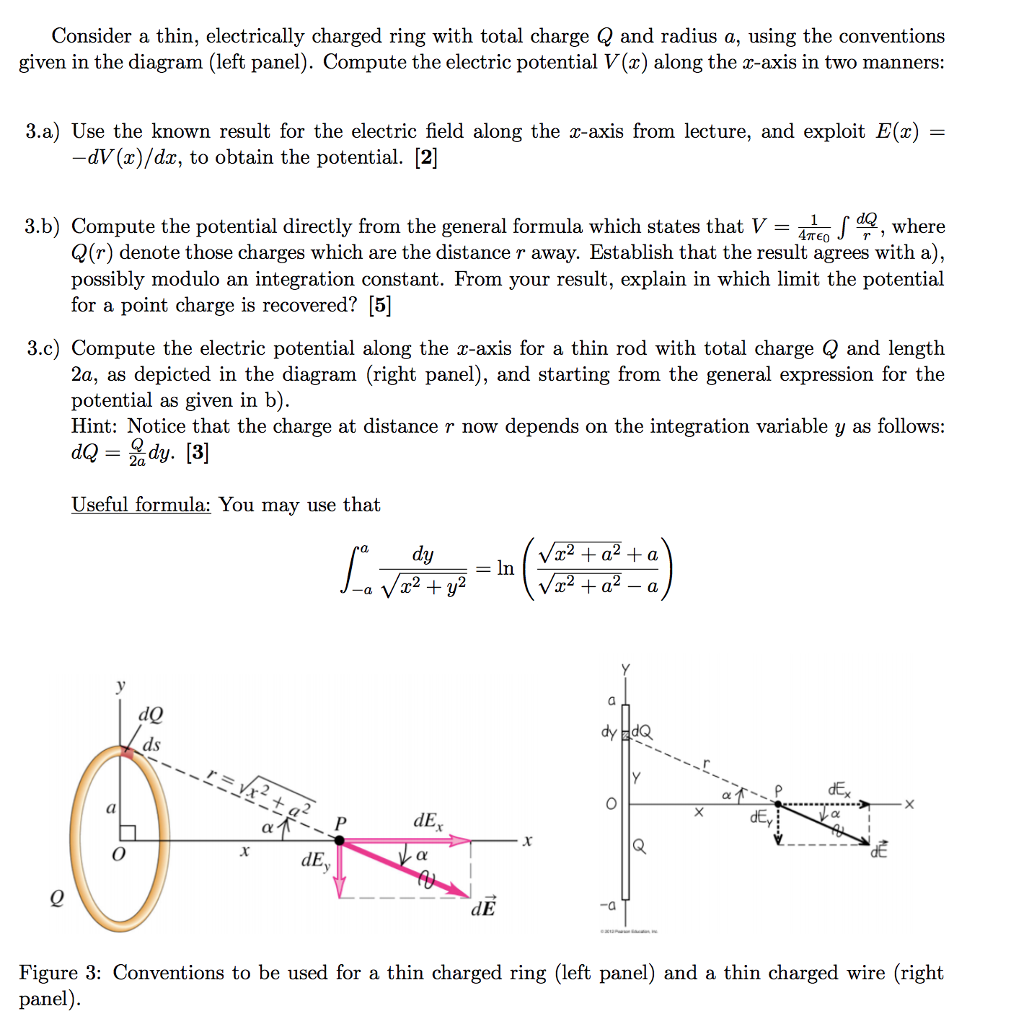
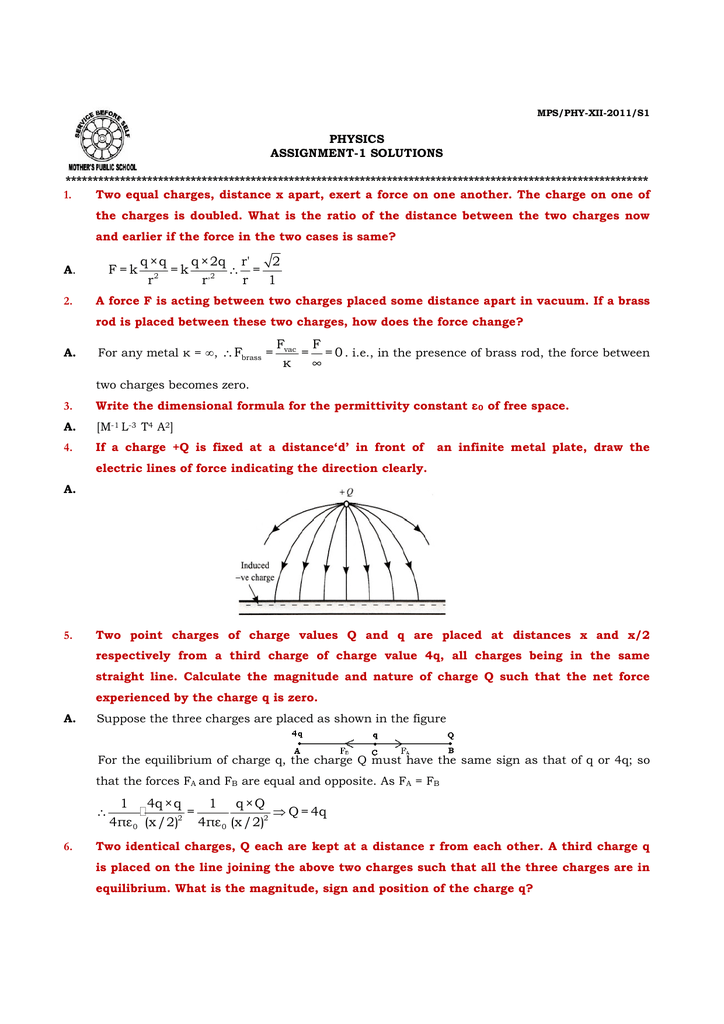
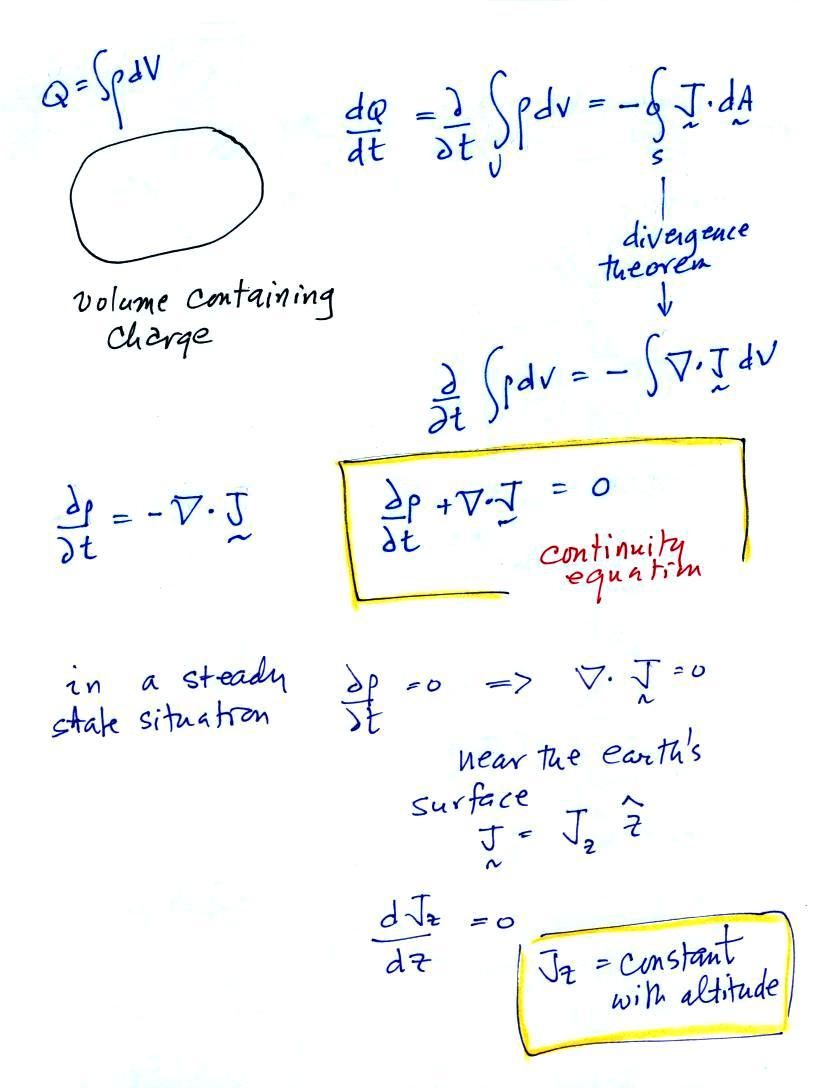
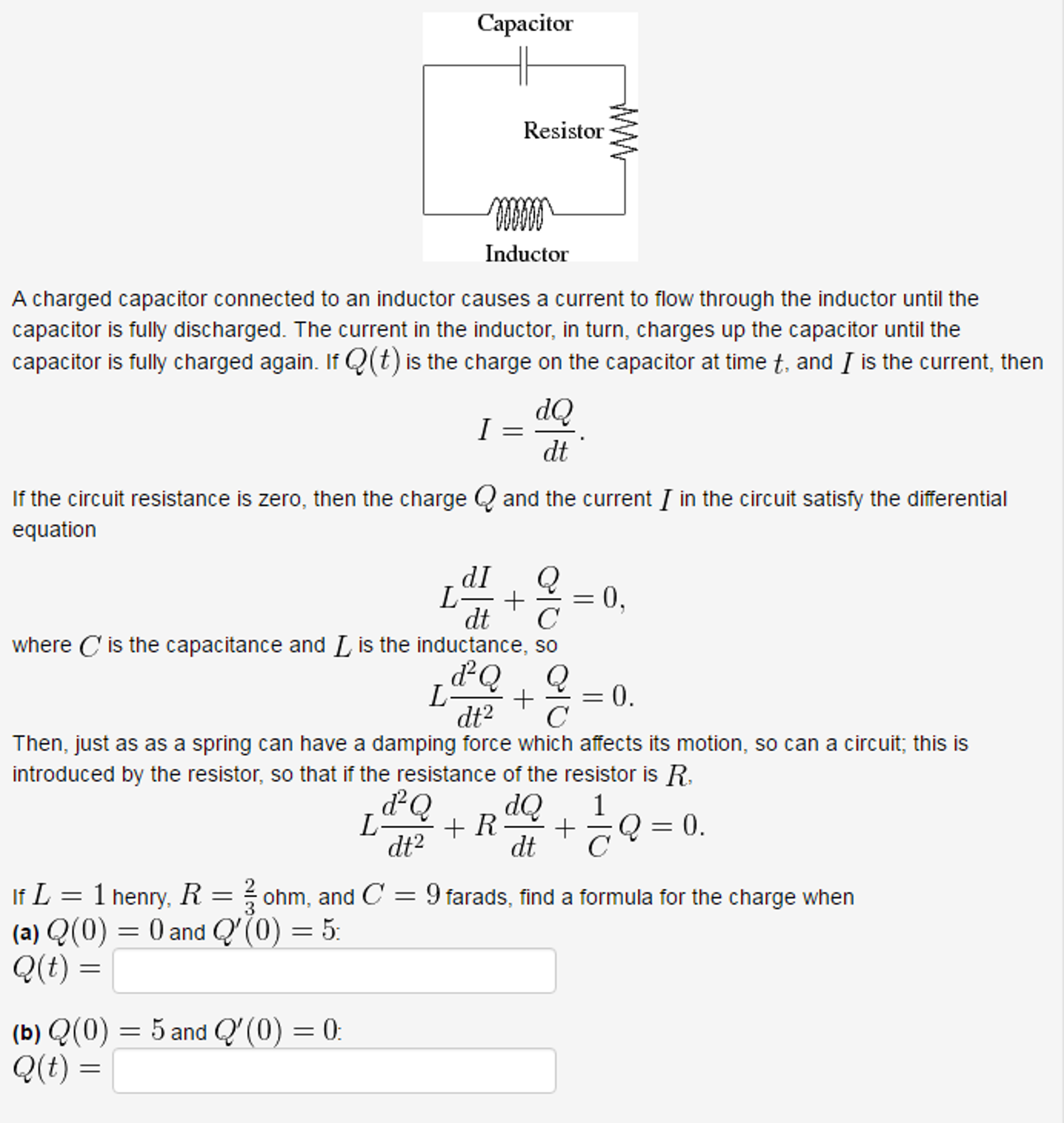
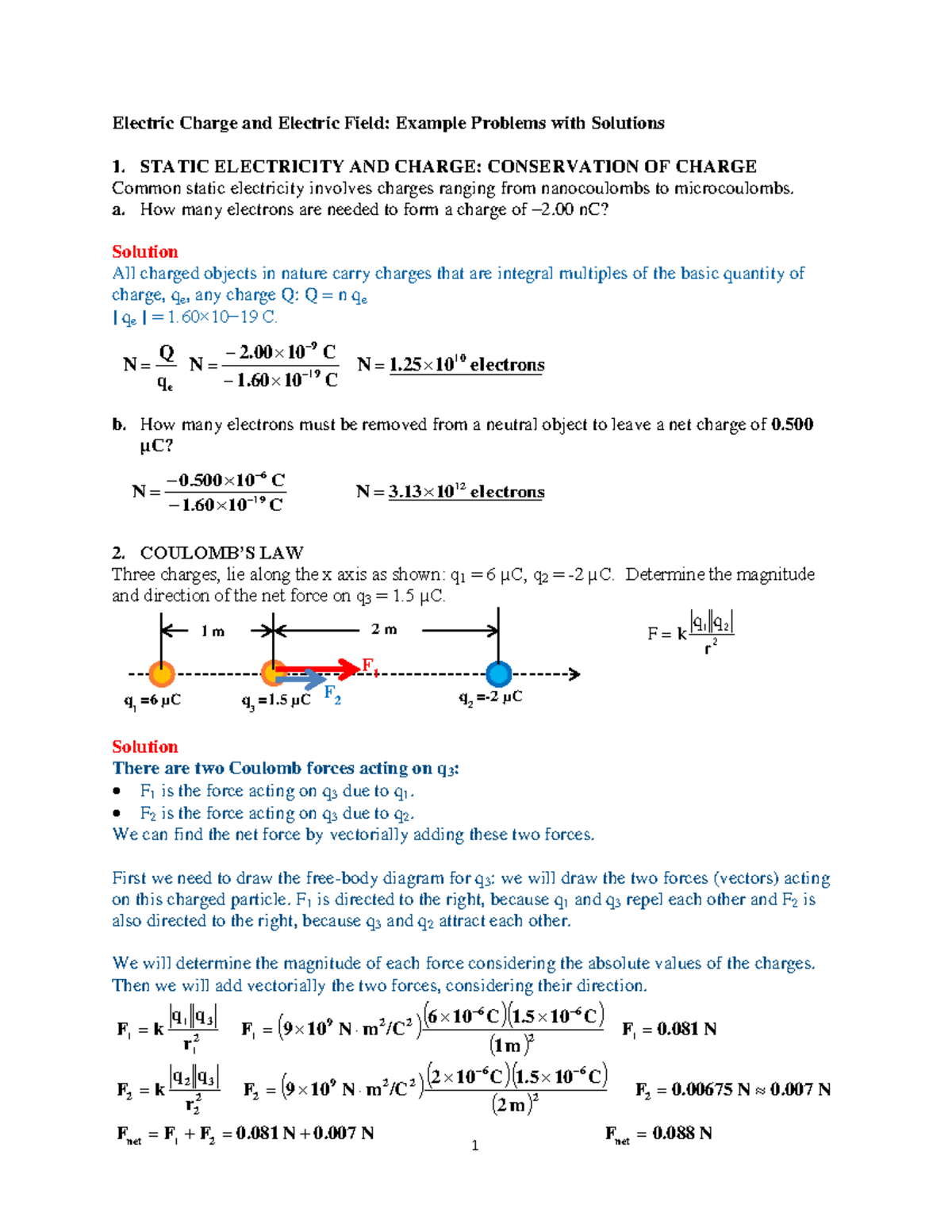
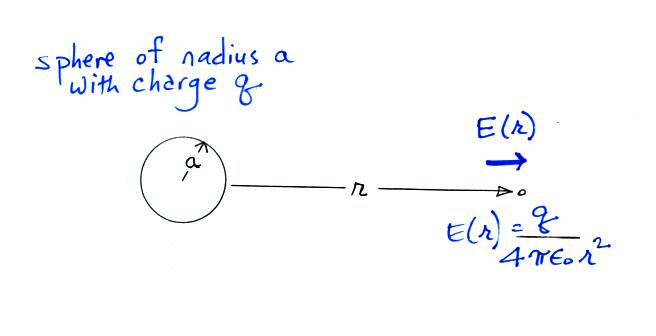
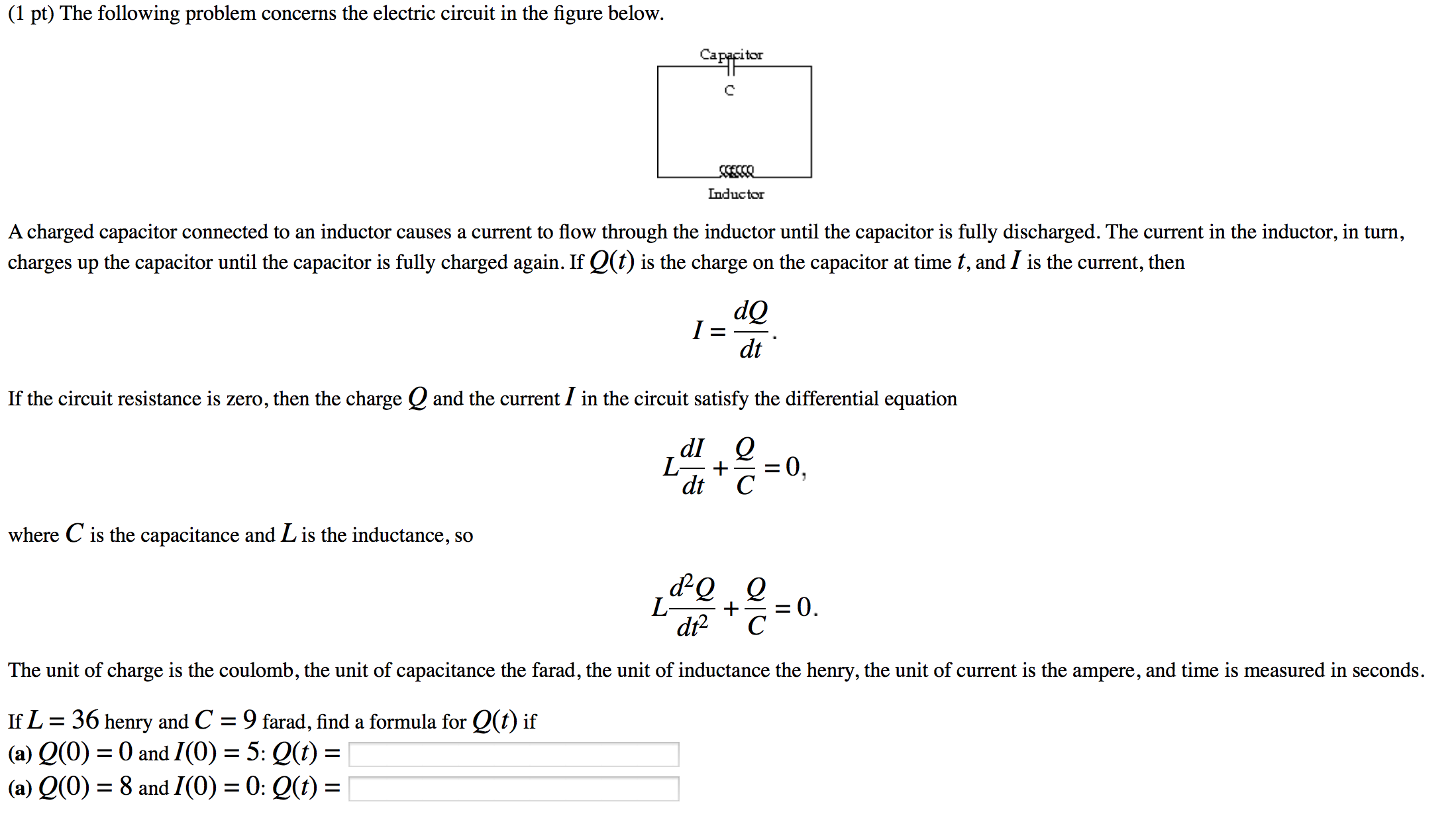
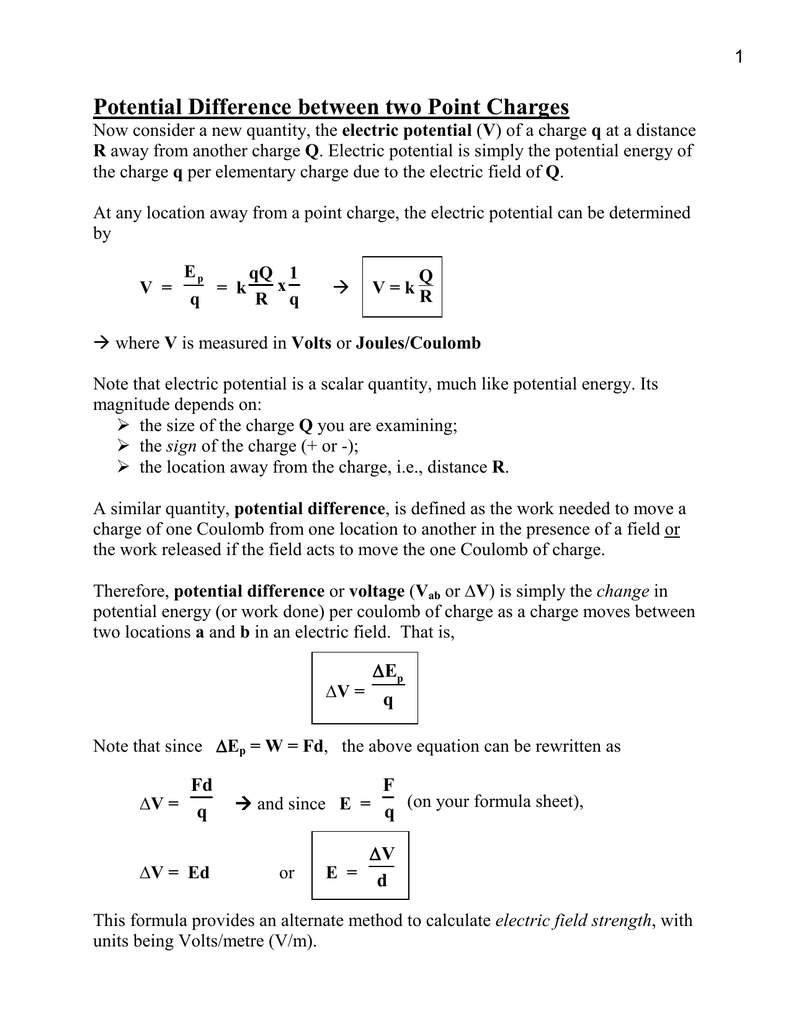
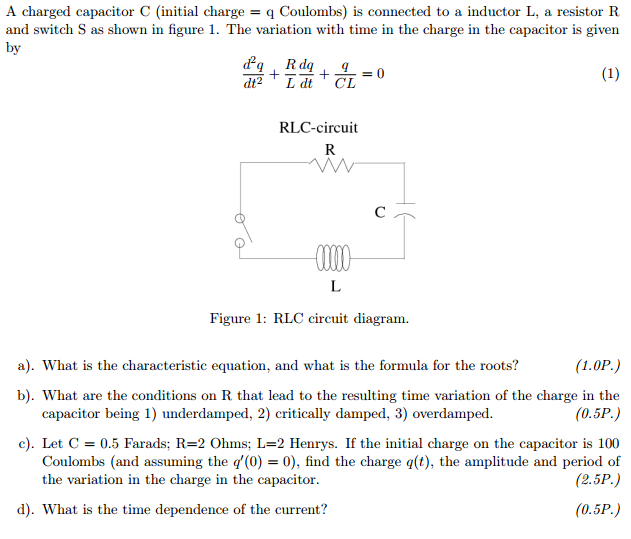
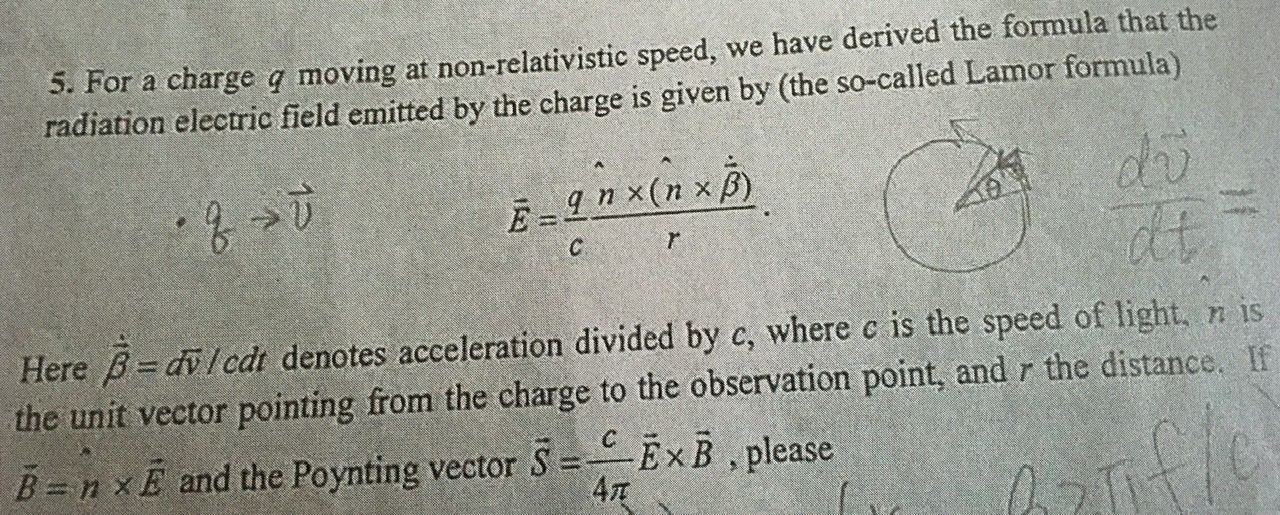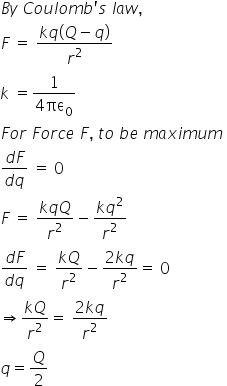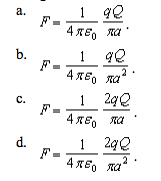Charge Q Formula
The law of conservation of charge states that the net charge of an isolated system remains constant.

Charge q formula. Charge q 8 c. T is the time period measured in seconds s. T is the.
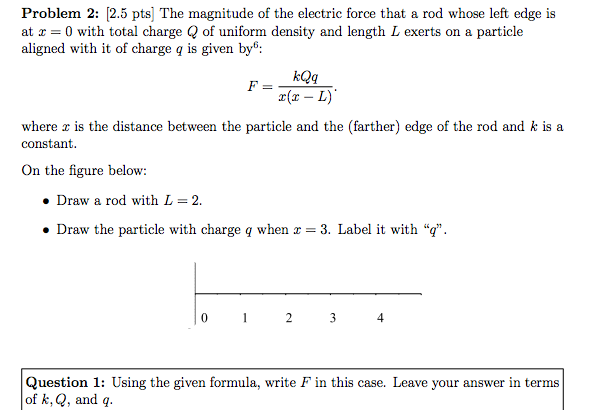
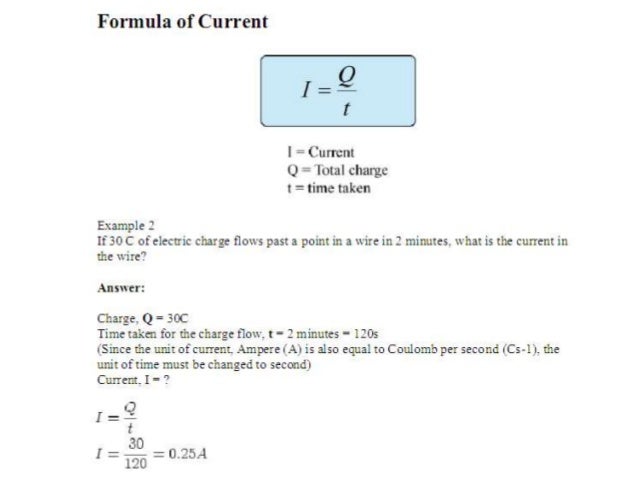
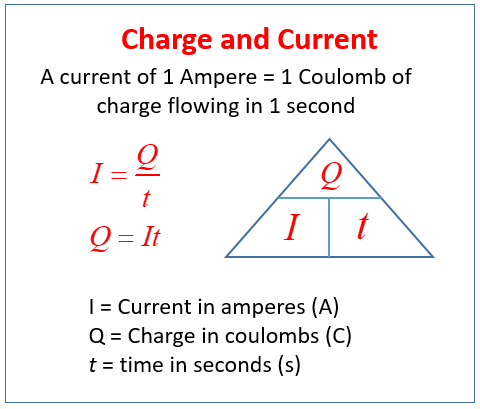
It is the momentary current measured in amperes a. State your solution to the problem calculate quantity of charge. Q is the electric charge measured in coulombs c.
This arrangement represents the actual position of each quantity in the capacitor charge. Where q is the charge and v is the volume over which it is distributed. Find the charge density if a charge of 8 c is present in a cube of 4 m 3.
Q ne where n is an integer. Two important properties of charge are quantization and conservation. A quantization of charge i electric charge can exist only as an integral multiple of charge on an electron e ie.
The value of charge of an electron is 160210 19 c. The si unit for the electric charge is coulomb and is equal to around 624210 18 e. Q 1500 c.
Putting charge is quantized in terms of an equation we say. Charge on electron is 1602 10 19 c and charge on proton is positive of this value. The elementary charge usually denoted by e or sometimes q e is the electric charge carried by a single proton or equivalently the magnitude of the negative electric charge carried by a single electron which has charge 1 e.
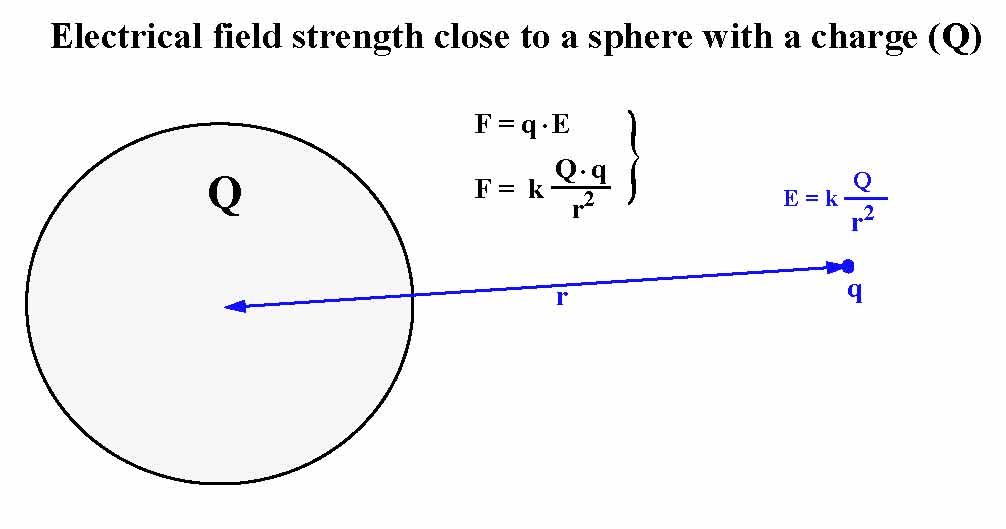
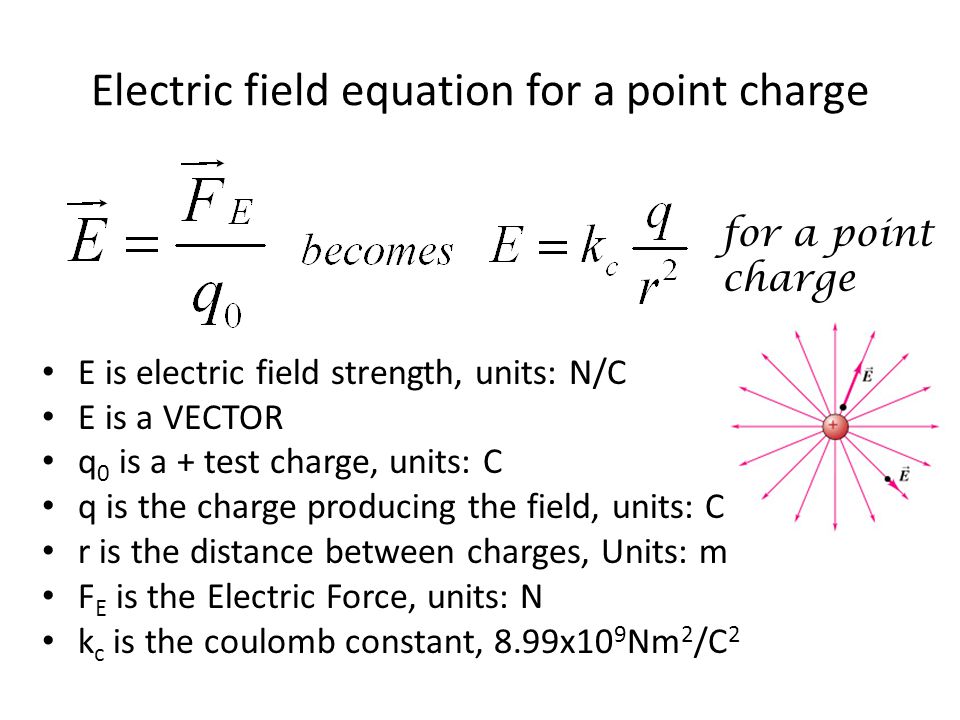
If the expression for electric force as given by coulombs law is substituted for force in the above e fq equation a new equation can be derived as shown below. Q is the electric charge measured in coulombs c. Q i t.
Si unit of linear charge density is coulomb solved example. Here the three quantities of q c and v have been superimposed into a triangle giving charge at the top with capacitance and voltage at the bottom. The charge density formula is given by.
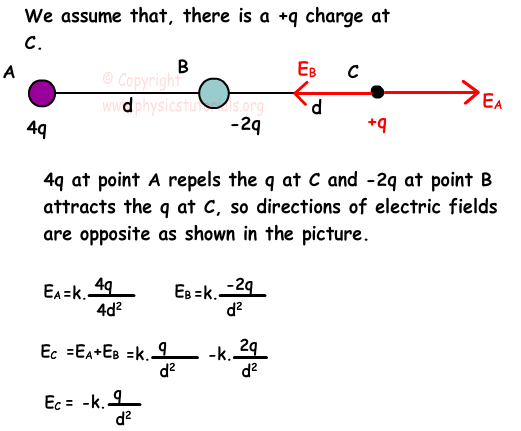
When applied to our two charges the source charge q and the test charge q the formula for electric force can be written as. The like charges usually repel each other and unlike charges attract each other. Volume v 4 m 3.
The law of conservation of charge. Q n e q is the symbol used to represent charge while n is a positive or negative integer and e is the electronic charge 160 x 10 19 coulombs. Q charge in coulombs c capacitance in farads x v voltage in volts it is sometimes easier to remember this relationship by using pictures.
T q i 1500 25 60 seconds 60 seconds 1 minute since the time calculated here agrees with that given in the question we are reasonably confident that our answer for q is correct. Coulomb is described as the quantity of the charge passing through a cross section of electrical conductor. This elementary charge is a fundamental physical constantto avoid confusion over its sign e is sometimes called the elementary positive charge.

Ant Att Vvc Then Q 7 In Given Figure A Point Charge Q Is Placed At The Origin O Work Done In Taking Another Point Charge From The Point A Co Ordinates 0
www.instasolv.com