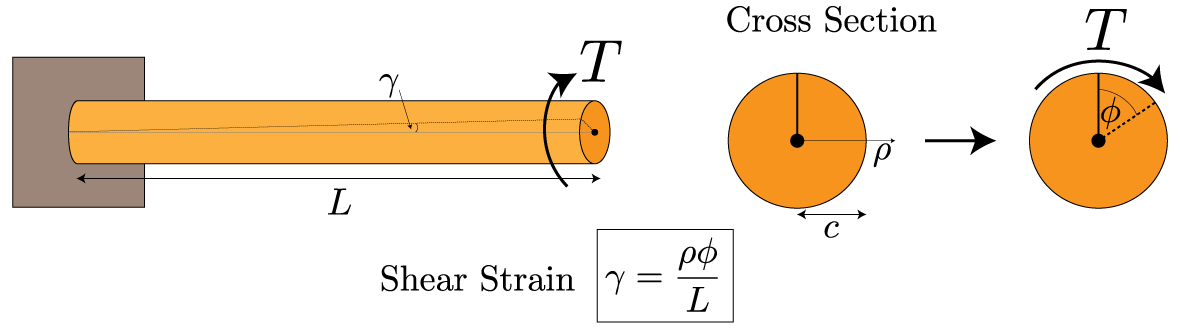
M 4 or mm 4. T is the internal torque at the region of interest as a result of external torque loadings applied to the member units. The above equation is called the torsion formula.
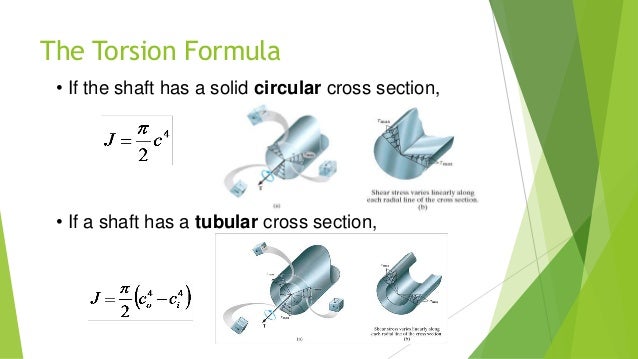
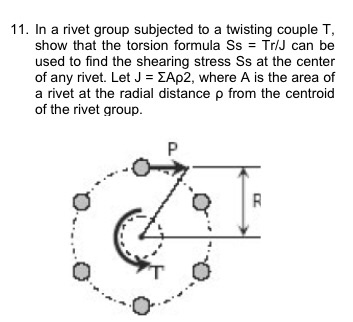
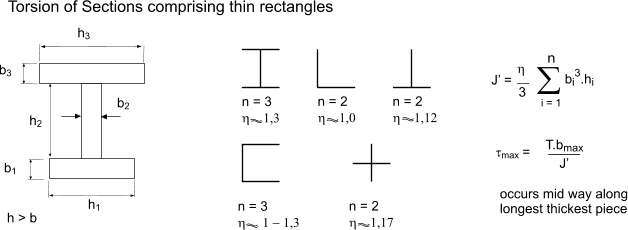
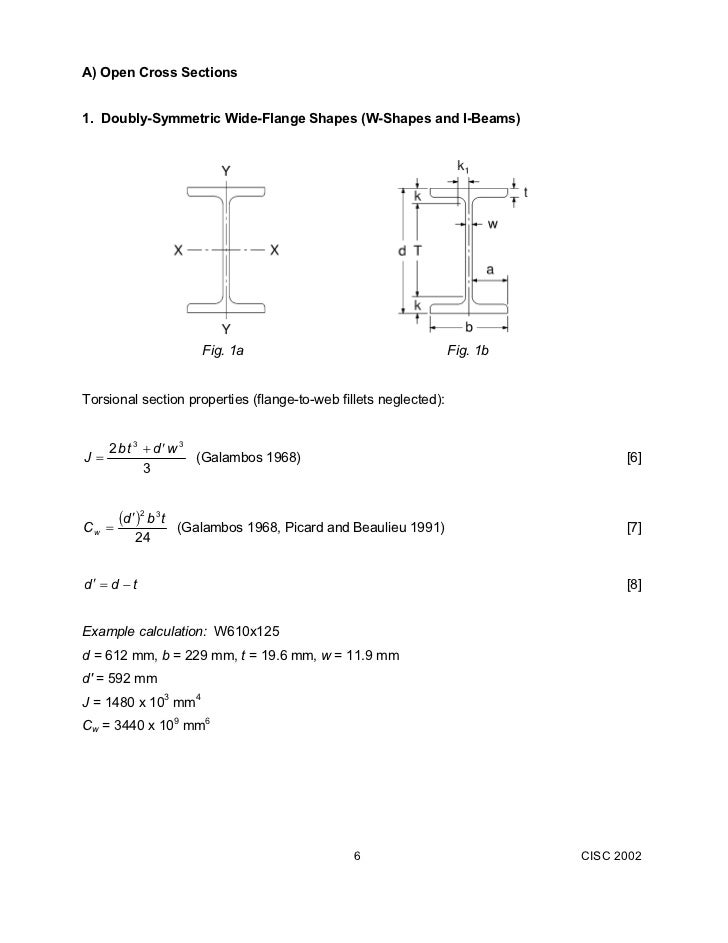
J polar moment of inertia of area m4 ft4. One of the most common examples of torsion in engineering design is the power generated by transmission shafts. Jt is the torsion constant for the section.
R is the radius of the point where we are calculating the shear stress units. Testing the values of j obtained using the above equations with h 1 with the values obtained from the table below the following values result. Now for a solid circular shaft we have j p32 d4 further for any point at distance r from the center of the shaft we have the shear stress t is given by.
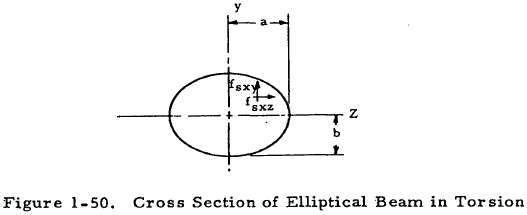
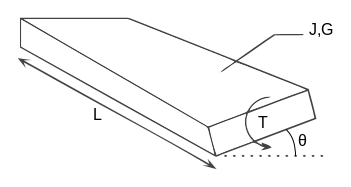
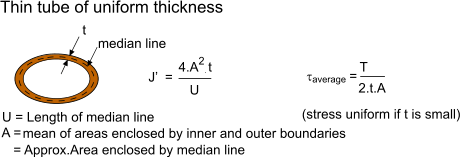
The torsional shear stress can be calculated using the following formula. J is the polar moment of inertia for the cross section units. The torsion constant together with material properties and length describes a bars torsional stiffnessthe si unit for torsion constant is m 4.
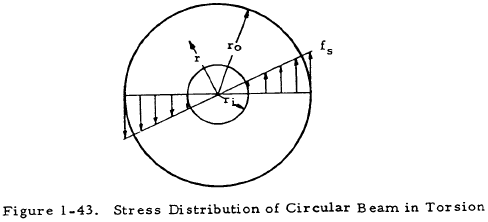
In the field of solid mechanics torsion is the twisting of an object due to an applied torquetorsion is expressed in either the pascal pa an si unit for newtons per square metre or in pounds per square inch psi while torque is expressed in newton metres nm or foot pound force ftlbf. For more accuracy finite element analysis fea is the best method. In sections perpendicular to the torque axis the resultant shear stress in this section is.
All torsion problems that you are expected to answer can be solved using the following formula. December 5 2013 by bernie roseke peng pmp 6 comments in structural steel design the torsion constant j represents the ability of the steel beam to resist torsion ie. The torsion constant is a geometrical property of a bars cross section which is involved in the relationship between angle of twist and applied torque along the axis of the bar for a homogeneous linear elastic bar.