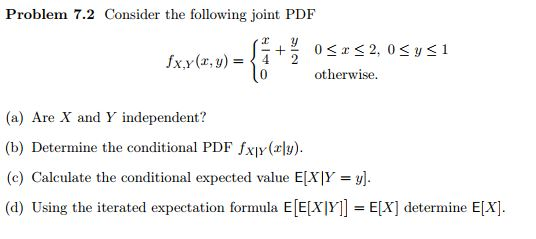
Ex2 Expected Value Formula
Each of the possible outcomes the probability of the.

Ex2 expected value formula. The expected value of x is given by the formula. Proposition if the rv x has a set of possible values d and pmf p x then the expected value of any function h x denoted by e h x or m. On the other hand project y is expected to achieve a value of 25 million with a probability of 04 and achieve a value of 15 million with a probability of 06.
In probability theory an expected value is the theoretical mean value of a numerical experiment over many repetitions of the experiment. The expected value of a function sometimes interest will focus on the expected value of some function h x rather than on just e x. X n p n.
X is the value of the continuous random variable x. Expected value is a measure of central tendency. Ex is the expectation value of the continuous random variable x.
Us consider the distance to the expected value ie jx exj. In probability and statistics the expectation or expected value is the weighted average value of a random variable. A value for which the results will tend to.
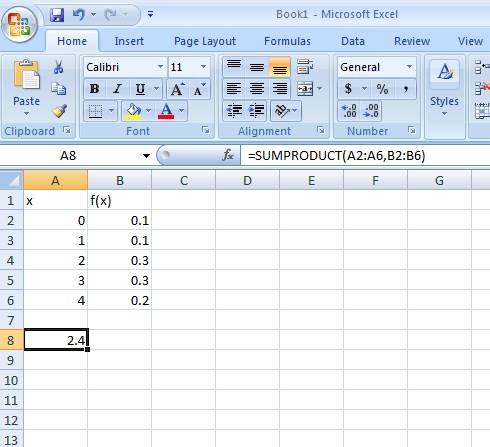
Any given random variable contains a wealth of information. Ex s x px x so the expected value is the sum of. Expectationthe expectation is the expected value of x written as ex or sometimes as mthe expectation is what you would expect to get if you were to carry out the experiment a large number of times and calculate the meanto calculate the expectation we can use the following formulaex xpx xit may look complicated but in fact is quite easy to useyou multiply each value of x.
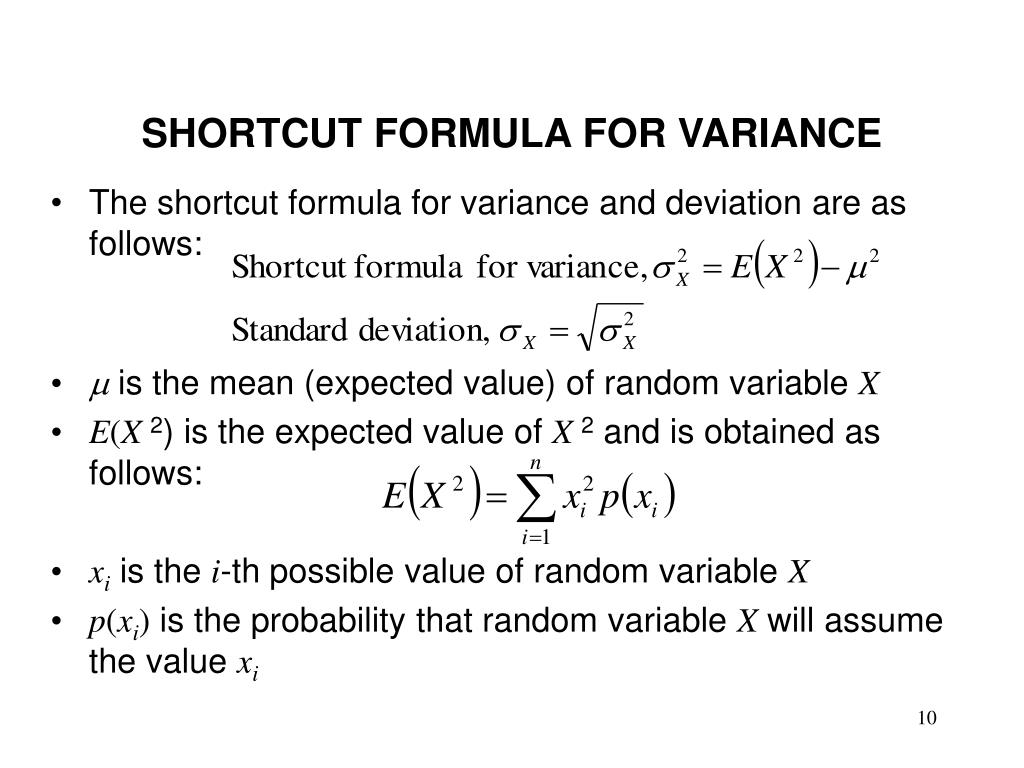
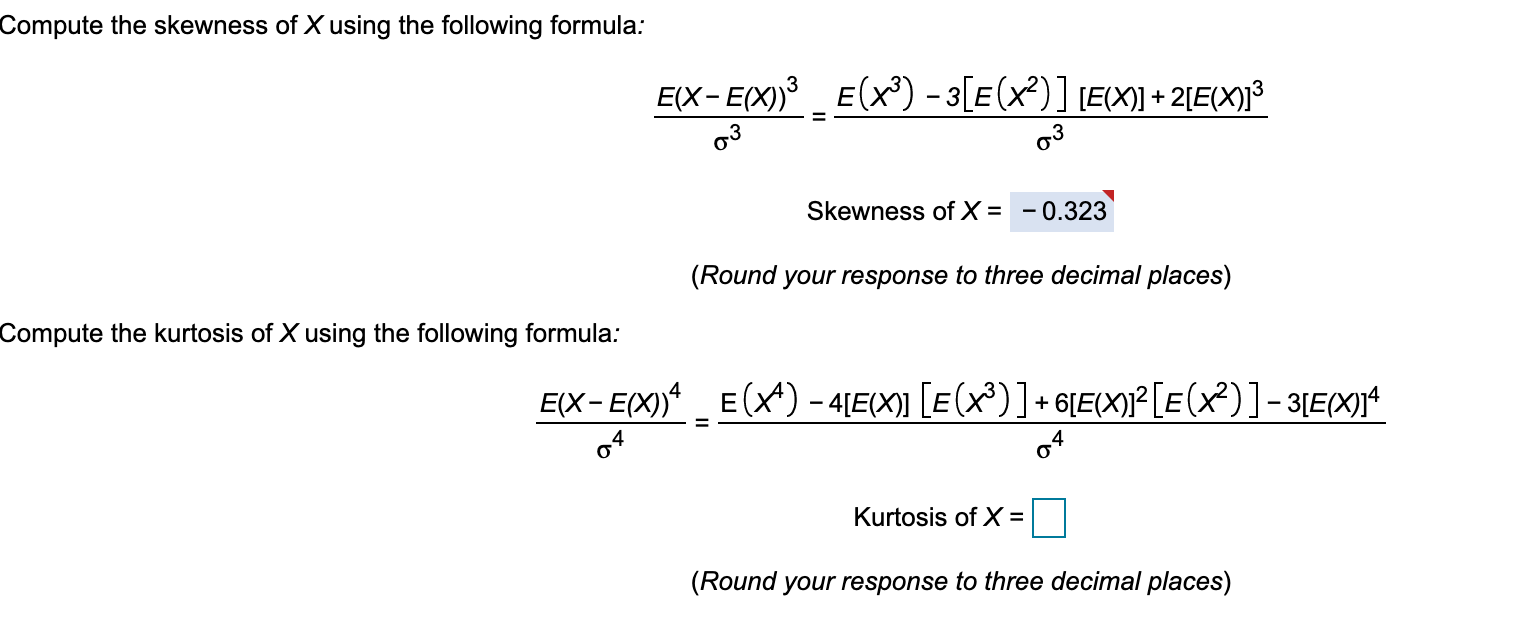
Expectation of continuous random variable. Using the probability mass function and summation notation allows us to more compactly write this formula as follows where the summation is taken over the index i. It is more convenient to look at the square of this distance x ex2 to get rid of the absolute value and the variance is then given by variance of x.
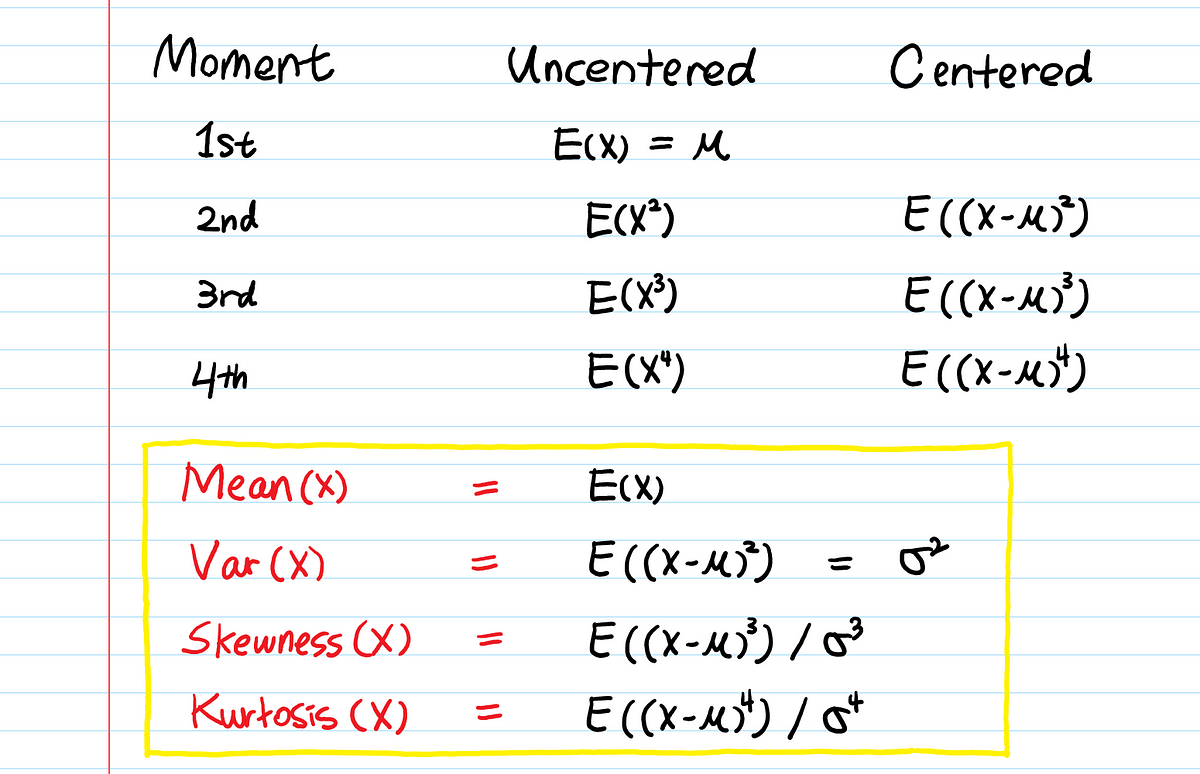
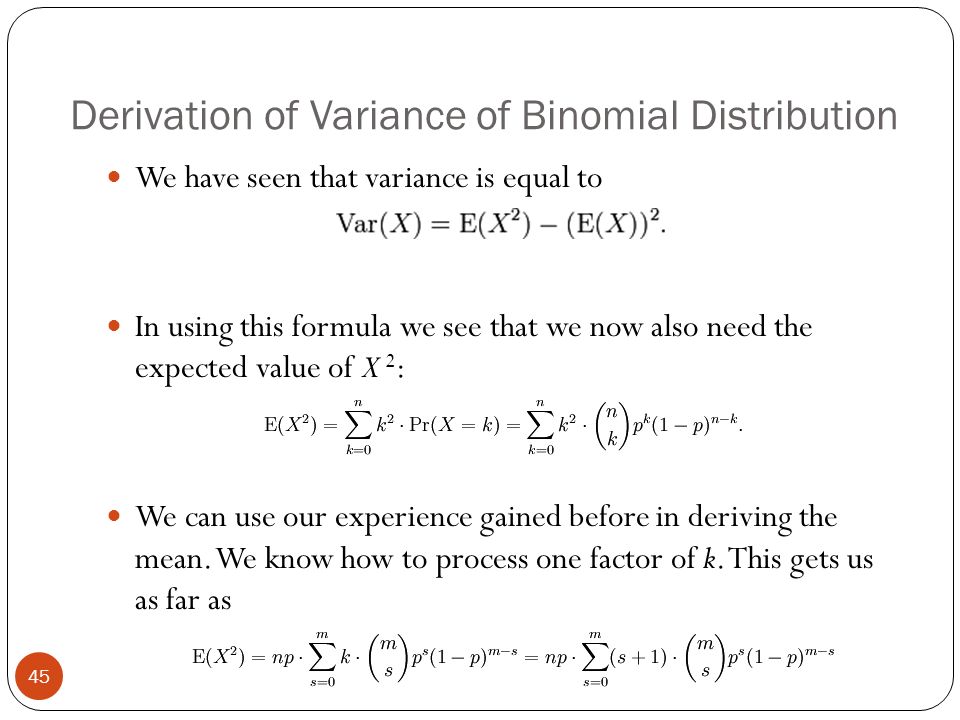
The expected value of x is usually written as ex or m. Varx e x ex2 we summarizesome elementary properties of expected value and variance in the fol lowing theorem 1. E x x 1 p 1 x 2 p 2 x 3 p 3.
In probability theory the expected value of a random variable denoted or is a generalization of the weighted average and is intuitively the arithmetic mean of a large number of independent realizations of the expected value is also known as the expectation mathematical expectation mean average or first momentexpected value is also a key concept in economics finance and many. The expected value or mean of x where x is a discrete random variable is a weighted average of the possible values that x can take each value being weighted according to the probability of that event occurring.

Variance And Standard Deviation Of A Discrete Random Variable Video Khan Academy
www.khanacademy.org







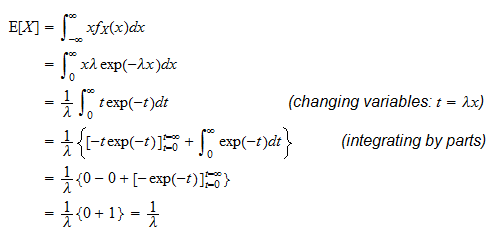




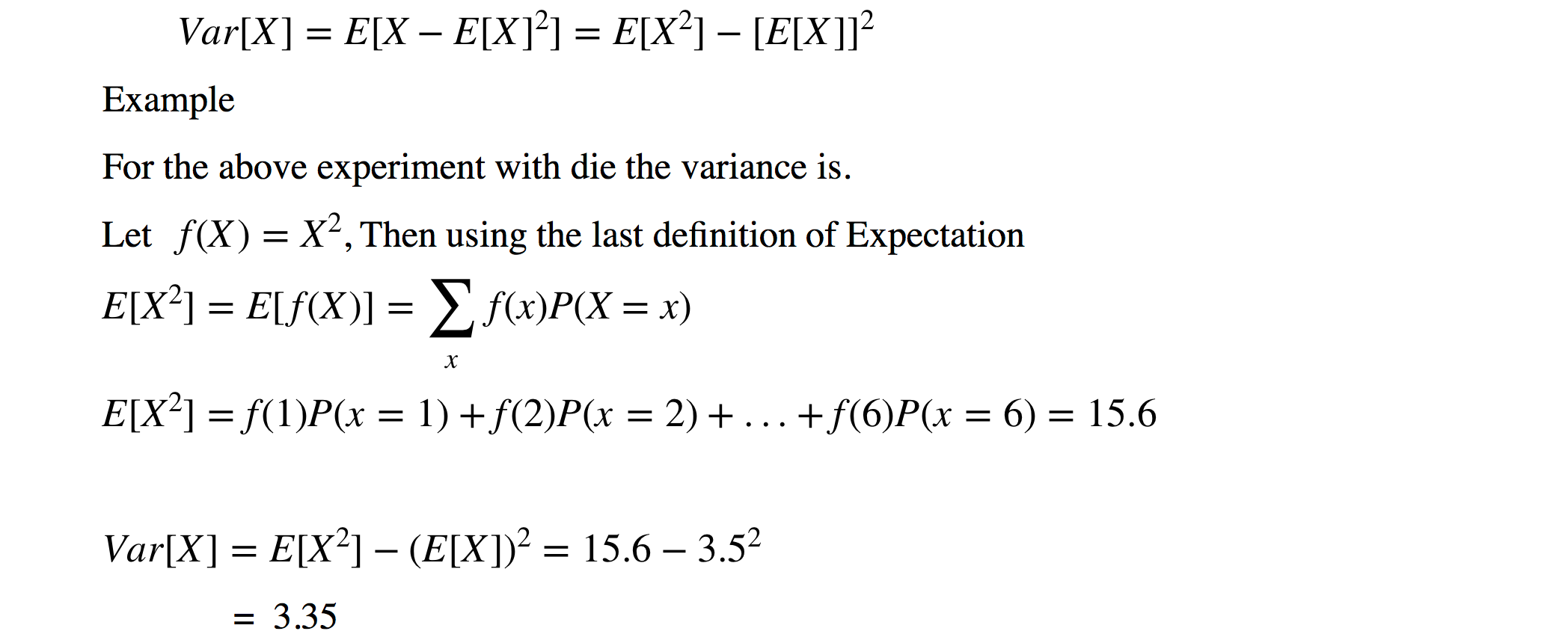



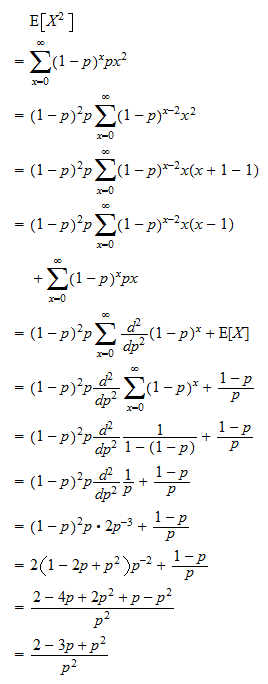
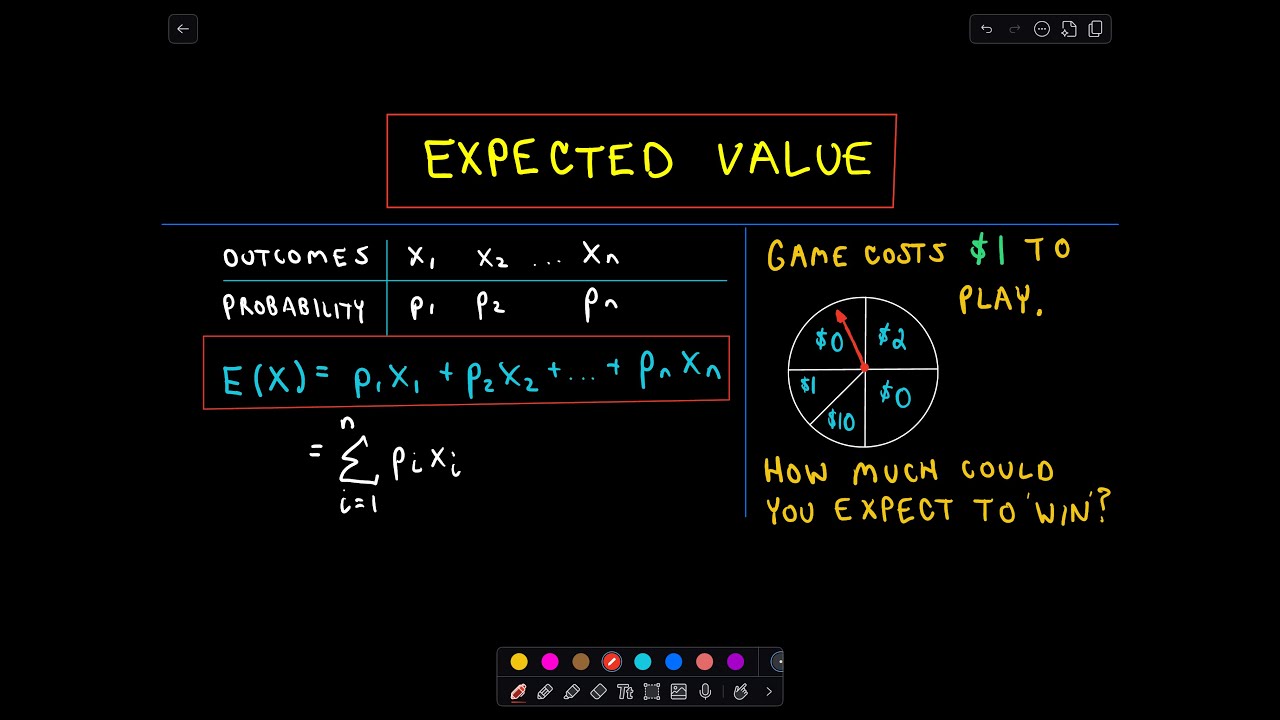



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/expected-5733972a5f9b58723d773687.png)





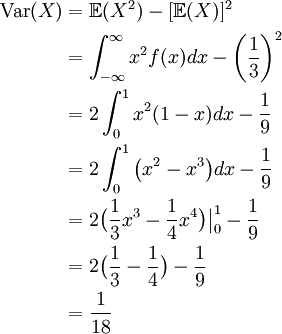
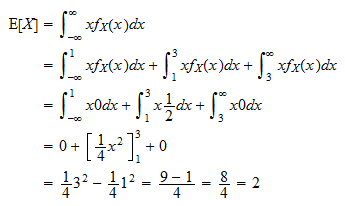
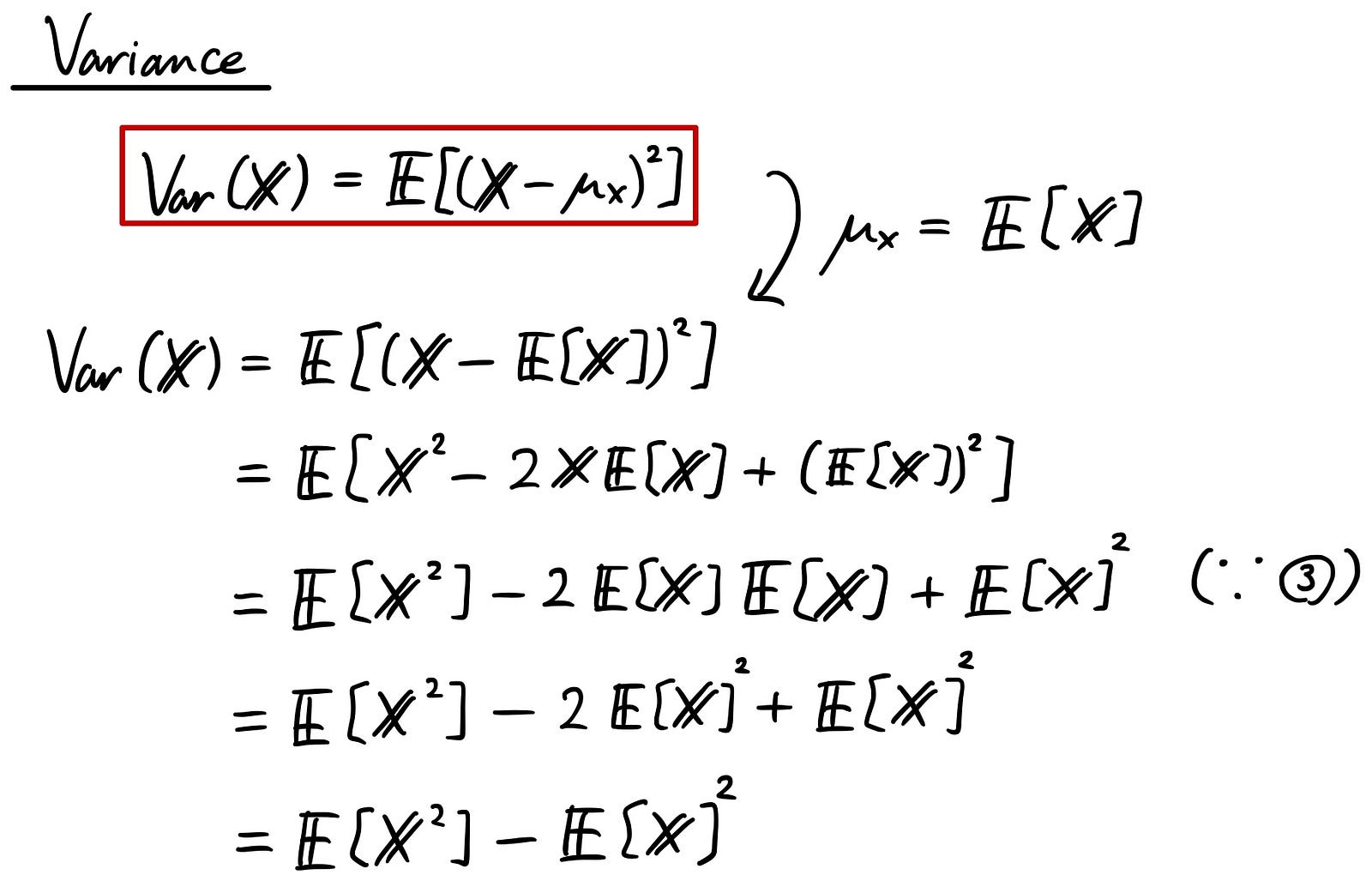


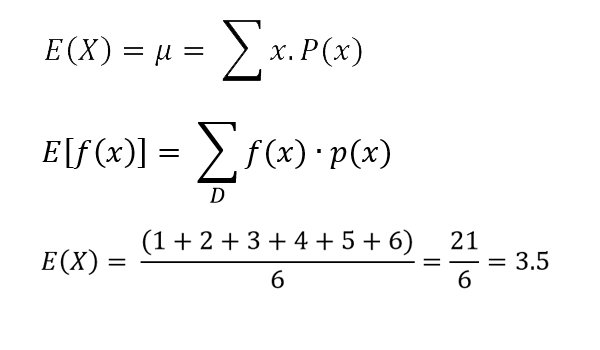


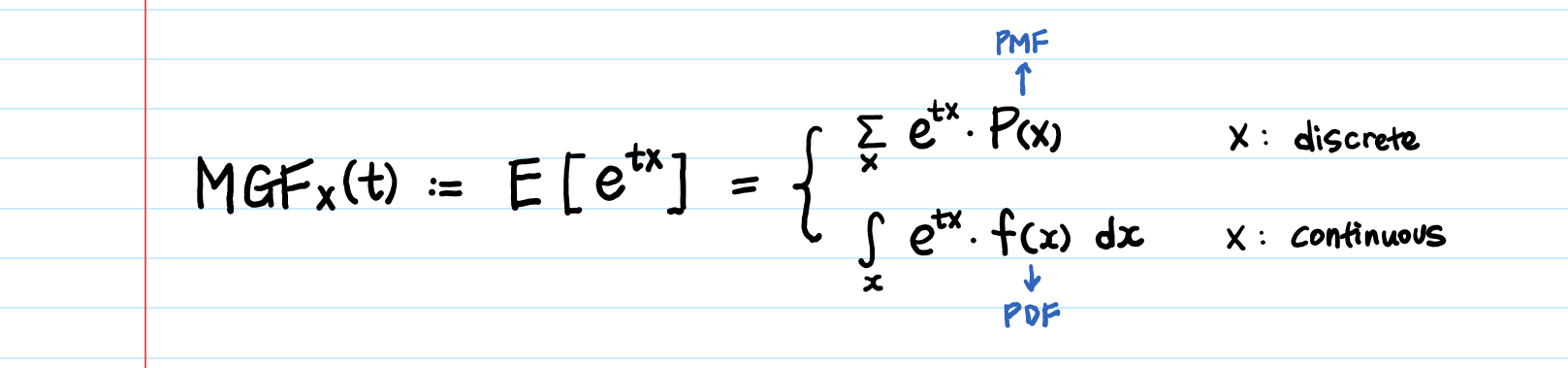


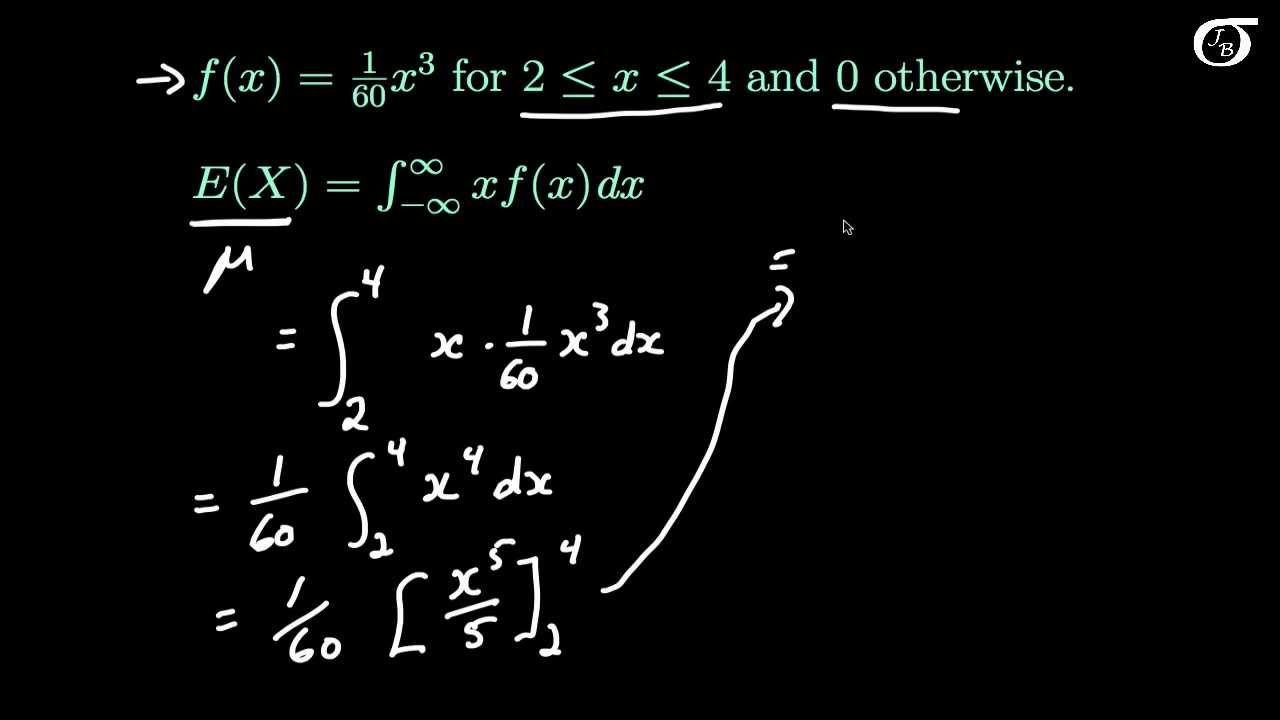








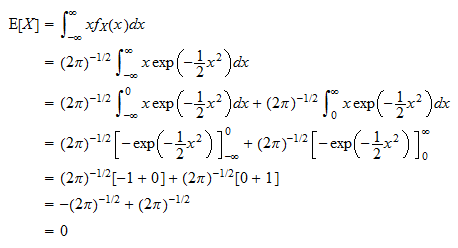



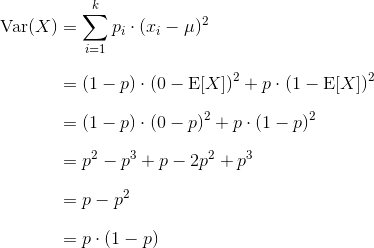









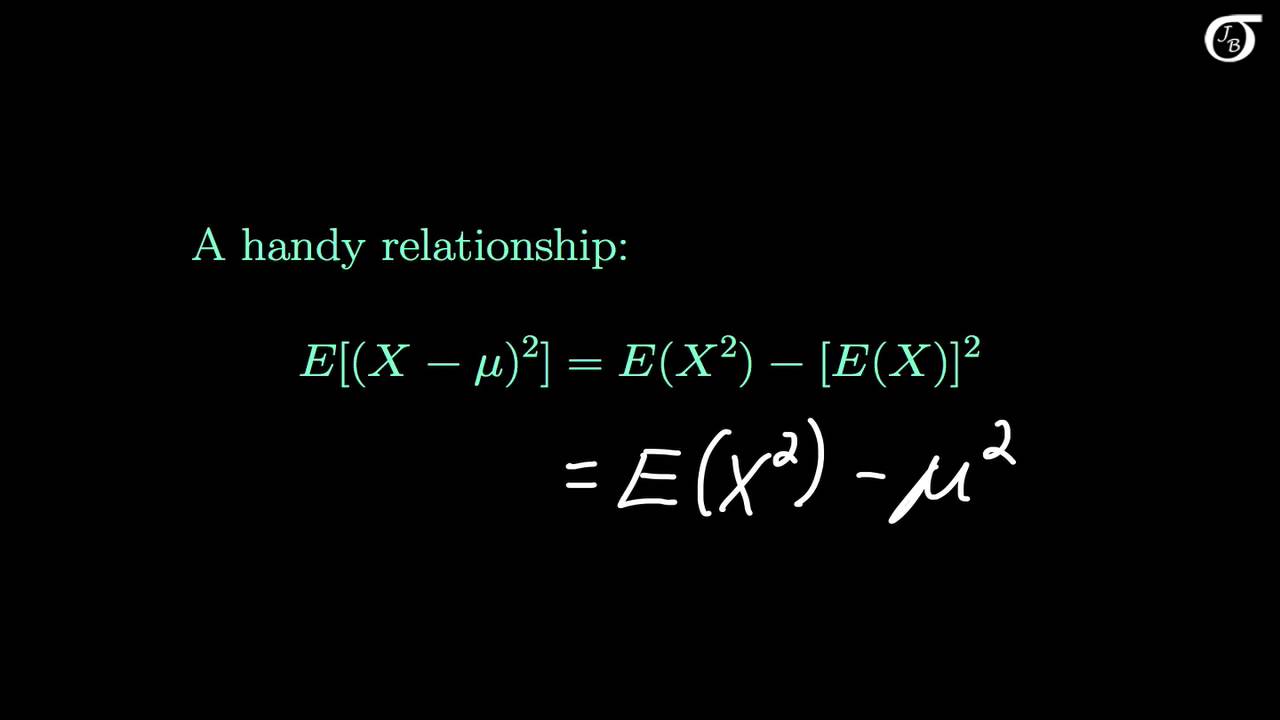

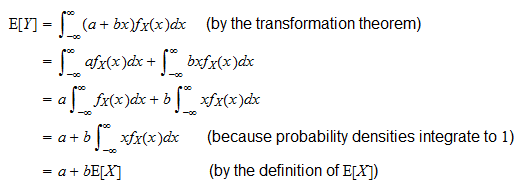








/FormulaForExpectedValue-58b8980d3df78c353cc32aff.jpg)
