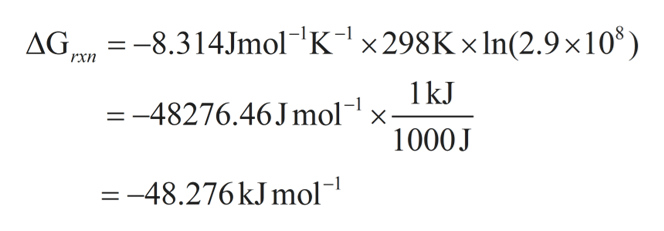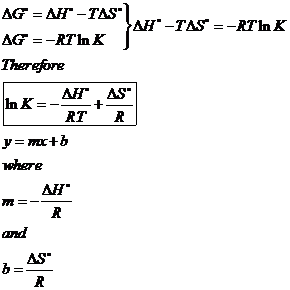Delta G Rxn Formula
C in which direction is the reaction as.
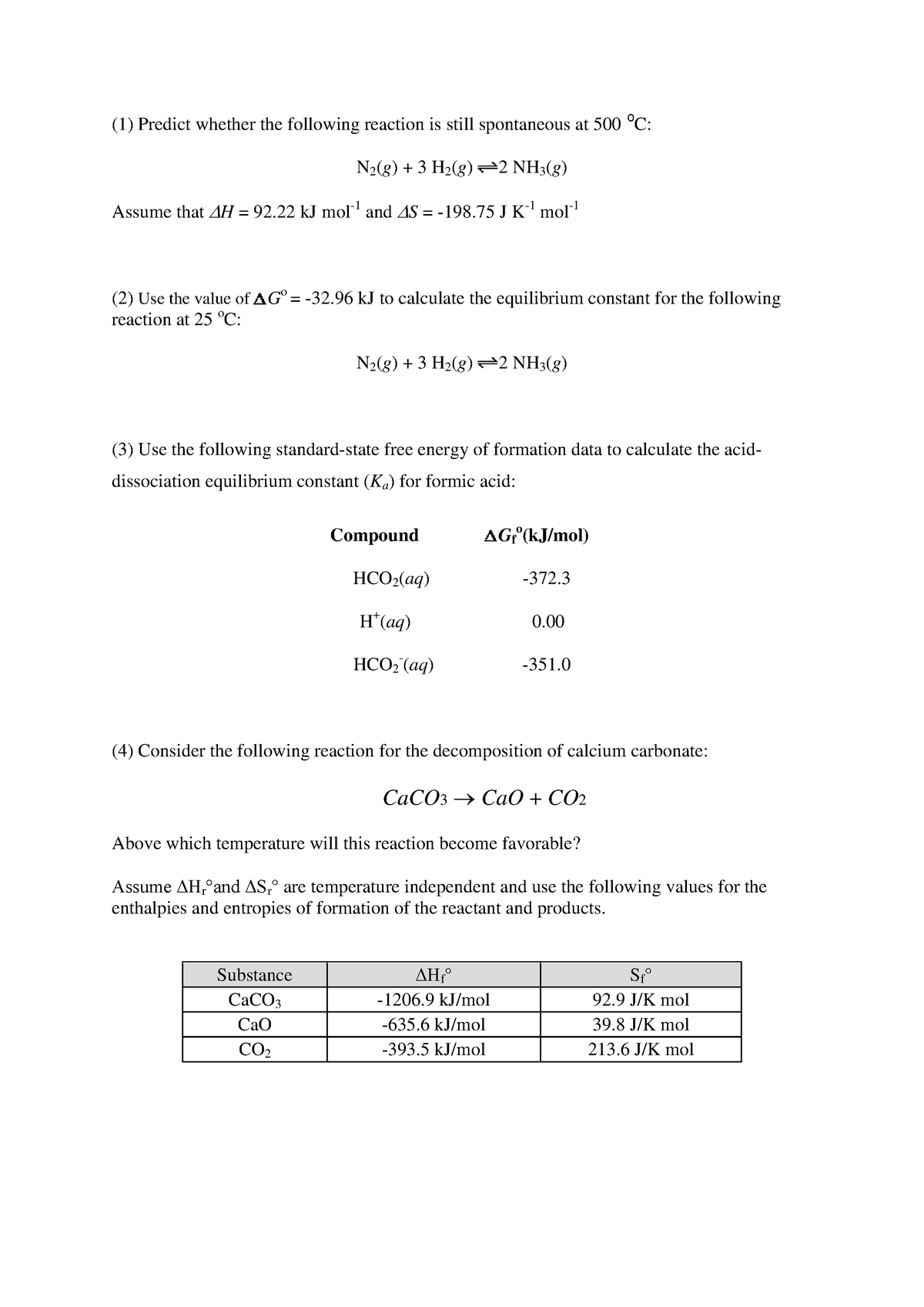
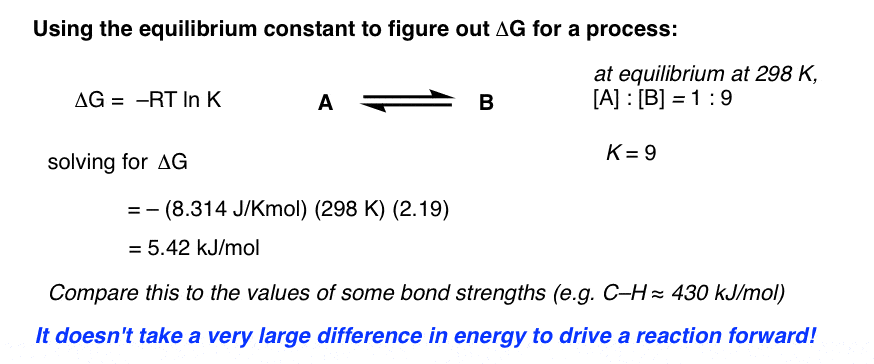
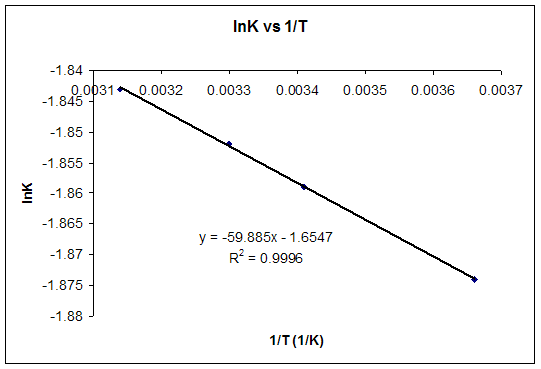
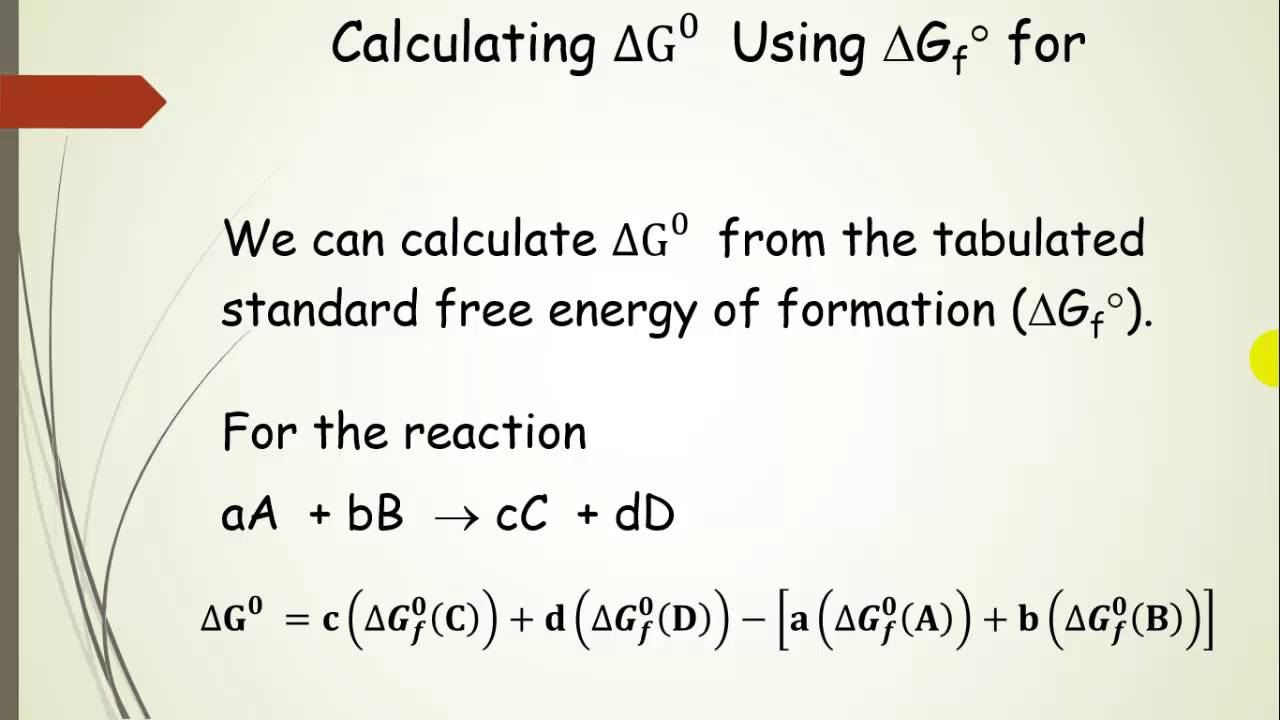
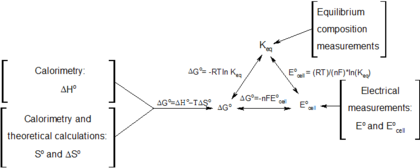
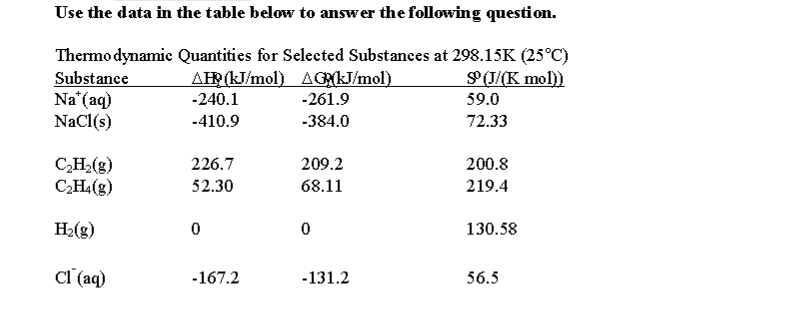
Delta g rxn formula. If we know the standard state free energy change g o for a chemical process at some temperature t we can calculate the equilibrium constant for the process at that temperature using the relationship between g o and k. R 8314 j mol 1 k 1 or 0008314 kj mol 1 k 1. Given the following data ethylbenzene c6h5 ch2ch3.
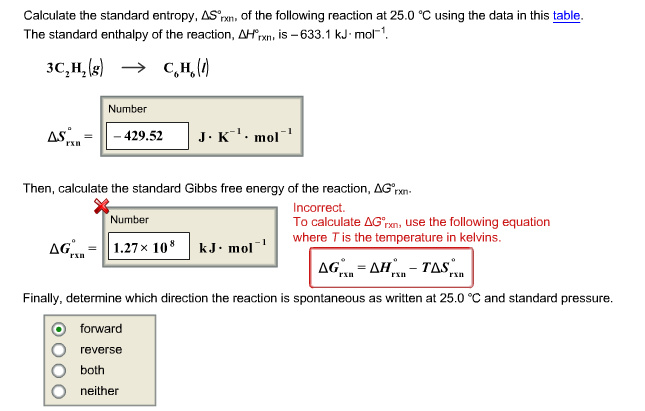
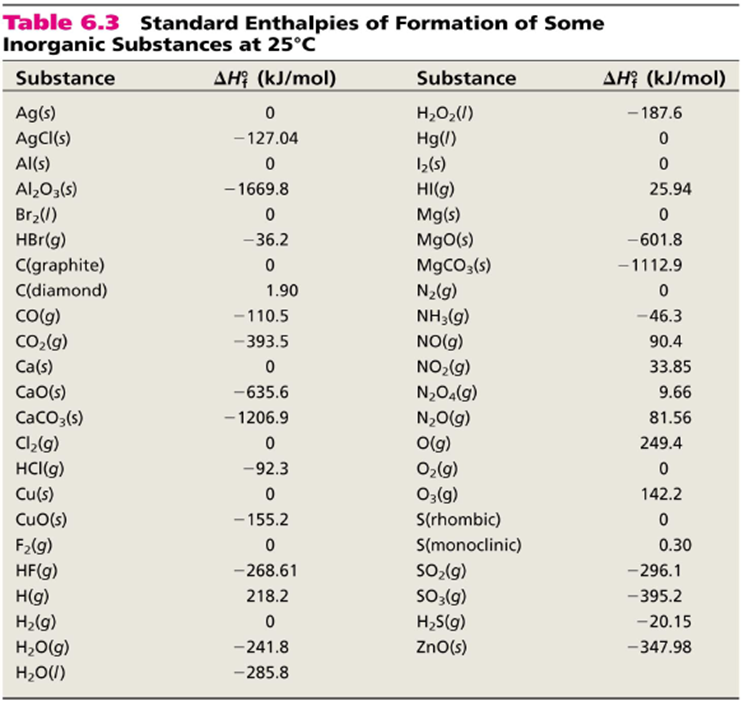
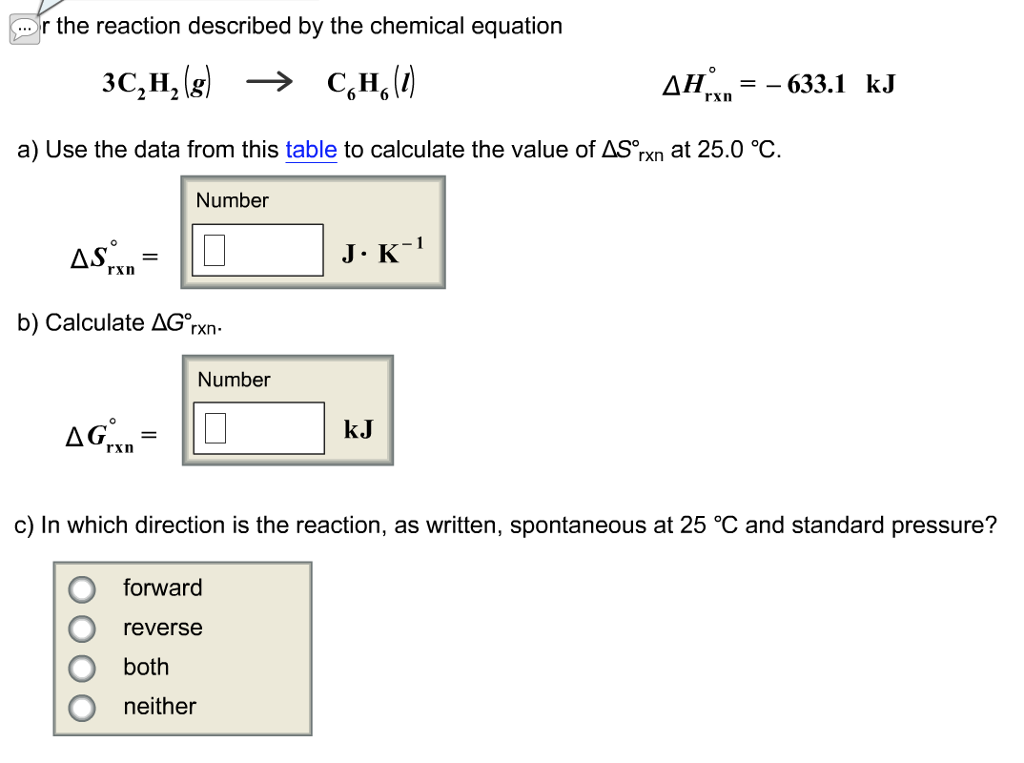
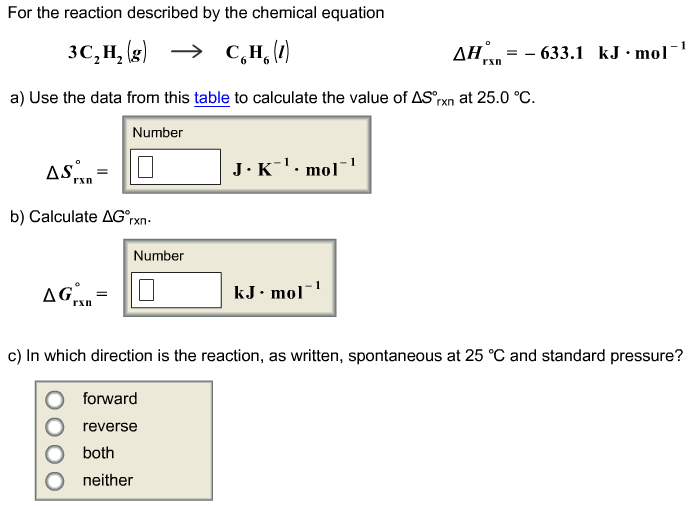
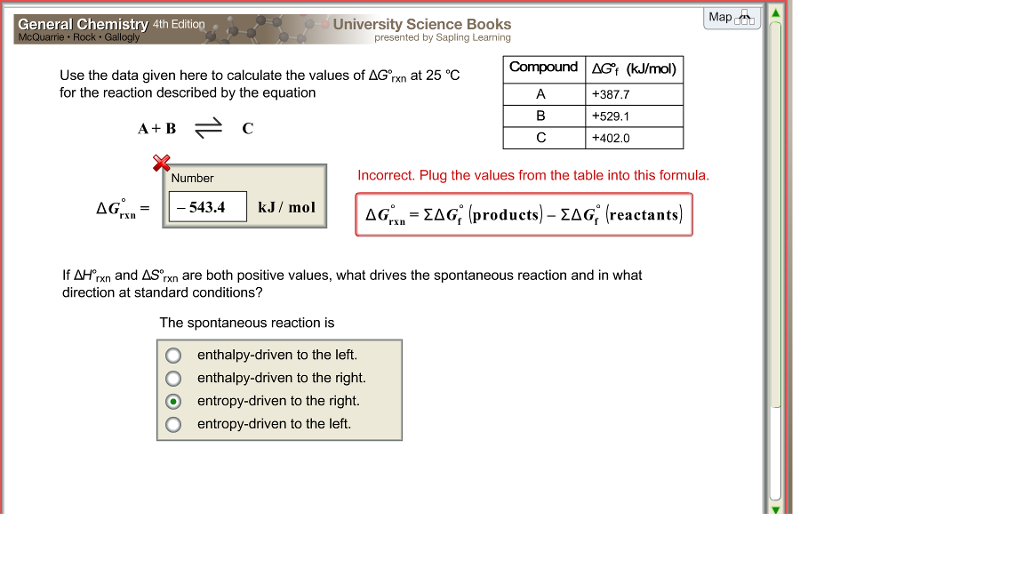
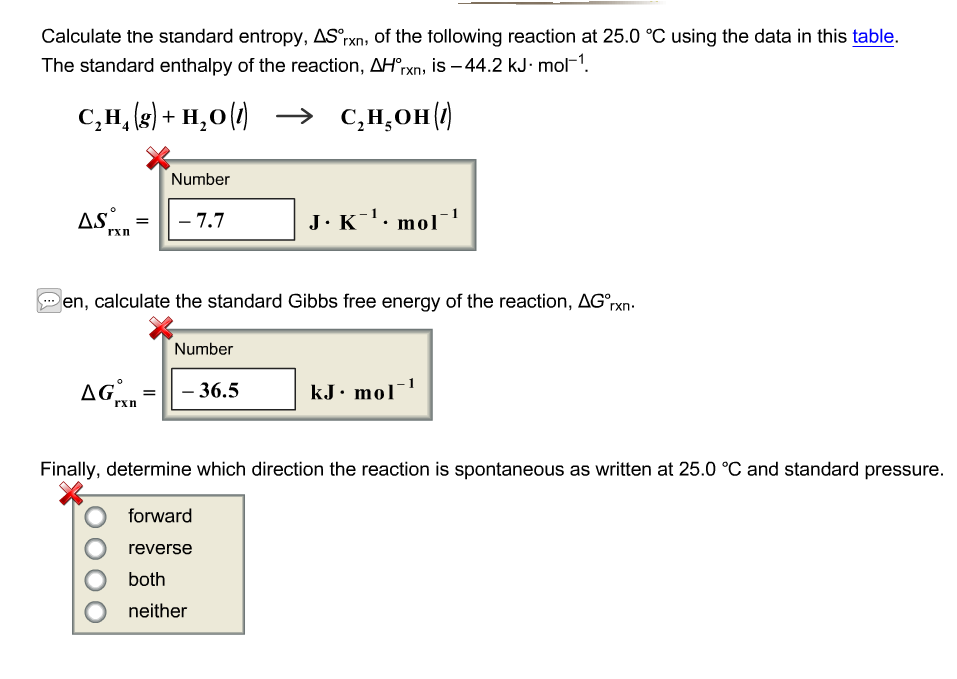
Delta h rxn 6331 kjmol a calculate the value of delta s rxn at 250 c. Co 2g 394 kjmol h 2 o g 242 kjmol. Consider the two equations that deal with delta g g.
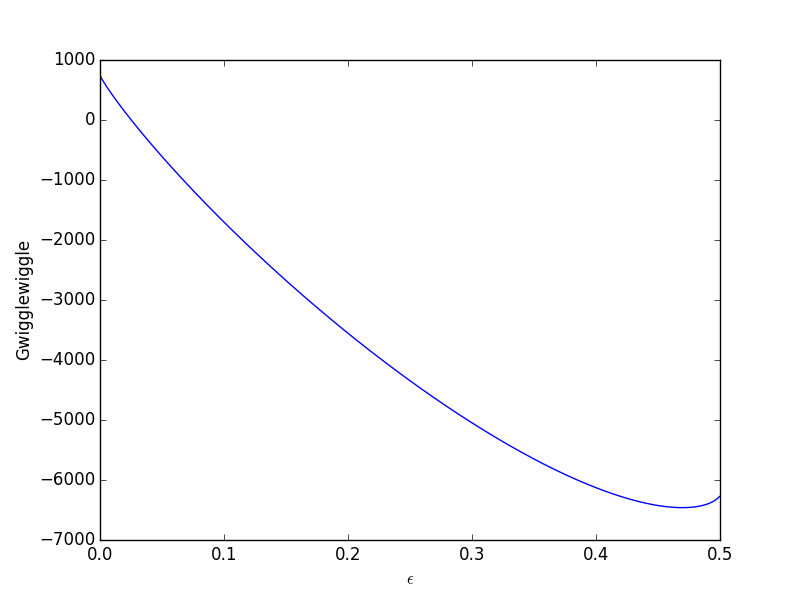
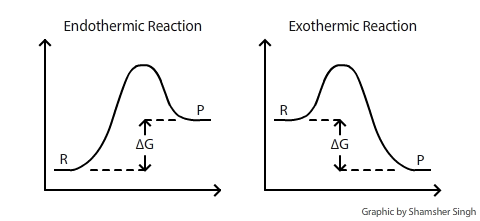
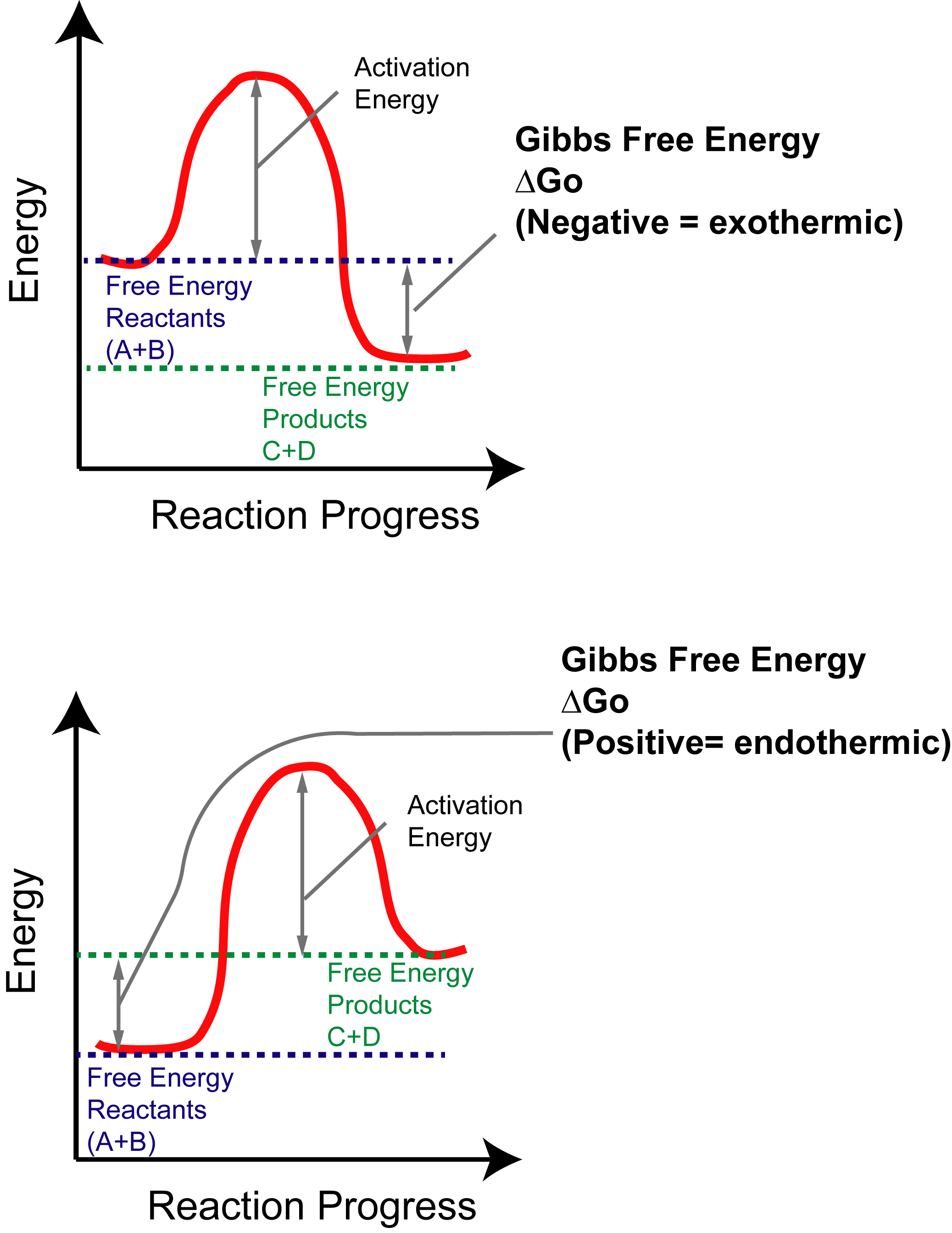
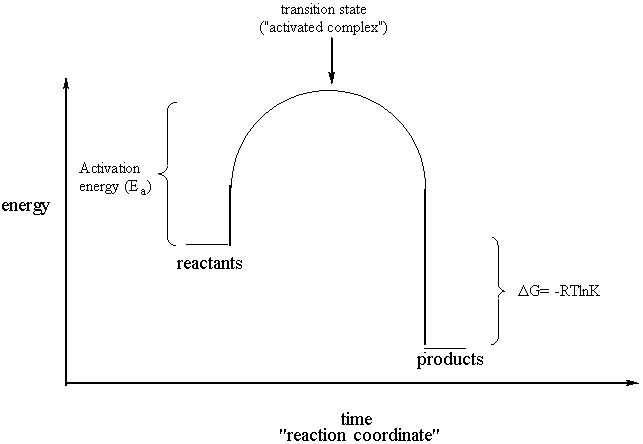
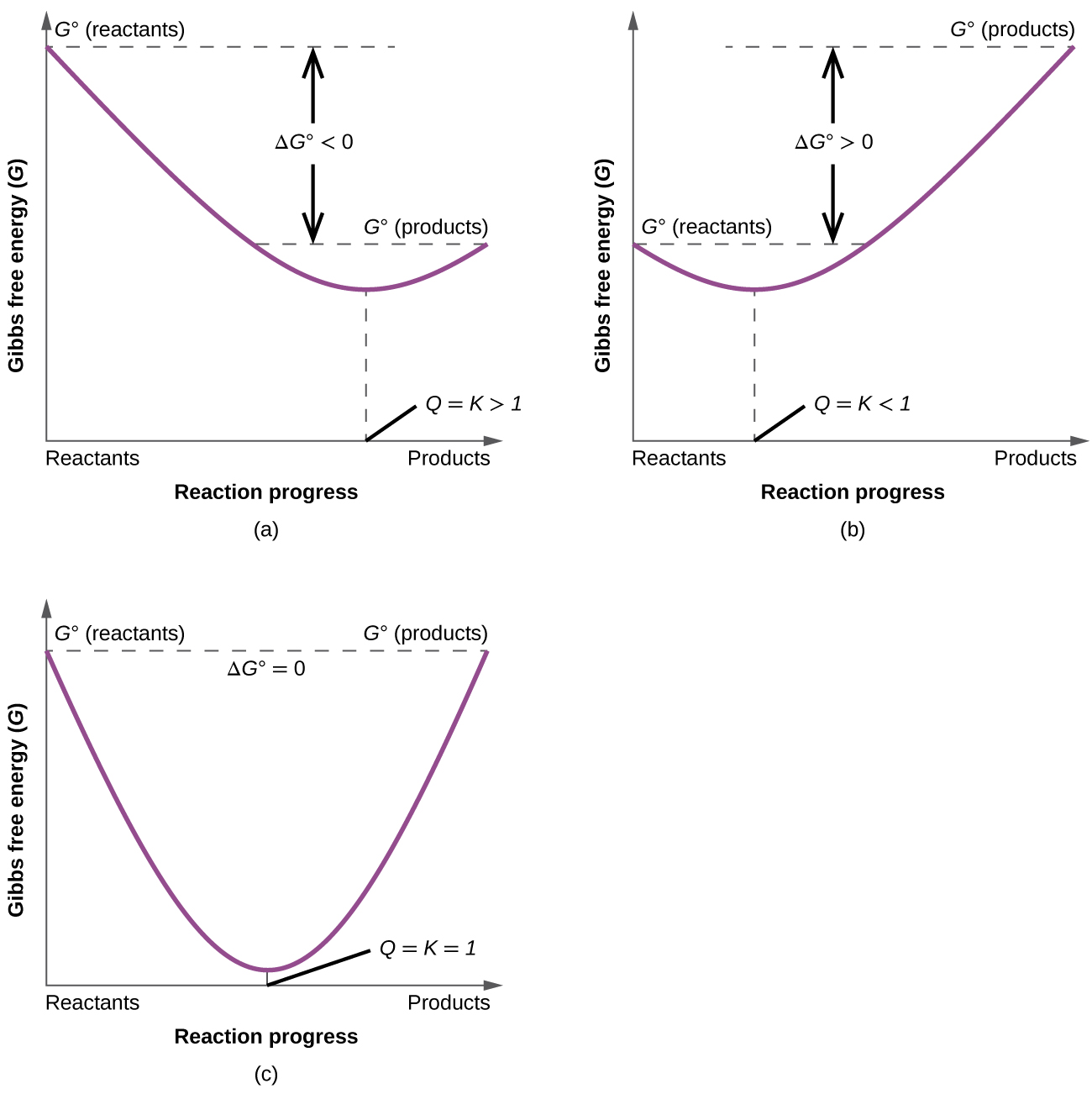
Styrene is produced by catalytic dehydrogenation of ethyl benzene at high temperature in the presence of superheated steam. Since this post was originally written in january 2012 the ap exam has changed. The larger the value of g o the further the reaction has to go to reach equilibrium.
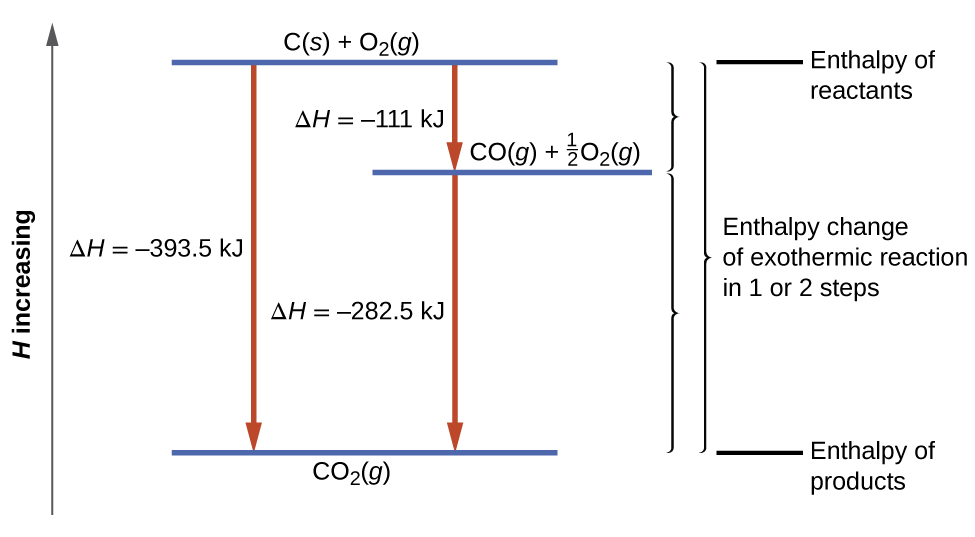
T is the temperature on the kelvin. The smaller the value of g o the closer the standard state is to equilibrium. Use this link look up the d h f values ch 4g 2 o 2g co 2g 2 h 2 o g what is the energy of the molecules of the products.
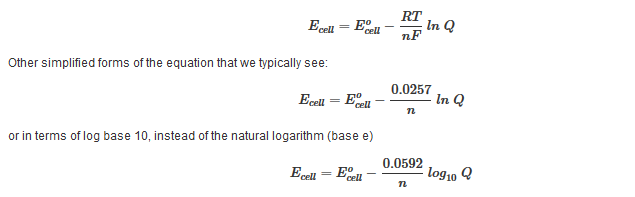
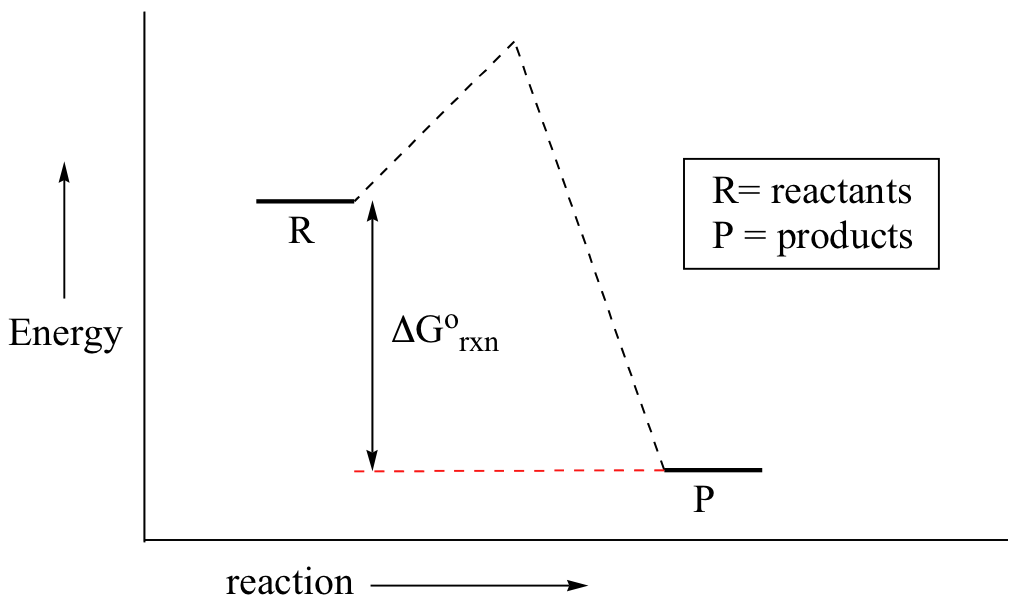
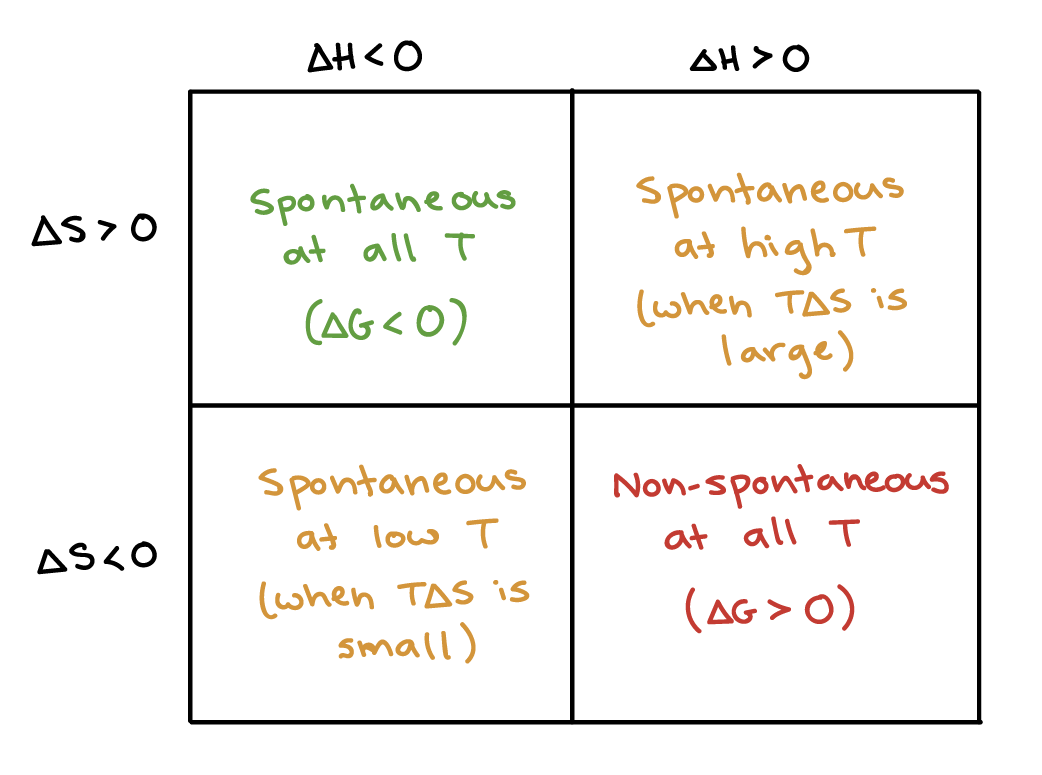
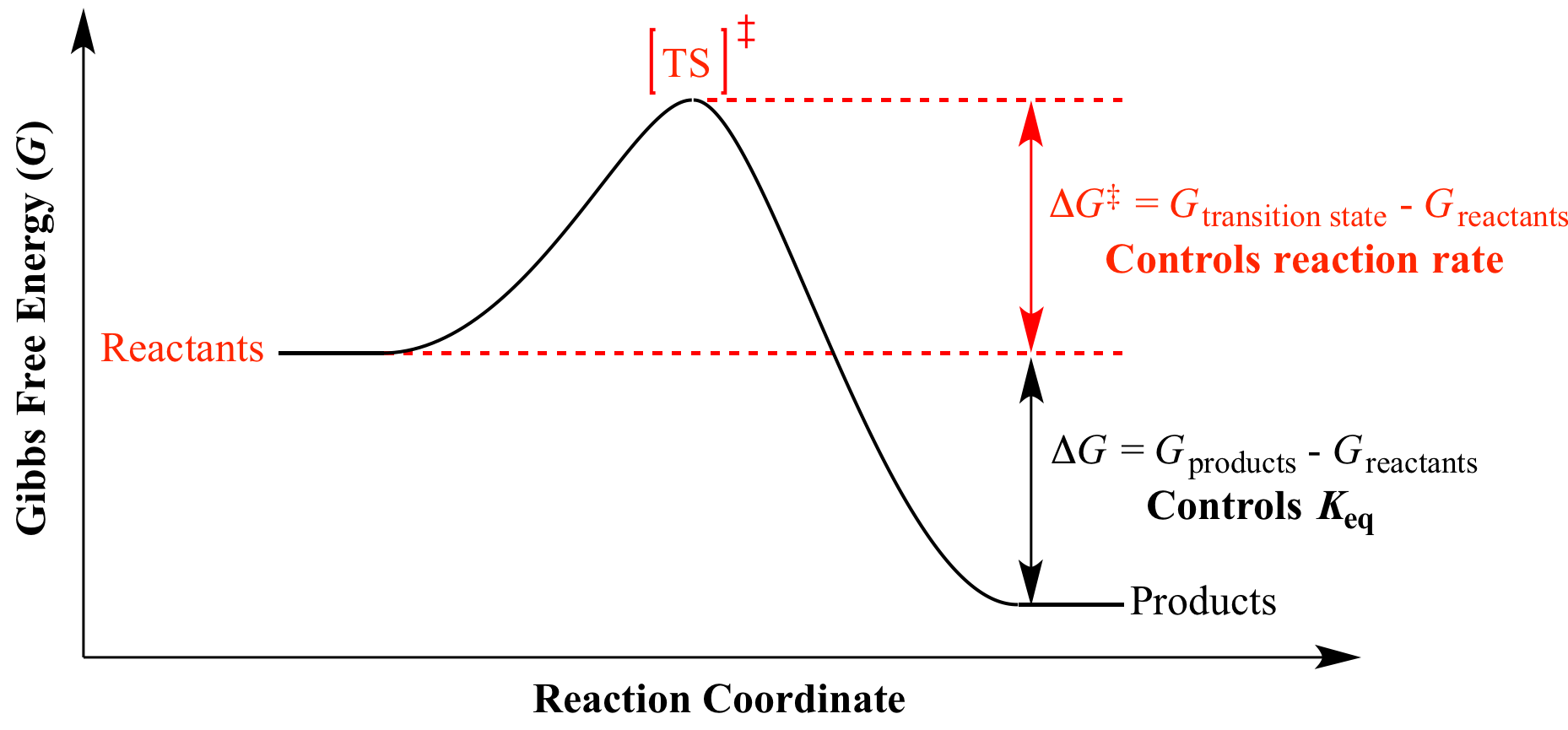
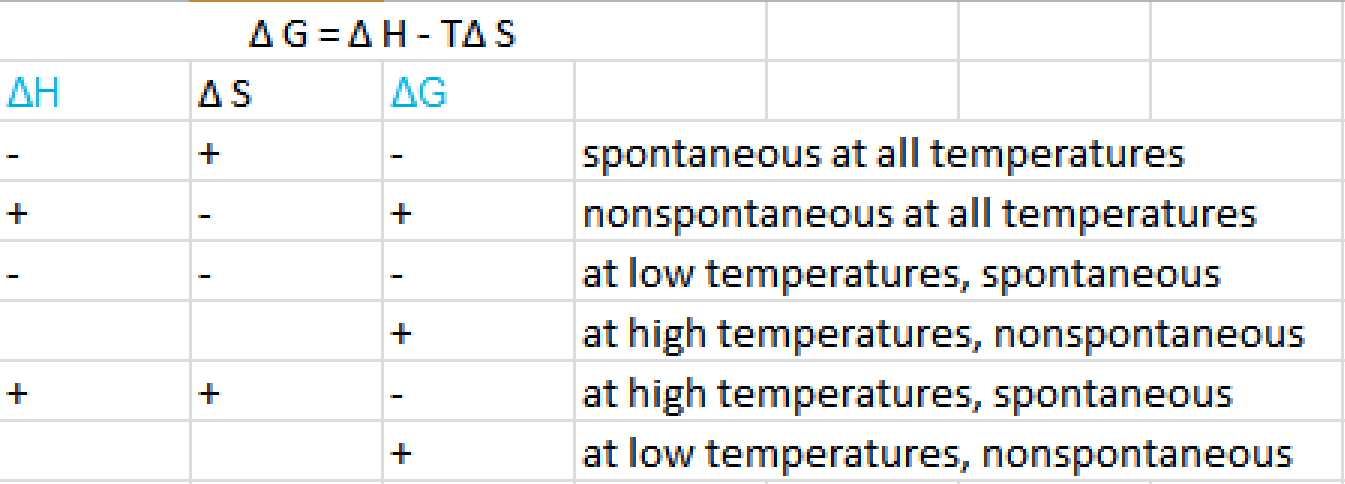
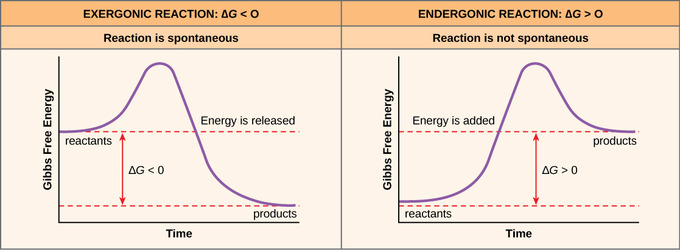
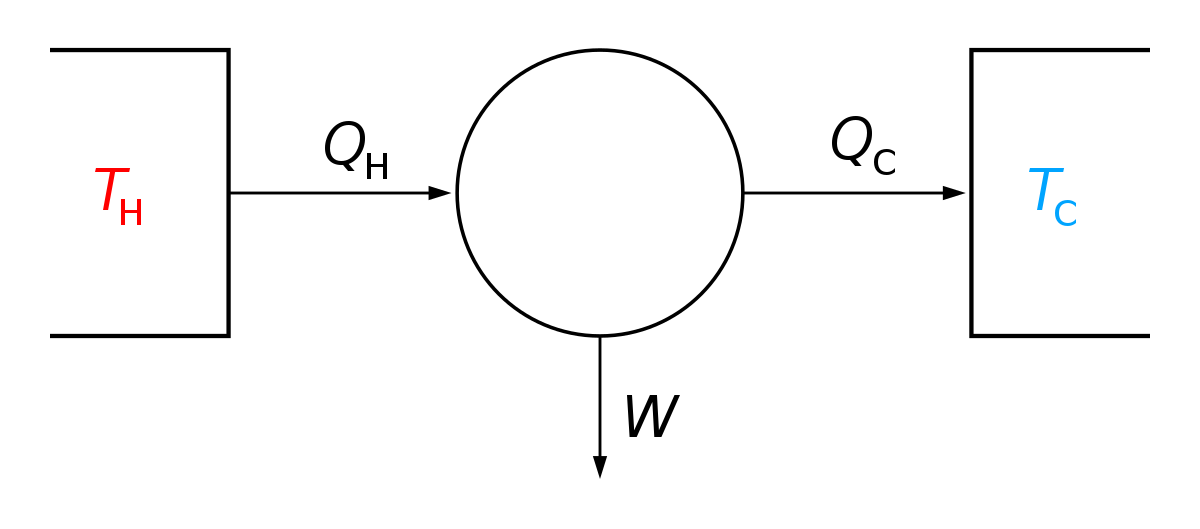
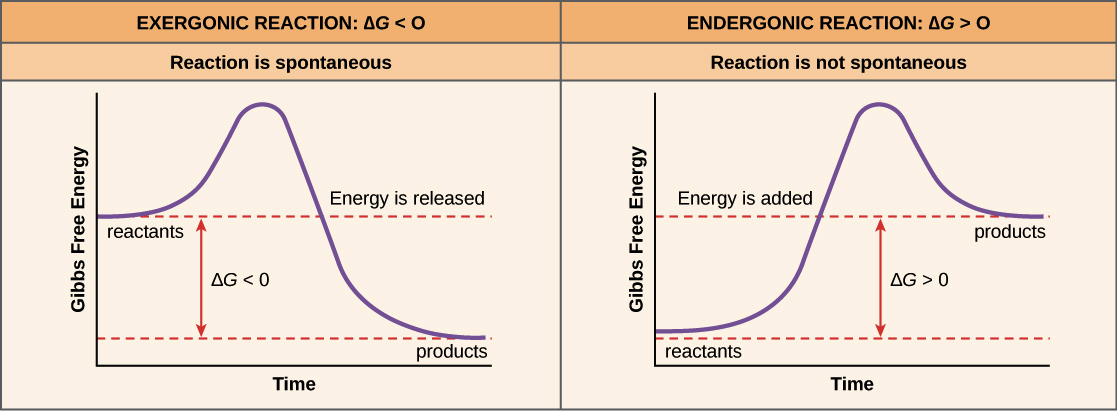
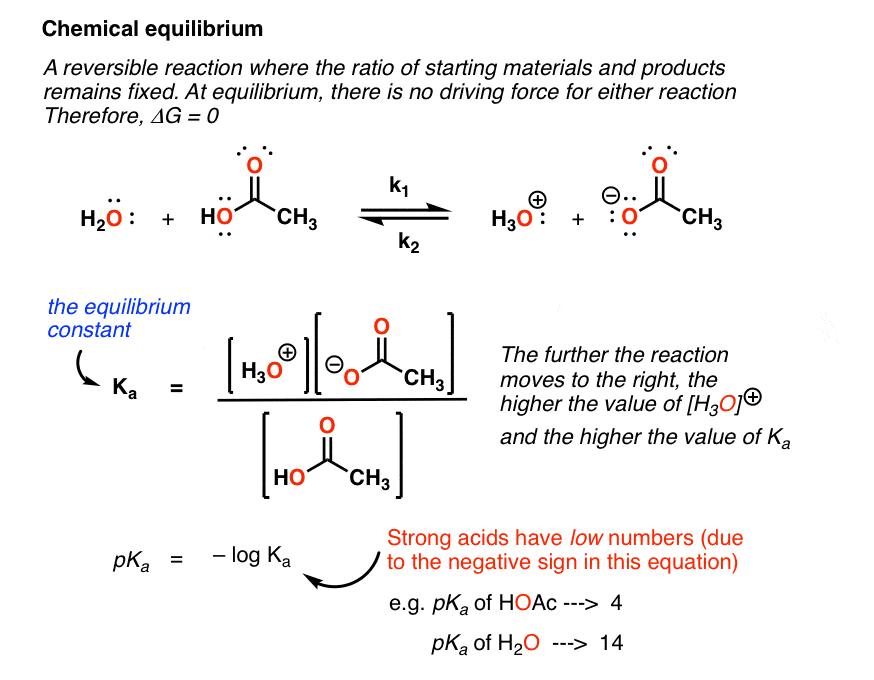
D g o a delta g with a superscript o is the free energy change for a reaction with everything in the standard states gases at 1 bar and solutions at 1 m concentration and at a specific temperature usually 250c d g just delta g. Video calculate d h delta h demonstrated example 1. This is the free energy change for a reaction that is not at the standard state.
The relationship between g o and the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction is illustrated by the data in the table below. B calculate delta g rxn. Rearrangement gives in this equation.
One of the changes was to remove equation 2 below from the equations constants sheet.
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gctgoo0rvqd3cbde8uk1hbwz8hzr I Nsockmy6lqifzjnuzcb3n Usqp Cau
encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com